Abstract
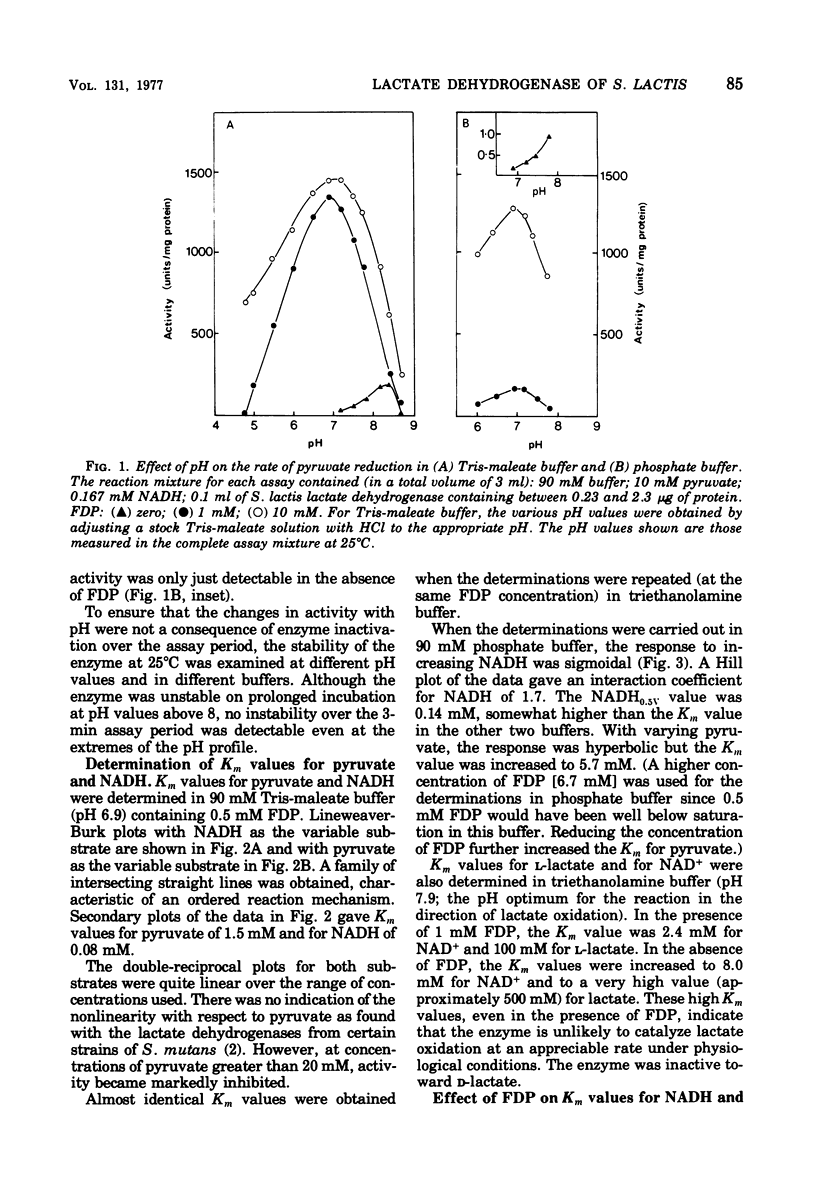
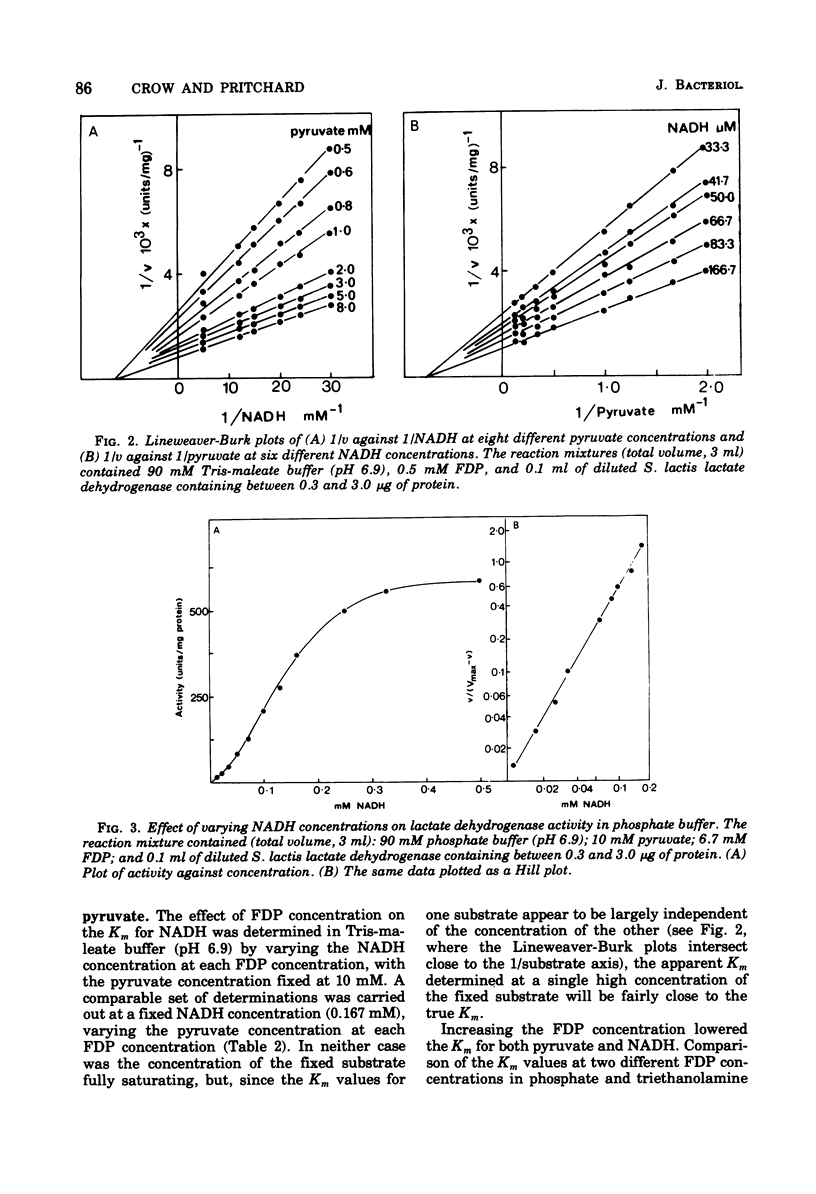
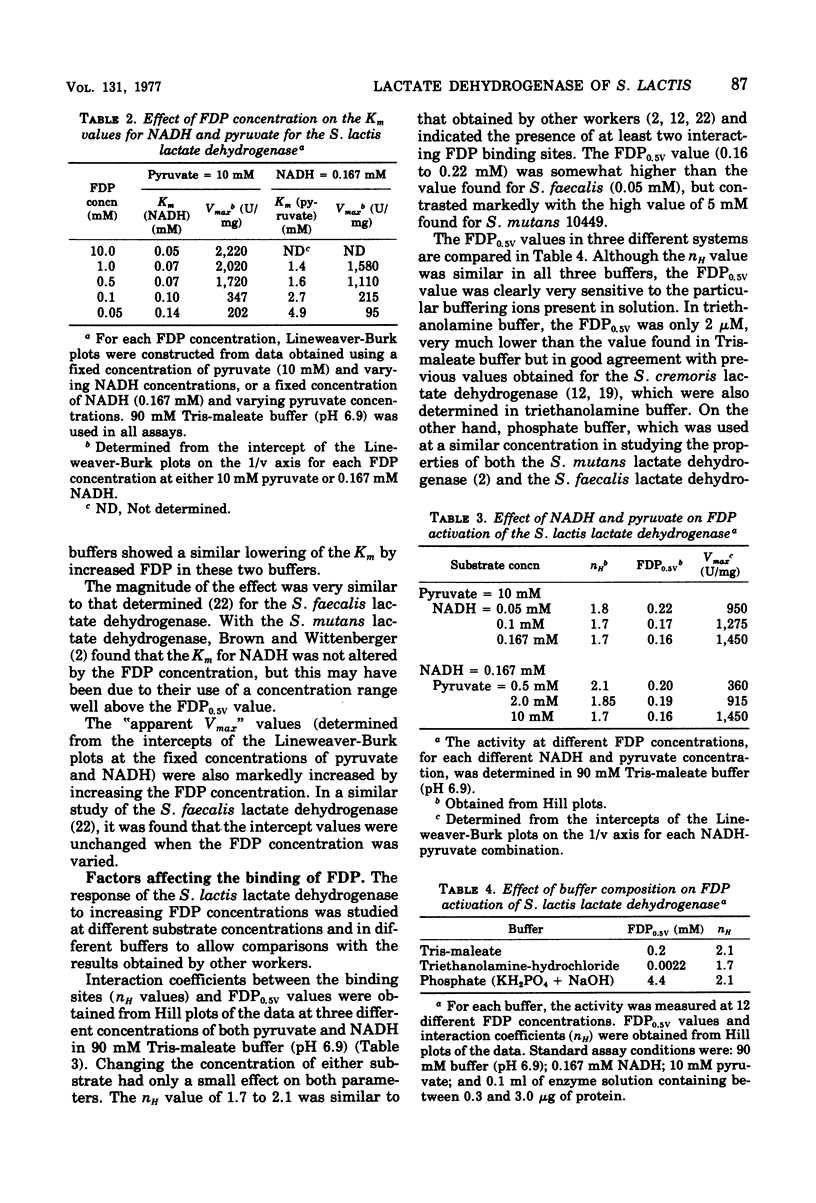
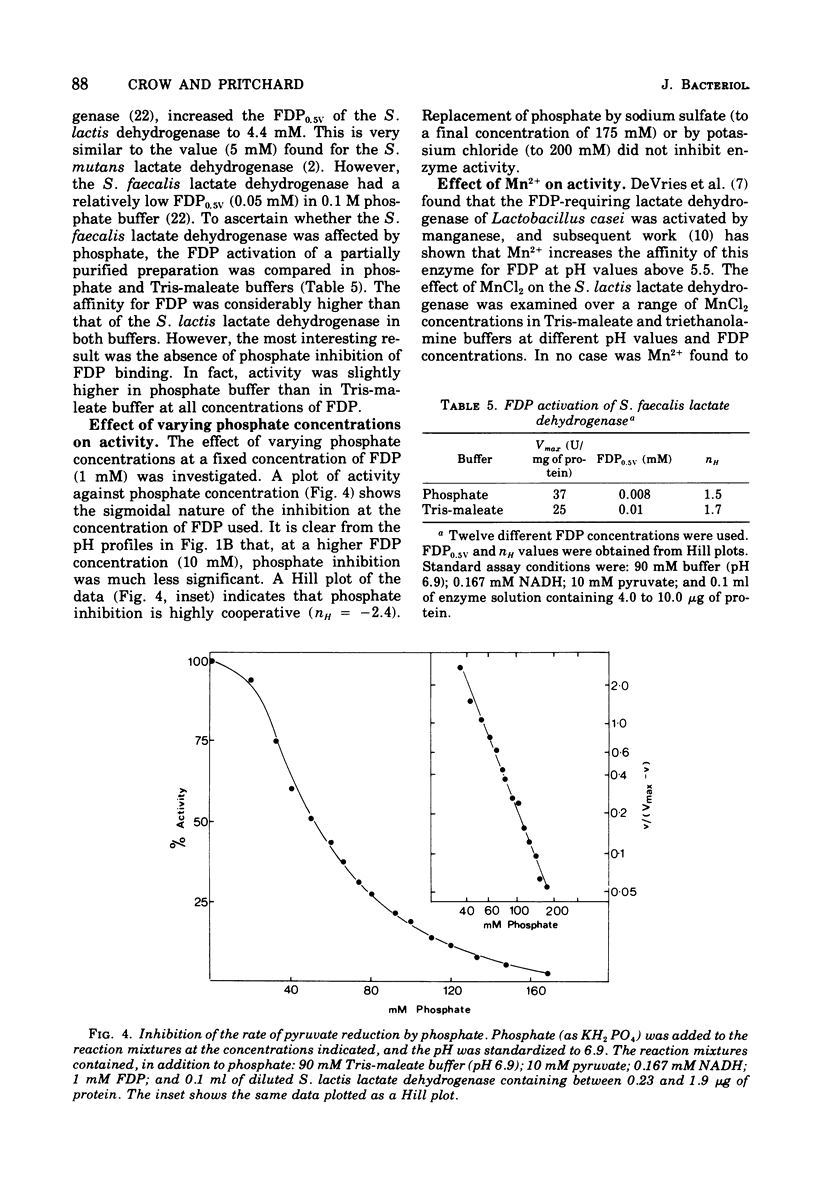
The L-(+)-lactate dehydrogenase (L-lactate:NAD+ oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.1.27) of Streptococcus lactis C10, like that of other streptococci, was activated by fructose 1,6-diphosphate (FDP). The enzyme showed some activity in the absence of FDP, with a pH optimum of 8.2; FDP decreased the Km for both pyruvate and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and shifted the pH optimum to 6.9. Enzyme activity showed a hyperbolic response to both NADH and pyruvate in all the buffers tried except phosphate buffer, in which the response to increasing NADH was sigmoidal. The FDP concentration required for half-maximal velocity (FDP0.5V) was markedly influenced by the nature of the assay buffer used. Thus the FDP0.5V was 0.002 mM in 90 mM triethanolamine buffer, 0.2 mM in 90 mM tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethanemaleate buffer, and 4.4 mM in 90 mM phosphate buffer. Phosphate inhibition of FDP binding is not a general property of streptococcal lactate dehydrogenase, since the FDP0.5V value for S. faecalis 8043 lactate dehydrogenase was not increased by phosphate. The S. faecalis and S. lactis lactate dehydrogenases also differed in that Mn2+ enhanced FDP binding in S. faecalis but had no effect on the S. lactis dehydrogenase. The FDP concentration (12 to 15 mM) found in S. lactis cells during logarithmic growth on a high-carbohydrate (3% lactose) medium would be adequate to give almost complete activation of the lactate dehydrogenase even if the high FDP0.5V value found in 90 mM phosphate were similar to the FDP requirement in vivo.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACK S. H., GERHARDT P. Permeability of bacterial spores. IV. Water content, uptake, and distribution. J Bacteriol. 1962 May;83:960–967. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.5.960-967.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. T., Wittenberger C. L. Fructose-1,6-diphosphate-dependent lactate dehydrogenase from a cariogenic streptococcus: purification and regulatory properties. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):604–615. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.604-615.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckmire F. L., MacLeod R. A. Penetrability of a marine pseudomonad by inulin, sucrose, and glycerol and its relation to the mechanism of lysis. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Feb;16(2):75–81. doi: 10.1139/m70-014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins L. B., Thomas T. D. Pyruvate kinase of Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.52-58.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow V. L., Pritchard G. G. Purification and properties of pyruvate kinase from Streptococcus lactis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jun 7;438(1):90–101. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(76)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Protein purification by affinity chromatography. Derivatizations of agarose and polyacrylamide beads. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun;245(12):3059–3065. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynon M. K., Jago G. R., Davidson B. E. The subunit structure of lactate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus cremoris US3. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct;30(2):348–353. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M., Spitz E. Accumulation of arsenate, phosphate, and aspartate by Sreptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):266–277. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.266-277.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland R., Pritchard G. G. Regulation of the L-lactase dehydrogenase from Lactobacillus casei by fructose-1,6-diphosphate and metal ions. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):777–784. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.777-784.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jago G. R., Nichol L. W., O'Dea K., Sawyer W. H. Physicochemical studies on the lactate dehydrogenase of Streptococcus cremoris US3: the effects of modifiers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Nov 13;250(2):271–285. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas H. A., Anders R. F., Jago G. R. Factors affecting the activity of the lactate dehydrognease of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):397–403. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.397-403.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashket E. R., Wilson T. H. Proton-coupled accumulation of galactoside in Streptococcus lactis 7962. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2866–2869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London J., Kline K. Aldolase of lactic acid bacteria: a case history in the use of an enzyme as an evolutionary marker. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Dec;37(4):453–478. doi: 10.1128/br.37.4.453-478.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry O. H., Carter J., Ward J. B., Glaser L. The effect of carbon and nitrogen sources on the level of metabolic intermediates in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1971 Nov;246(21):6511–6521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIZUSHIMA S., KITAHARA K. QUANTITATIVE STUDIES ON GLYCOLYTIC ENZYMES IN LACTOBACILLUS PLANTARUM. II. INTRACELLULAR CONCENTRATIONS OF GLYCOLYTIC INTERMEDIATES IN GLUCOSE-METABOLIZING WASHED CELLS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Jun;87:1429–1435. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.6.1429-1435.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Carra P., Barry S. Affinity chromatography of lactate dehydrogenase Model studies demonstrating the potential of the technique in the mechanistic investigation as well as in the purification of multi-substrate enzymes. FEBS Lett. 1972 Apr 1;21(3):281–285. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80183-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D. Activator specificity of pyruvate kinase from lactic streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1240–1242. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1240-1242.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas T. D. Tagatose-1, 6-diphosphate activation of lactate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus cremoris. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Apr 21;63(4):1035–1042. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90673-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN M. J. FRUCTOSE-1,6-DIPHOSPHATE REQUIREMENT OF STREPTOCOCCAL LACTIC DEHYDROGENASES. Science. 1964 Nov 6;146(3645):775–777. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3645.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittenberger C. L., Angelo N. Purificationa and properties of a fructose-1,6-diphosphate-activated lactate dehydrogenase from Streptococcus faecalis. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):717–724. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.717-724.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Carlsson J. Regulation of lactate dehydrogenase and change of fermentation products in streptococci. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.55-61.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries W., Kapteijn W. M., van der Beek E. G., Stouthamer A. H. Molar growth yields and fermentation balances of Lactobacillus casei L3 in batch cultures and in continuous cultures. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Nov;63(3):333–345. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-3-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


