Abstract
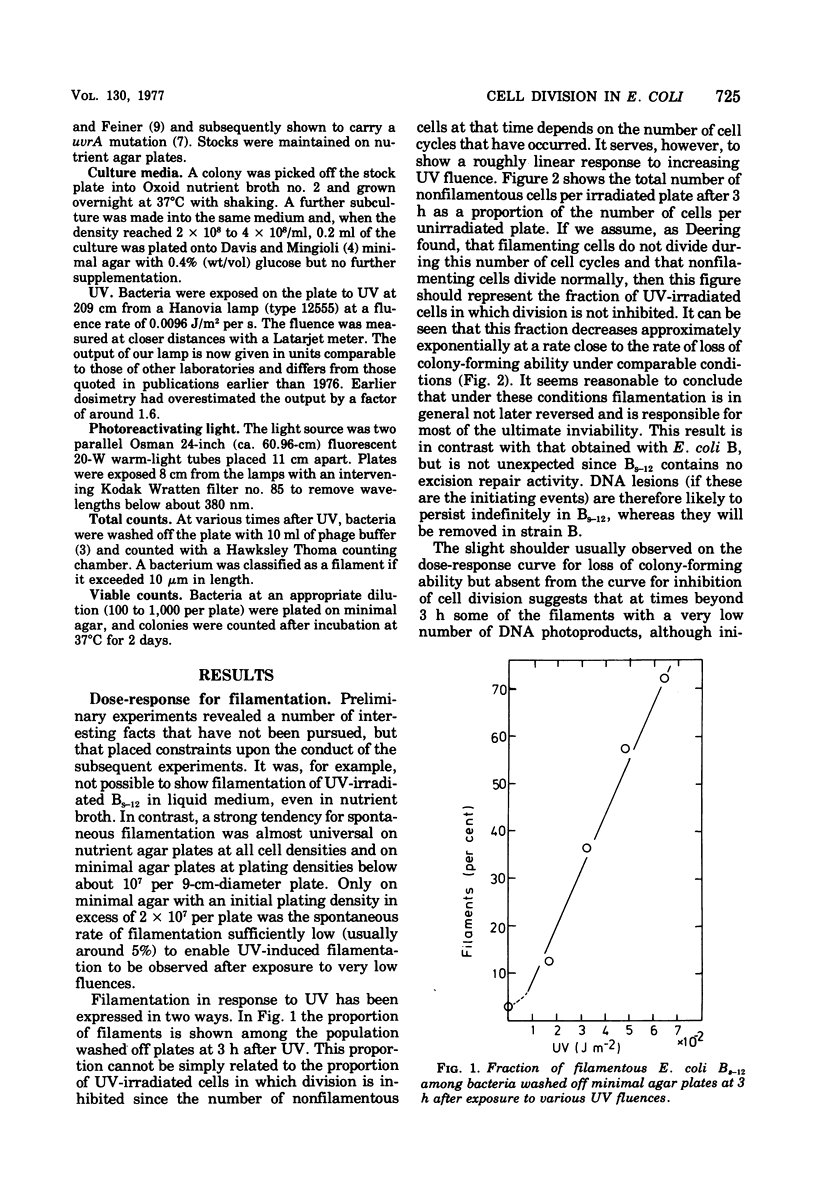
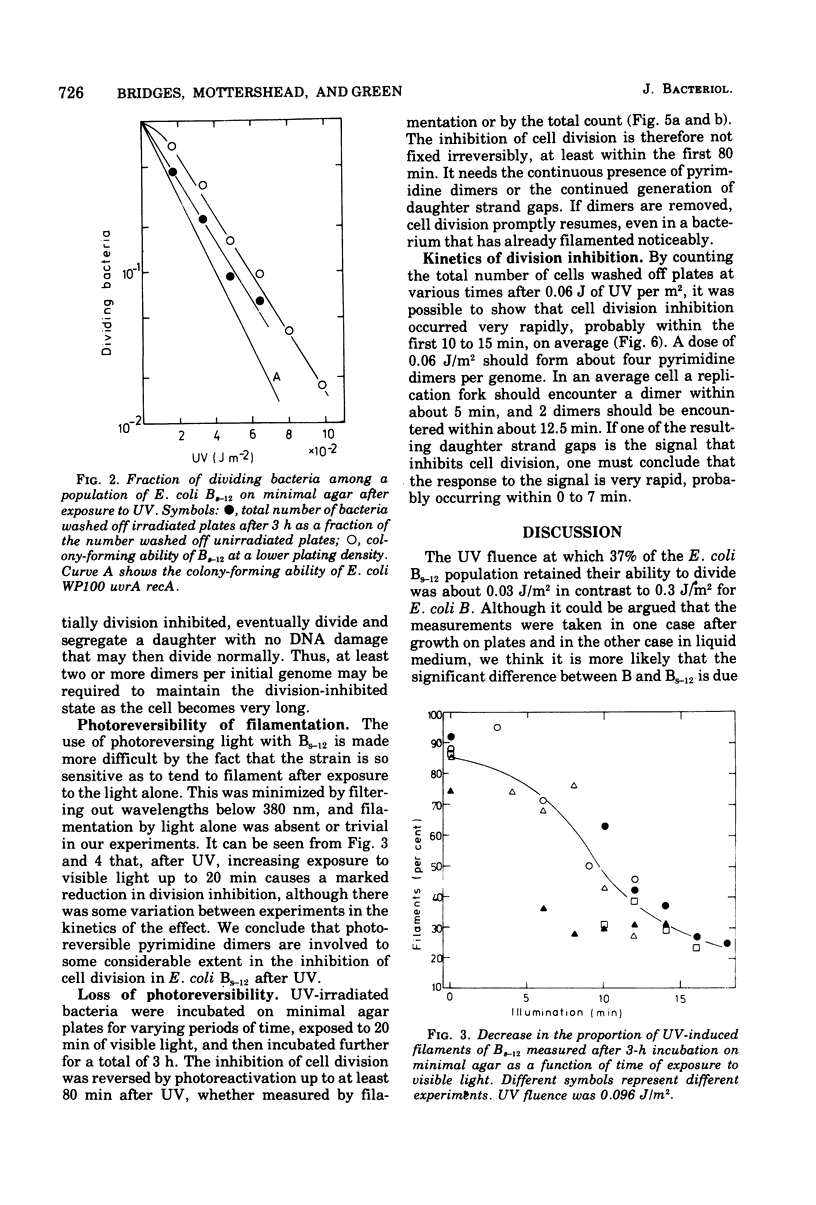
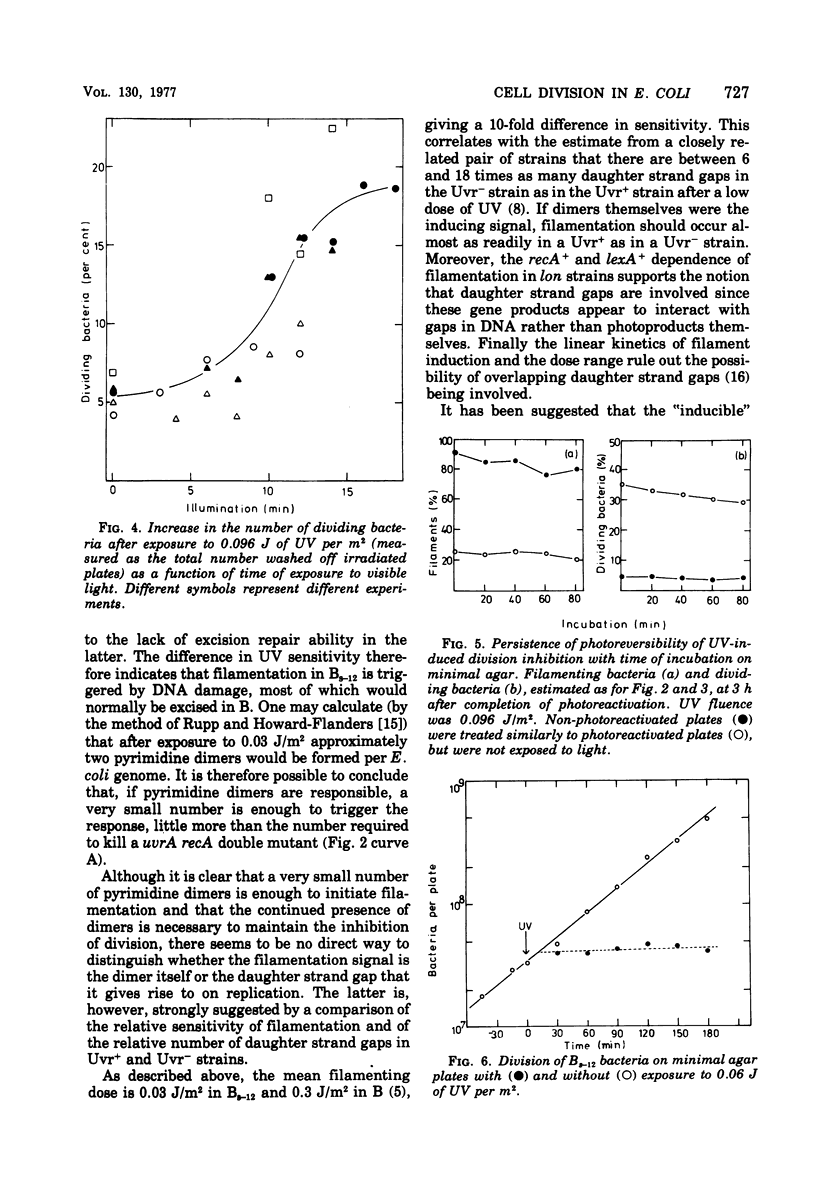
Escherichia coli BS-12 uvrA lon is hypersensitive to ultraviolet light. On minimal agar plates at densities in excess of about 10(7) bacteria per plate, as few as one or two photoreversible pyrimidine dimers in the entire genome are sufficient to cause inhibition of cell division. Most of the resulting filaments are unable to divide or form a viable colony. Inhibition of cell division appears to be a rapid consequence of replication of deoxyribonucleic acid containing a pyrimidine dimer. Photoreversibility of the inhibition of cell division persists indefinitely, indicating that the continued presence of the pyrimidine dimers (or the continued generation of daughter strand gaps) is necessary to maintain the division-inhibited state. In view of the kinetics for the production of filamentation by ultraviolet light and the extremely low average inducing fluence (0.03 J/m2), it is concluded that the initiating signal is not the same as that causing other inducible phenomena such as prophage induction or Weigle reactivation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER H. I., COPELAND J. C. Genetic analysis of radiation response in Escherichia coli. Genetics. 1962 Jun;47:701–712. doi: 10.1093/genetics/47.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ADLER H. I., HARDIGREE A. A. POSTIRRADIATION GROWTH, DIVISION, AND RECOVERY IN BACTERIA. Radiat Res. 1965 May;25:92–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. M., Symonds N. Radiation-sensitive mutants of T4D. I. T4y: a new radiation-sensitive mutant; effect of the mutation on radiation survival, growth and recombination. Mutat Res. 1969 Nov-Dec;8(3):431–439. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(69)90060-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEERING R. A. Studies on division inhibition and filament formation of Escherichia coli by ultraviolet light. J Bacteriol. 1958 Aug;76(2):123–130. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.2.123-130.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defais M., Fauquet P., Radman M., Errera M. Ultraviolet reactivation and ultraviolet mutagenesis of lambda in different genetic systems. Virology. 1971 Feb;43(2):495–503. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90321-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donch J., Greenberg J. Loci of radiation sensitivity in Bs strains of Escherichia coli. Genet Res. 1968 Apr;11(2):183–191. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300011356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HILL R. F., FEINER R. R. FURTHER STUDIES OF ULTRAVIOLET-SENSITIVE MUTANTS OF ESCHERICHIA COLI STRAIN B. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Apr;35:105–114. doi: 10.1099/00221287-35-1-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monk M., Peacey M., Gross J. D. Repair of damage induced by ultraviolet light in DNA polymerase-defective Escherichia coli cells. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jun 14;58(2):623–630. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90376-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard E. C., Randall E. P. Studies on the inducible inhibitor of radiation-induced DNA degradation of Escherichia coli. Radiat Res. 1973 Aug;55(2):265–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RORSCH A., EDELMAN A., van der KAMP, COHEN J. A. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of radiation sensitivity in Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 20;61:278–289. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radman M. SOS repair hypothesis: phenomenology of an inducible DNA repair which is accompanied by mutagenesis. Basic Life Sci. 1975;5A:355–367. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-2895-7_48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp W. D., Howard-Flanders P. Discontinuities in the DNA synthesized in an excision-defective strain of Escherichia coli following ultraviolet irradiation. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jan 28;31(2):291–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick S. G. Genetic and kinetic evidence for different types of postreplication repair in Escherichia coli B. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):154–161. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.154-161.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson P. A., Schenley R. L. Respiration, growth and viability of repair-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli after ultraviolet irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1974 Jan;25(1):51–60. doi: 10.1080/09553007414550051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. Genetics of Resistance to Radiation in ESCHERICHIA COLI. Genetics. 1947 May;32(3):221–248. doi: 10.1093/genetics/32.3.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witkin E. M. The radiation sensitivity of Escherichia coli B: a hypothesis relating filament formation and prophage induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1275–1279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


