Abstract
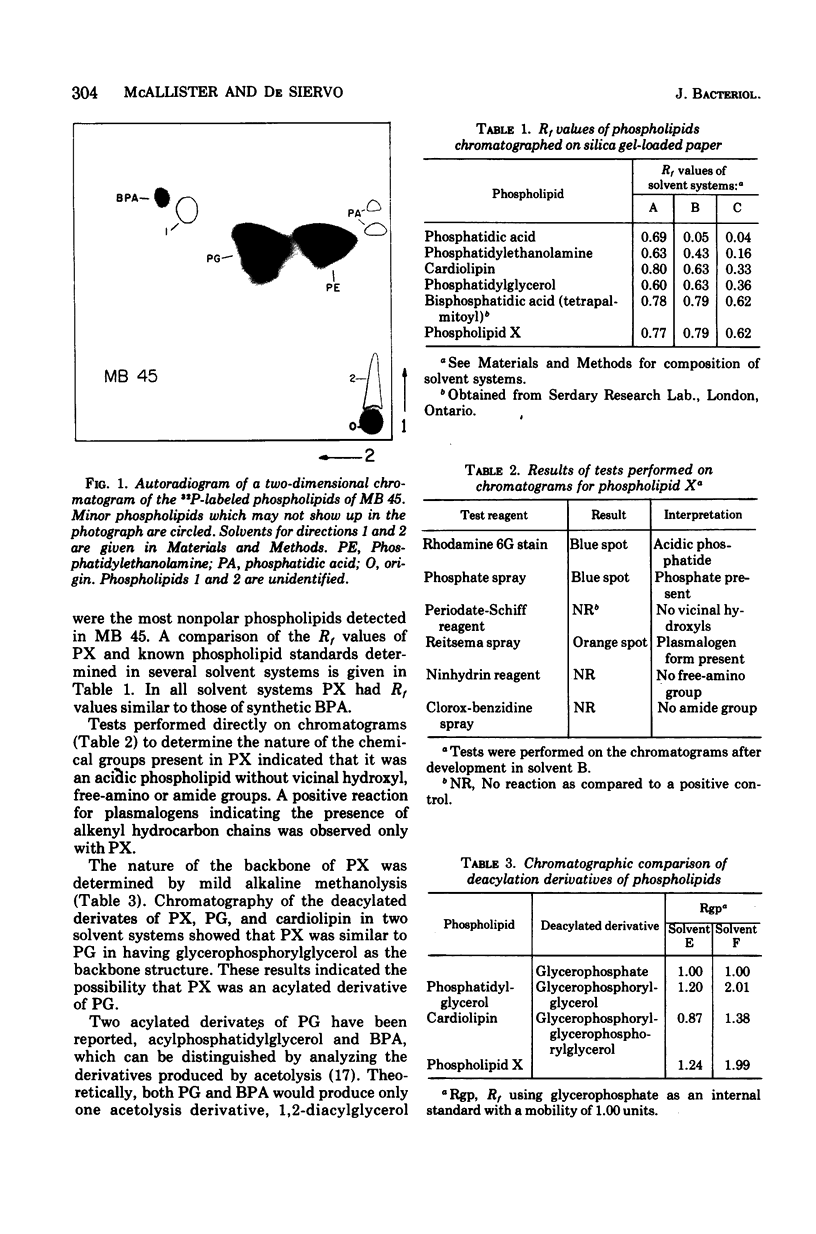
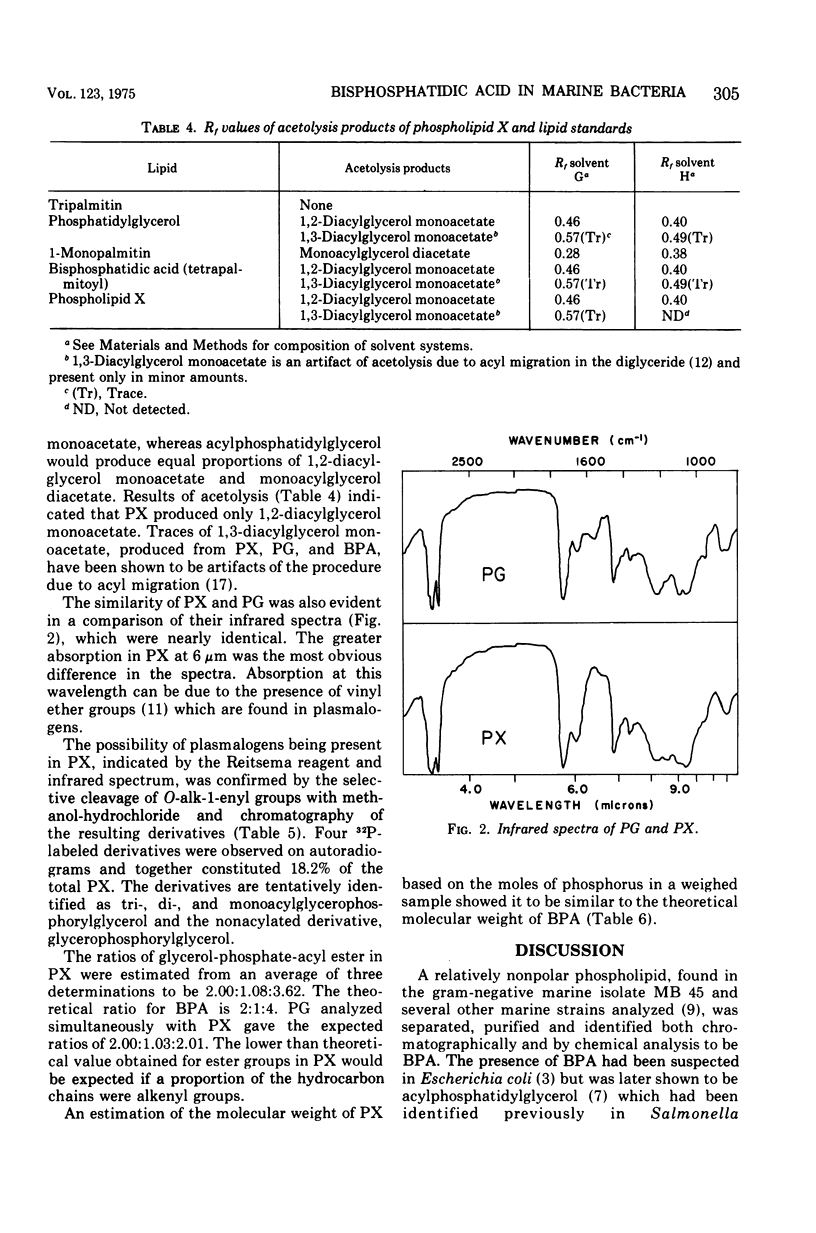
A relatively nonpolar unidentified phospholipid (phospholipid X) , isolated from the gram-negative marine bacterium MB 45, was characterized both chromatographically and by chemical analysis. Phospholipid X was shown to be an acidic phospholipid without vicinal hydroxyl, free-amino, or amide groups. The presence of O-alkenyl groups was indicated by a positive reaction for plasmalogen. Mild alkaline methanolysis of phospholipid X yielded only glycerophosphoryglycerol as the derivative. Acetolysis produced only diacyl-glycerol monoacetate. Clevage of O-alkenyl chains by methanolic hydrochloride resulted in the formation of three lyso derivatives. It was estimated that 18.2% of phospholipid X was plasmalogen. From these data, together with chromatographic comparisons with standards, infrared spectra, a molecular weight estimation, and the determination of the glycerol-phosphate-acyl ester ratio, it was concluded that phospholipid X was bisphosphatidic acid mixed with its plasmalogen analogues.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMES B. N., DUBIN D. T. The role of polyamines in the neutralization of bacteriophage deoxyribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1960 Mar;235:769–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benns G., Proulx P. Formation of a new phosphatidyl glycerol derivative in E. coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jul 16;44(2):382–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90611-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho K. S., Benns G., Proulx P. Formation of acyl phosphatidyl glycerol by Escherichia coli extracts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Dec 20;326(3):355–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debuch H., Rotsch E. Uber ein unbekanntes N-freies Glycerinphosphatid aus grünen Blättern von Spinacia oleracea. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1966;347(1):79–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diervo A. J., Reynolds J. W. Phospholipid composition and cardiolipin synthesis in fermentative and nonfermentative marine bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):294–301. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.294-301.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer W., Ishizuka I., Landgraf H. R., Herrmann J. Glycerophosphoryl diglucosyl diglyceride, a new phosphoglycolipid from Streptococci. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 8;296(3):527–545. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(73)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTFRIED E. L., RAPPORT M. M. The biochemistry of plasmalogens. I. Isolation and characterization of phosphatidal choline, a pure native plasmalogen. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:329–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLLEY J. The lipids of fish. 7. Phosphate esters in the lipids of haddock and cod flesh. Biochem J. 1956 Jan;62(1):107–114. doi: 10.1042/bj0620107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Ballou C. E. Acyl phosphatidylglycerol. A new phospholipid from Salmonella typhimurium. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3305–3313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENKONEN O. Determination of glycerol in phosphatides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Jan 29;56:367–369. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90580-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RENKONEN O. INDIVIDUAL MOLECULAR SPECIES OF DIFFERENT PHOSPHOLIPID CLASSES. II. A METHOD OF ANALYSIS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Apr;42:298–304. doi: 10.1007/BF02540133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Kritchevsky G., Knudson A. G., Jr, Simon G. Accumulation of a glycerolphospholipid in classical niemann-pick disease. Lipids. 1968 May;3(3):287–290. doi: 10.1007/BF02531203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SNYDER F., STEPHENS N. A simplified spectrophotometric determination of ester groups in lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1959 Jul;34:244–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(59)90255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Spritz N., Geyer B. Studies of brain myelin in the "quaking mouse". J Lipid Res. 1971 Jul;12(4):473–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Smolowe A. F., Barclay M. Separation of neutral glycosphingolipids and sulfatides by thin-layer chromatography. J Lipid Res. 1967 Jul;8(4):295–299. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYLER M. E., BIELLING M. C., PRATT D. B. Mineral requirements and other characters of selected marine bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Aug;23:153–161. doi: 10.1099/00221287-23-1-153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VORBECK M. L., MARINETTI G. V. SEPARATION OF GLYCOSYL DIGLYCERIDES FROM PHOSPHATIDES USING SILICIC ACID COLUMN CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jan;6:3–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White D. C., Frerman F. E. Extraction, characterization, and cellular localization of the lipids of Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol. 1967 Dec;94(6):1854–1867. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.6.1854-1867.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuthier R. E. Two-dimensional chromatography on silica gel-loaded paper for the microanalysis of polar lipids. J Lipid Res. 1966 Jul;7(4):544–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto A., Adachi S., Kitani T., Shinji Y., Seki K. Drug-induced lipidosis in human cases and in animal experiments. Accumulation of an acidic glycerophospholipid. J Biochem. 1971 Mar;69(3):613–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



