Abstract
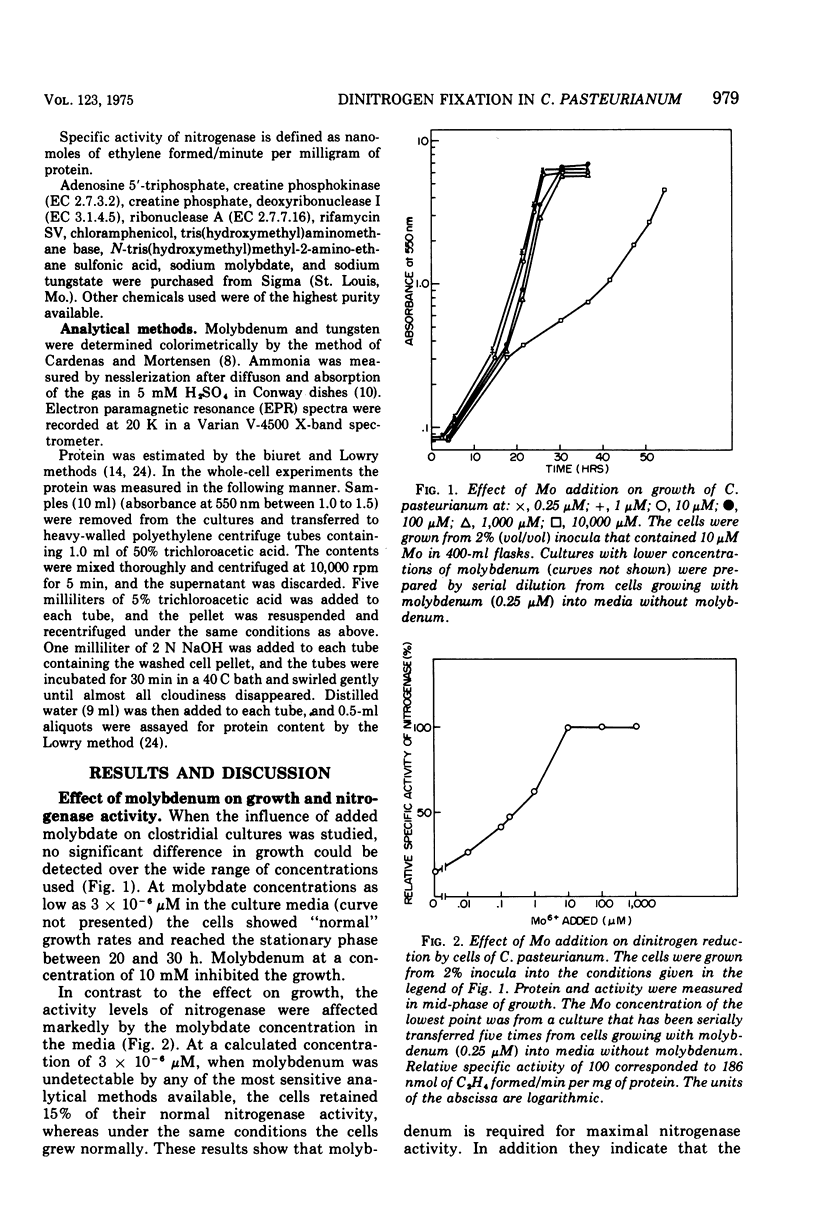
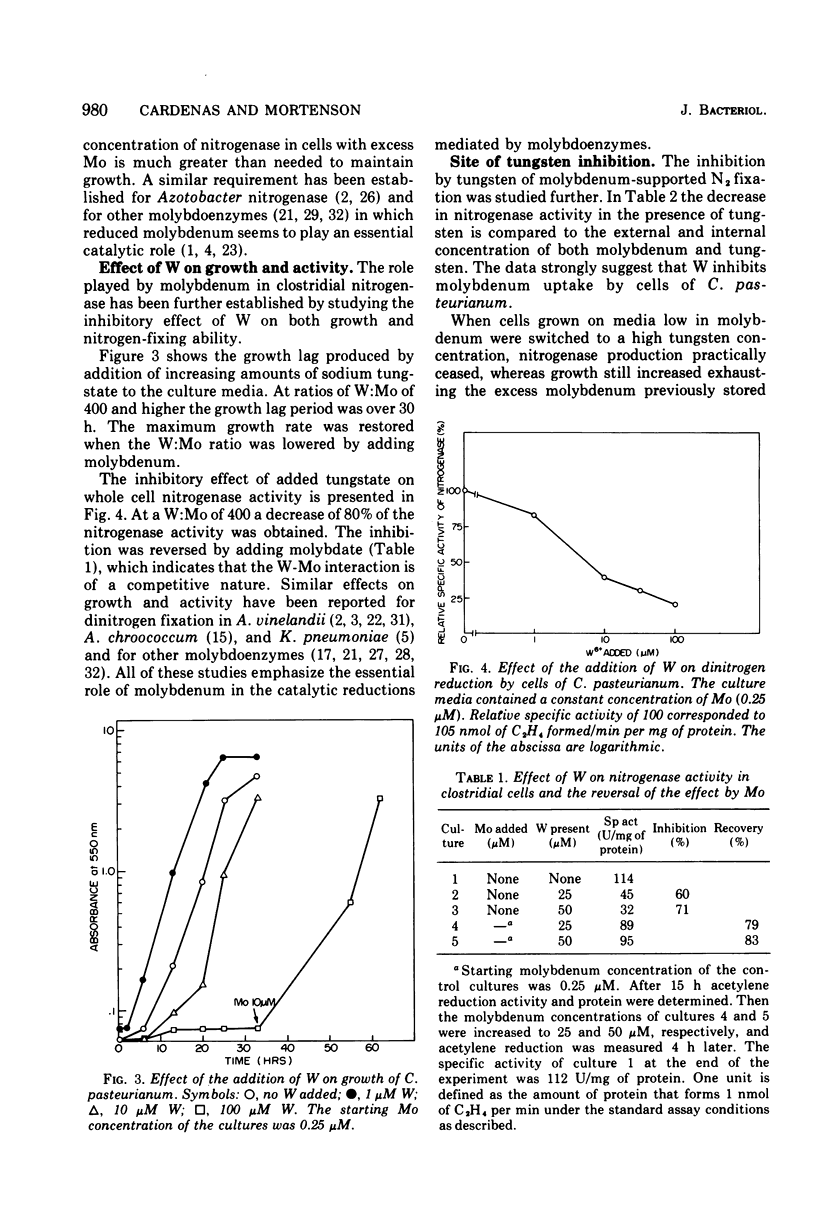
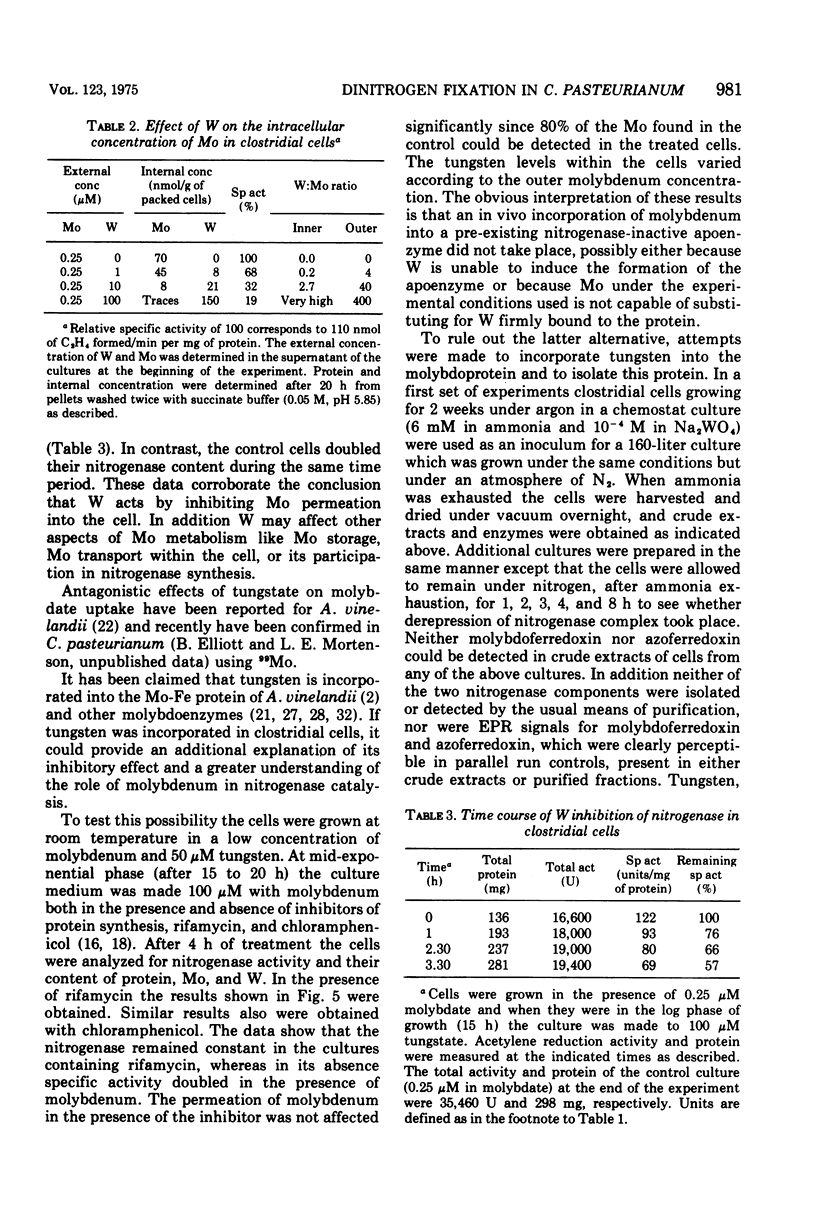
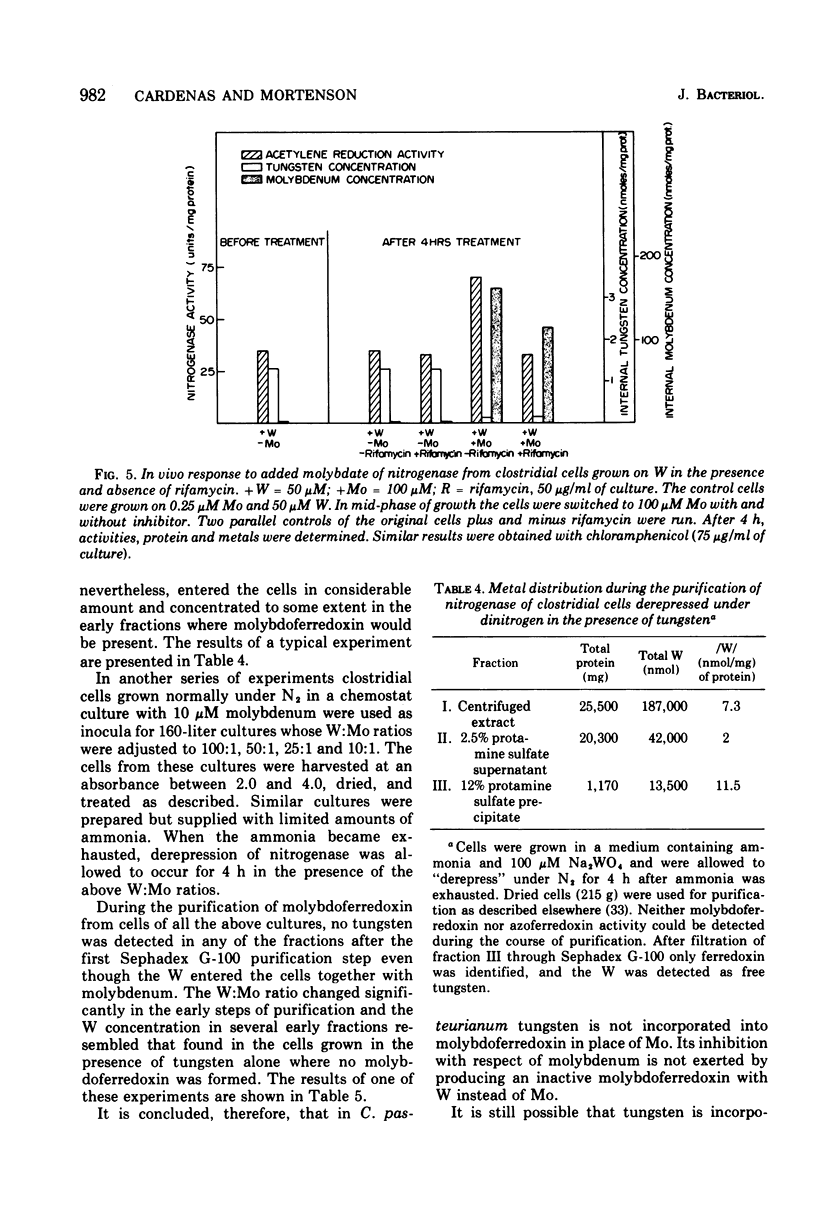
The role of Mo in the activity and synthesis of the nitrogenase components of Clostridium pasteurianum has been studied by observing the competition of Mo with its structural analogue W. Clostridial cells when fixing N2 appeared strictly dependent upon the available Mo, showing maximal N2-fixing activity at molybdate concentrations in the media of 10 muM. Cells grown in media with 3 times 10(-6) muM Mo, although showing good growth, had only 15% as much N2-fixing activity. In the presence of W the synthesis of both nitrogenase components, molybdoferredoxin and azoferredoxin, was affected. Attempts to produce nitrogenase in W-grown cells by addition of high molybdenum to the media in the presence of inhibitors of protein synthesis showed that Mo incorporation into a possible inactive preformed apoenzyme did not occur. Unlike other molybdoenzyme-containing cells, in which W either is incorporated in place of Mo to yield inactive protein or initiates the production of apoprotein, C. pasteurianum forms neither a tungsten substituted molybdoferredoxin nor an apoprotein. It is concluded that in C. pasteurianum molybdenum is an essential requirement for both the biosynthesis and activity of its nitrogenase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRAY R. C., MALMSTROM B. G., VANNGARD T. The chemistry of xanthine oxidase. Electron-spin resonance of xanthine oxidase solutions. Biochem J. 1959 Sep;73:193–197. doi: 10.1042/bj0730193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benemann J. R., Smith G. M., Kostel P. J., McKenna C. E. Tungsten incorporation into Azotobacter vinelandii nitrogenase. FEBS Lett. 1973 Feb 1;29(3):219–221. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brill W. J., Steiner A. L., Shah V. K. Effect of molybdenum starvation and tungsten on the synthesis of nitrogenase components in Klebsiella pneumonia. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jun;118(3):986–989. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.3.986-989.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulen W. A., LeComte J. R. The nitrogenase system from Azotobacter: two-enzyme requirement for N2 reduction, ATP-dependent H2 evolution, and ATP hydrolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):979–986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. C., Holsten R. D., Hardy R. W. Isolation by crystallization of the Mo-Fe protein of Azotobacter nitrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Apr 8;39(1):90–99. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90762-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardenas J., Mortenson L. E. Determination of molybdenum and tungsten in biological materials. Anal Biochem. 1974 Aug;60(2):372–381. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H. J., Drew R. T., Johnson J. L., Rajagopalan K. V. Molecular basis of the biological function of molybdenum: the relationship between sulfite oxidase and the acute toxicity of bisulfite and SO2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3655–3659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth M. J. Acetylene reduction by nitrogen-fixing preparations from Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 31;127(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90383-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eady R. R., Smith B. E., Cook K. A., Postgate J. R. Nitrogenase of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Purification and properties of the component proteins. Biochem J. 1972 Jul;128(3):655–675. doi: 10.1042/bj1280655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Telfer A., Smith R. V. The purification and some properties of the molybdenum-iron protein of Chromatium nitrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 15;310(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero M. G., Vega J. M., Leadbetter E., Losada M. Preparation and characterization of a soluble nitrate reductase from Azotobacter chroococcum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Jun 25;91(4):287–304. doi: 10.1007/BF00425049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGGINS E. S., RICHERT D. A., WESTERFELD W. W. Tungstate antagonism of molybdate in Aspergillus niger. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jul;92(3):509–511. doi: 10.3181/00379727-92-22527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel D. W., Howard R. L., Evans H. J., Russell S. A. Purification and characterization of the molybdenum-iron protein component of nitrogenase from soybean nodule bacteroids. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):500–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Cohen H. J., Rajagopalan K. V. Molecular basis of the biological function of molybdenum. Molybdenum-free sulfite oxidase from livers of tungsten-treated rats. J Biol Chem. 1974 Aug 25;249(16):5046–5055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. L., Rajagopalan K. V., Cohen H. J. Molecular basis of the biological function of molybdenum. Effect of tungsten on xanthine oxidase and sulfite oxidase in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):859–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEELER R. F., VARNER J. E. Tungstate as an antagonist of molybdate in Azotobacter vinelandii. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Aug;70(2):585–590. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortenson L. E., Morris J. A., Jeng D. Y. Purification, metal composition and properties of molybdoferredoxin and azoferredoxin, two of the components of the nitrogen-fixing system of Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Aug 29;141(3):516–522. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90180-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatani H. H., Brill W. J. Nitrogenase V. The effect of Mo, W and V on the synthesis of nitrogenase components in Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 7;362(1):160–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(74)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notton B. A., Hewitt E. J. The role of tungsten in the inhibition of nitrate reductase activity in spinach (spinacea oleracea L.) leaves. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Aug 6;44(3):702–710. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(71)80140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHERT D. A., WESTERFELD W. W. Isolation and identification of the xanthine oxidase factor as molybdenum. J Biol Chem. 1953 Aug;203(2):915–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto B., Mortenson L. E. In vivo kinetics of nitrogenase formation in Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):822–830. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.822-830.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKAHASHI H., NASON A. Tungstate as competitive inhibitor of molybdate in nitrate assimilation and in N2 fixation by Azotobacter. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Feb;23(2):433–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega J. M., Herrera J., Aparicio P. J., Paneque A., Losada M. Role of molybdenum in nitrate reduction by chlorella. Plant Physiol. 1971 Sep;48(3):294–299. doi: 10.1104/pp.48.3.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zumft W. G., Mortensson L. E. Evidence for a catalytic-centre heterogeneity of molybdoferredoxin from Clostridium pasteurianum. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun 15;35(3):401–409. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


