Abstract
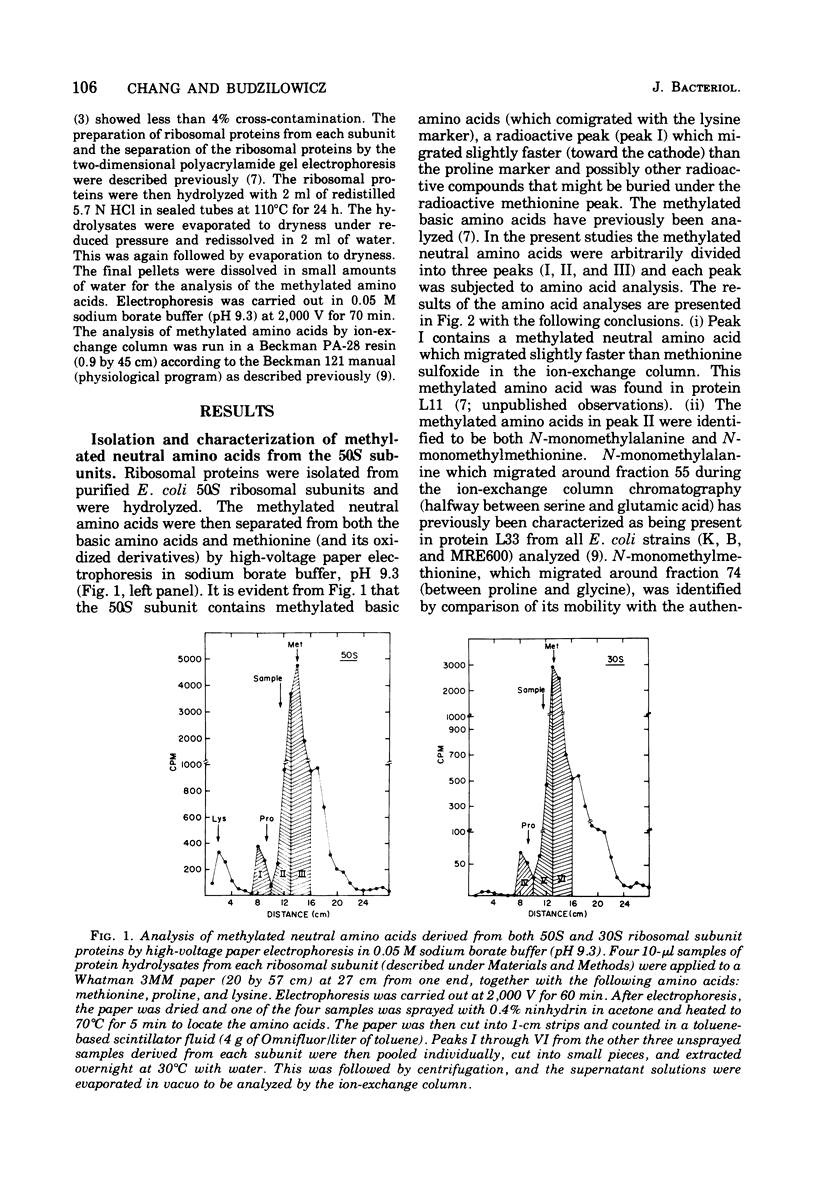
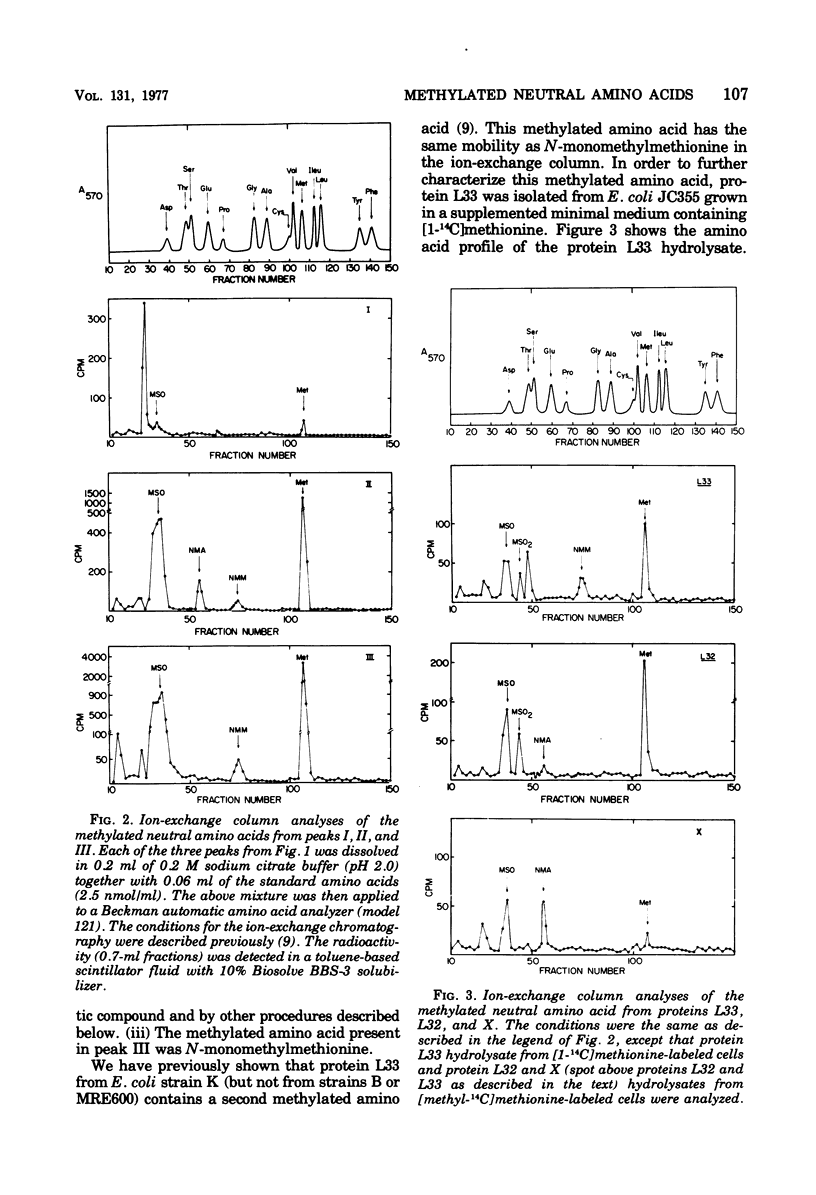
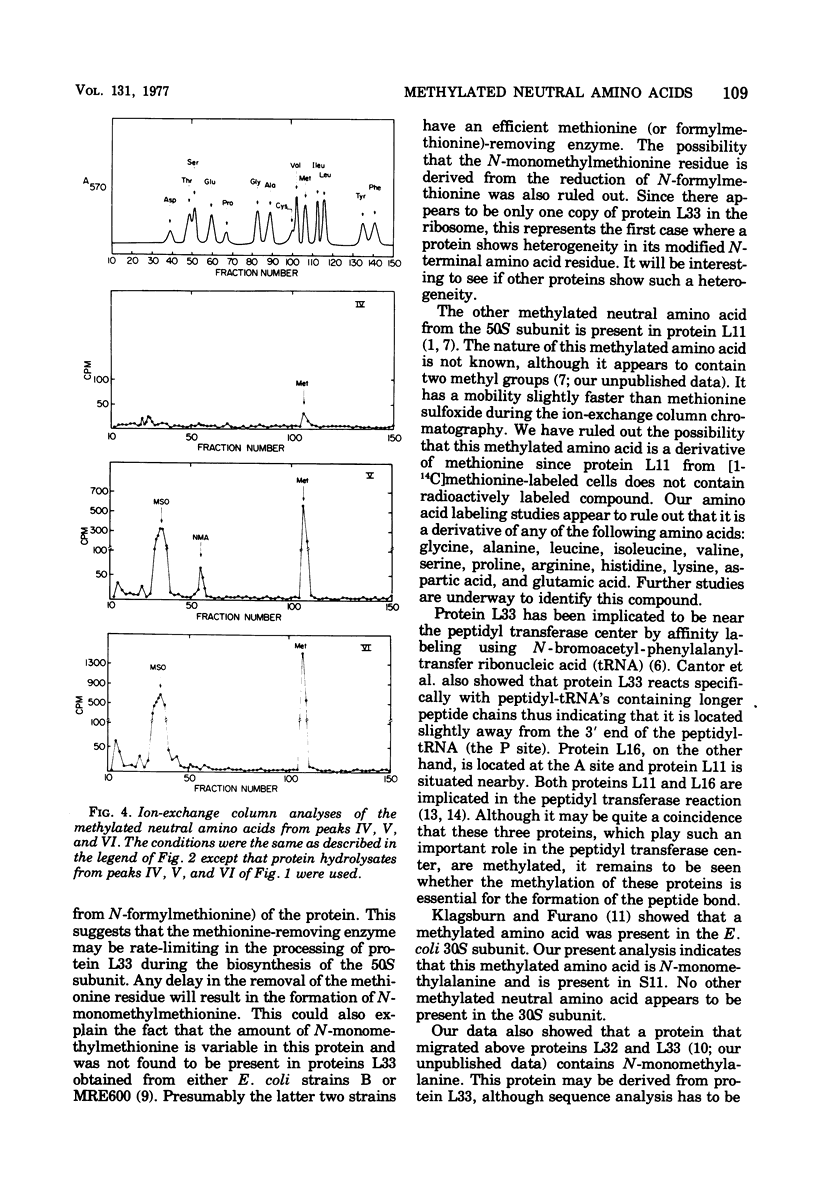
The methylated neutral amino acids from both 30S and 50S ribosomal subunits of an Escherichia coli K strain were characterized. The 50S ribosomal subunit contains three methylated neutral amino acids: N-monomethylalanine, N-monomethylmethionine, and an as yet unidentified methylated amino acid found in protein L11. Both N-monomethylalanine and N-monomethylmethionine were found in protein L33. The amount of N-monomethylmethionine in this protein, however, is variable but not more than 0.25 molecules per protein. Thus protein L33 from this E. coli K strain has heterogeneity in its N-terminal amino acid and can start with either N-monomethylalanine or N-monomethylmethionine. The N-monomethylmethionine residue was not derived from the reduction of N-formylmethionine in the protein. The 30S ribosomal subunit contains only one methylated neutral amino acid: N-monomethylalanine.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alix J. H., Hayes D. Properties of ribosomes and RNA synthesized by Escherichia coli grown in the presence of ethionine. 3. Methylated proteins in 50 S ribosomes of E. coli EA2. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 15;86(1):139–159. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(74)80013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. H., Claybrook J. R., Spiegelman S. Electrophoretic separation of viral nucleic acids on polyacrylamide gels. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 28;26(3):373–387. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Chen R. The primary structure of protein L16 located at the peptidyltransferase center of Escherichia coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):105–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80415-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. N., Chang N. Methylation of the ribosomal proteins in Escherichia coli. Nature and stoichiometry of the methylated amino acids in 50S ribosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 11;14(3):468–477. doi: 10.1021/bi00674a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. N., Schwartz M., Chang F. N. Identification and characterization of a new methylated amino acid in ribosomal protein L33 of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Nov 22;73(2):233–239. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90698-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang F. N., Chang C. N., Paik W. K. Methylation of ribosomal proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):651–656. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.651-656.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. VII. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for fingerprinting of ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1970 Aug;36(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Furano A. V. Methylated amino acids in the proteins of bacterial and mammalian cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Aug;169(2):529–539. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90196-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means G. E., Feeney R. E. Reductive alkylation of amino groups in proteins. Biochemistry. 1968 Jun;7(6):2192–2201. doi: 10.1021/bi00846a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore V. G., Atchison R. E., Thomas G., Moran M., Noller H. F. Identification of a ribosomal protein essential for peptidyl transferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):844–848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Montejo V. A protein involved in the peptidyltransferase activity of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1931–1935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reporter M. Methylation of basic residues in structural proteins. Mech Ageing Dev. 1973 Mar;1(5):367–372. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(73)90043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staehelin T., Maglott D. M., Monro R. E. On the catalytic center of peptidyl transfer: a part of the 50 S ribosome structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:39–48. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1969.034.01.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terhorst C., Wittmann-Liebold B., Möller W. 50-S ribosomal proteins. Peptide studies on two acidic proteins, A 1 and A 2 , isolated from 50-S ribosomes of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 31;25(1):13–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01661.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann-Liebold B., Greuer B., Pannenbecker R. The primary structure of protein L32 from the 50S subunit of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1975 Dec;356(12):1977–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann-Liebold B., Pannenbecker R. Primary structure of protein L33 from the large subunit of the Escherichia coli ribosome. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80417-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


