Abstract
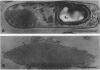
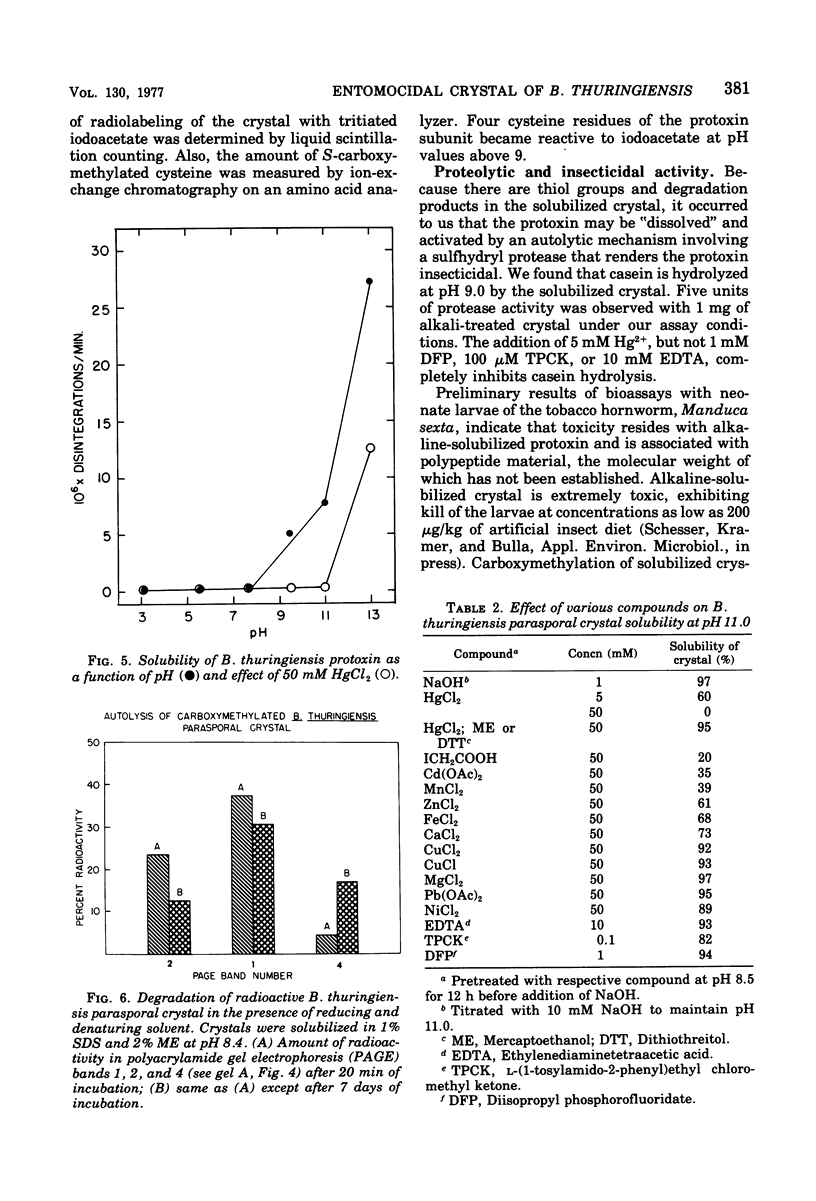
The parasporal crystalline protoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis contains a single glycoprotein subunit that has a molecular weight of approximately 1.2 X 10(5). The carbohydrate consists of glucose (3.8%) and mannose (1.8%). At alkaline pH, the proendotoxin is apparently solubilized and activated by an autolytic mechanism involving an inherent sulfhydryl protease that renders the protoxin insecticidal. Activation generates protons, degraded polypeptides, sulfhydryl group reactivity, proteolytic activity, and insect toxicity. Chemical modification of the sulfhydryl groups inhibits the proteolytic and insecticidal activities, suggesting that cysteine residues may be present in the active site of the protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arai K., Wallace H. W. Electrophoretic determination of glycoprotein: an improved method with cleared cellulose acetate membrane. Anal Biochem. 1969 Oct 1;31(1):71–76. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90242-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla L. A. Bacteria as insect pathogens. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:163–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIS D. A. A new universal buffer system. Nature. 1961 Sep 9;191:1099–1100. doi: 10.1038/1911099a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glatron M. F., Lecadet M. M., Dedonder R. Structure of the parasporal inclusion of Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner: characterization of a repetitive subunit. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct;30(2):330–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert B. N., Gould H. J., Chain E. B. Crystal protein of Bacillus thuringiensis var. tolworthi. Subunit structure and toxicity to Pieris brassicae. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Dec;24(2):366–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb19695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. C., Monro R. E. Studies on the structure of parasporal inclusions from Bacillus thuringiensis. J Mol Biol. 1965 Dec;14(2):572–581. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Comparative aspects of glycoprotein structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:217–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu T. Y., Chang Y. H. Hydrolysis of proteins with p-toluenesulfonic acid. Determination of tryptophan. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 10;246(9):2842–2848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Fish W. W. Protein polypeptide chain molecular weights by gel chromatography in guanidinium chloride. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:28–42. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickerson K. W., Bulla L. A., Jr Physiology of sporeforming bacteria associated with insects: minimal nutritional requirements for growth, sporulation, and parasporal crystal formation of Bacillus thuringiensis. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Jul;28(1):124–128. doi: 10.1128/am.28.1.124-128.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad S. S., Shethna Y. I. Enhancement of immune response by the proteinaceous crystal of Bacillus thuringiensis var thuringiensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Feb 3;62(3):517–523. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90429-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prasad S. S., Shethna Y. I. Purification, crystallization and partial characterization of the antitumour and insecticidal protein subunit from the delta-endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis var. thuringiensis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Oct 8;362(3):558–566. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90151-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROE J. H. The determination of sugar in blood and spinal fluid with anthrone reagent. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jan;212(1):335–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogoff M. H., Yousten A. A. Bacillus thuringiensis: microbiological considerations. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1969;23:357–386. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.23.100169.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A. L., Nordin J. H. Enzymes that hydrolyze fungal cell wall polysaccharides. The carbonhydrate constitution of mycodextranse, an endo-alpha (1 yields 4)-D-glucanase from Pencillium melinii. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5295–5303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayles V. B., Jr, Aronson J. N., Rosenthal A. Small polypeptide components of the Bacillus thuringiensis parasporal crystalline inclusion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Dec 9;41(5):1126–1133. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90202-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe E. S., Nickerson K. W., Bulla L. A., Jr, Aronson J. N. Separation of spores and parasporal crystals of Bacillus thuringiensis in gradients of certain x-ray contrasting agents. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Dec;30(6):1052–1053. doi: 10.1128/am.30.6.1052-1053.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloneker J. H. Determination of cellulose and apparent hemicellulose in plant tissue by gas-liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1971 Oct;43(2):539–546. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville H. J. Means for insect regulation. Microbial toxins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Jun 22;217:93–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb32752.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARREN L. The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acids. J Biol Chem. 1959 Aug;234(8):1971–1975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Pringle J. R., Osborn M. Measurement of molecular weights by electrophoresis on SDS-acrylamide gel. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:3–27. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YPHANTIS D. A. EQUILIBRIUM ULTRACENTRIFUGATION OF DILUTE SOLUTIONS. Biochemistry. 1964 Mar;3:297–317. doi: 10.1021/bi00891a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]