Abstract
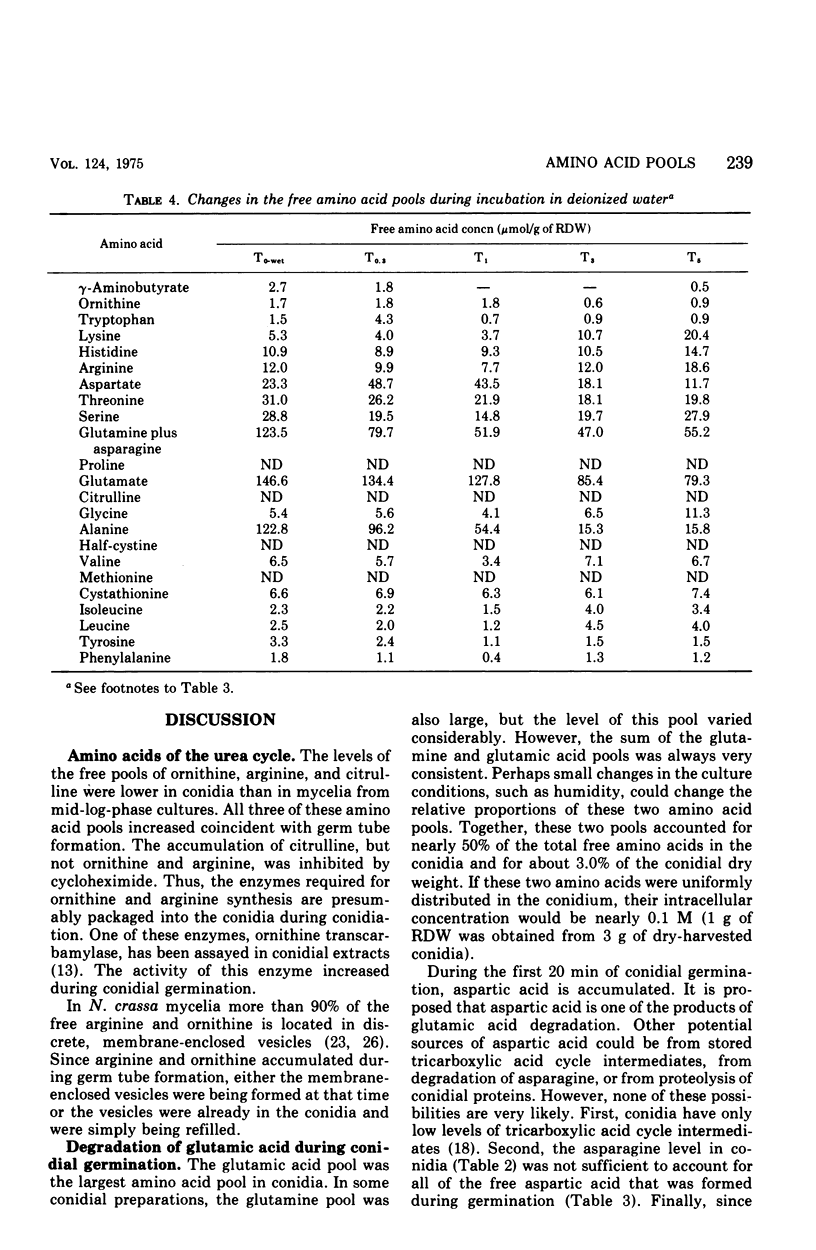
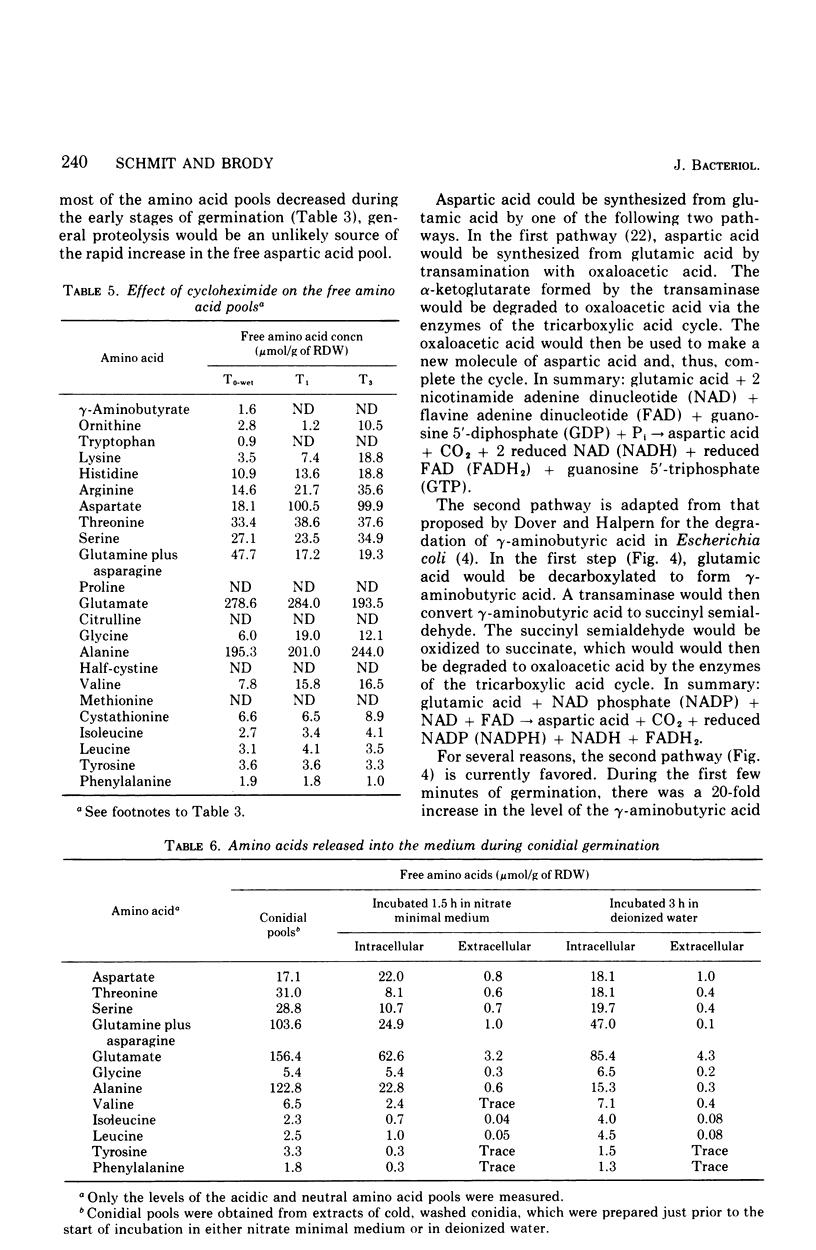
The levels of the endogenous amino acid pools in conidia, germinating conidia, and mycelia of wild-type Neurospora crassa were measured. Three different chromatographic procedures employing the amino acid analyzer were used to identify and quantitatively measure 28 different ninhydrin-positive compounds. All of the common amino acids were detected in conidial extracts except proline, methionine, and cystine. The levels of these three amino acid pools were also very low in mycelia. During the first hour of germination in minimal medium, the levels of most of the free amino acid pools decreased. The pool of glutamic acid, the predominant free amino acid in conidia, decreased 70% during the first hour. Very little glutamic acid or any other amino acid was excreted into the medium. During the first 20 min of germination, the decrease in the glutamic acid pool was nearly equivalent to the increase in the aspartic acid pool. The aspartic acid and lambda-aminobutyric acid pools were the only amino acid pools that increased to maximum levels within the first 20 min of germination and then decreased. It is proposed that an important metabolic event that occurs during the early stages of conidial germination is the production of reduced pyridine nucleotides. The degradation of the large glutamic acid pool existing in the conidia (2.5% of the conidial dry weight) could produce these reduced coenzymes.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken W. B., Niederpruem D. J. Isotopic studies of carbohydrate metabolism during basidiospore germination in Schizophyllum commune. II. Changes in specifically labeled glucose and sugar alcohol utilization. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973;88(4):331–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00409944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceccarini C. The biochemical relationship between trehalase and trehalose during growth and differentiation in the cellular slime mold, Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 9;148(1):114–124. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(67)90285-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. H., Lawless M. B., Port L. A. Arginaseless Neurospora: genetics, physiology, and polyamine synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):299–305. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.299-305.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
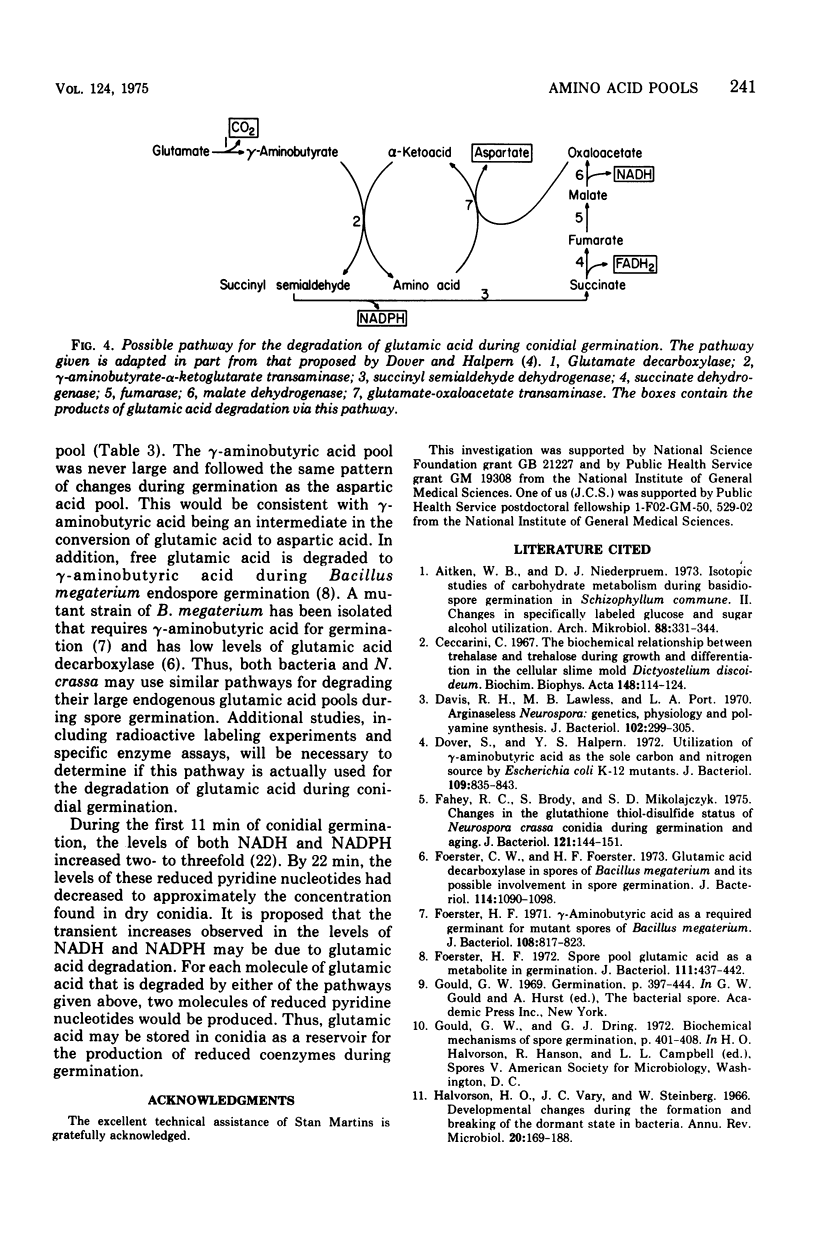
- Dover S., Halpern Y. S. Utilization of -aminobutyric acid as the sole carbon and nitrogen source by Escherichia coli K-12 mutants. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):835–843. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.835-843.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahey R. C., Brody S., Mikolajczyk S. D. Changes in the glutathione thiol-disulfide status of Neurospora crassa conidia during germination and aging. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):144–151. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.144-151.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foerster C. W., Foerster H. F. Glutamic acid decarboxylase in spores of Bacillus megaterium and its possible involvement in spore germination. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1090–1098. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1090-1098.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foerster H. F. -aminobutyric acid as a required germinant for mutant spores of Bacillus megaterium. J Bacteriol. 1971 Nov;108(2):817–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.2.817-823.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foerster H. F. Spore pool glutamic acid as a metabolite in germination. J Bacteriol. 1972 Aug;111(2):437–442. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.2.437-442.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halvorson H. O., Vary J. C., Steinberg W. Developmental changes during the formation and breaking of the dormant state in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1966;20:169–188. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.20.100166.001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks D. L., Sussman A. S. The relation between growth, conidiation and trehalase activity in Neurospora crassa. Am J Bot. 1969 Nov-Dec;56(10):1152–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobbágy A. J., Wagner R. P. Changes in enzyme activity of germinating conidia of Neurospora crassa. Dev Biol. 1973 Apr;31(2):264–274. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90263-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkes P. E. Polysomes, ribonucleic acid, and protein synthesis during germination of Neurospora crassa conidia. J Bacteriol. 1974 Jan;117(1):196–202. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.1.196-202.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. L., Kornberg A. Biochemical studies of bacterial sporulation and germination. 18. Free amino acids in spores. J Biol Chem. 1970 Mar 10;245(5):1128–1136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMIREZ C., MILLER J. J. THE METABOLISM OF YEAST SPORULATION. VI. CHANGES IN AMINO ACID CONTENT DURING SPOROGENESIS. Can J Microbiol. 1964 Oct;10:623–631. doi: 10.1139/m64-082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODE L. J., FOSTER J. W. Ionic germination of spores of Bacillus megaterium QM B 1551. Arch Mikrobiol. 1962;43:183–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00406435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau P., Halvorson H. O. Macromolecular synthesis during the germanation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae spores. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1289–1295. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1289-1295.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N., Weiss R. L., Davis R. H. Use of external, biosynthetic, and organellar arginine by Neurospora. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):284–290. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.284-290.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss R. L. Intracellular localization of ornithine and arginine pools in Neurospora. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5409–5413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebers J. L., Garner H. R. Interrelationships of sulfur amino acids in the pool and cellular protein of Neurospora crassa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Apr 25;117(2):403–409. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90091-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZALOKAR M. Kinetics of amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in Neurospora. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jan 29;46:423–432. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90573-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


