Abstract
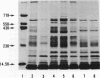
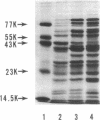
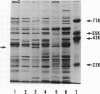
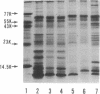
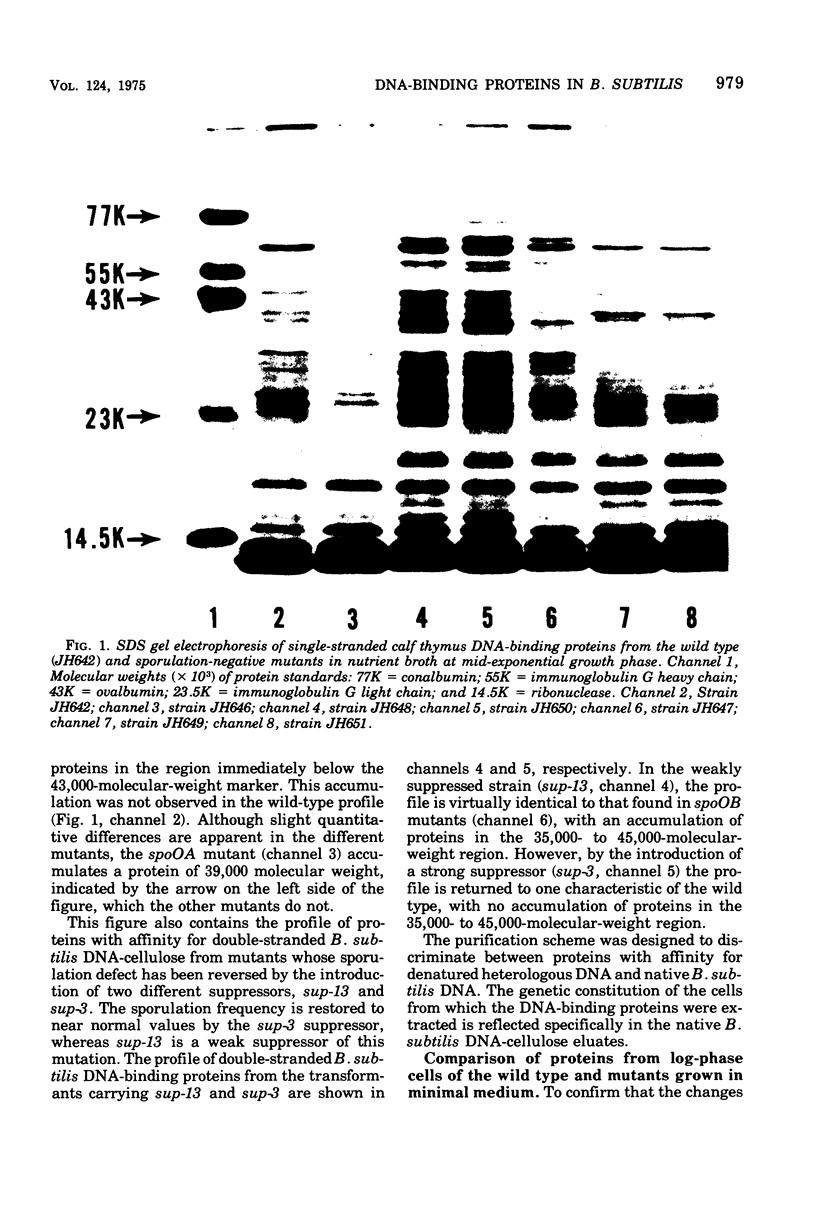
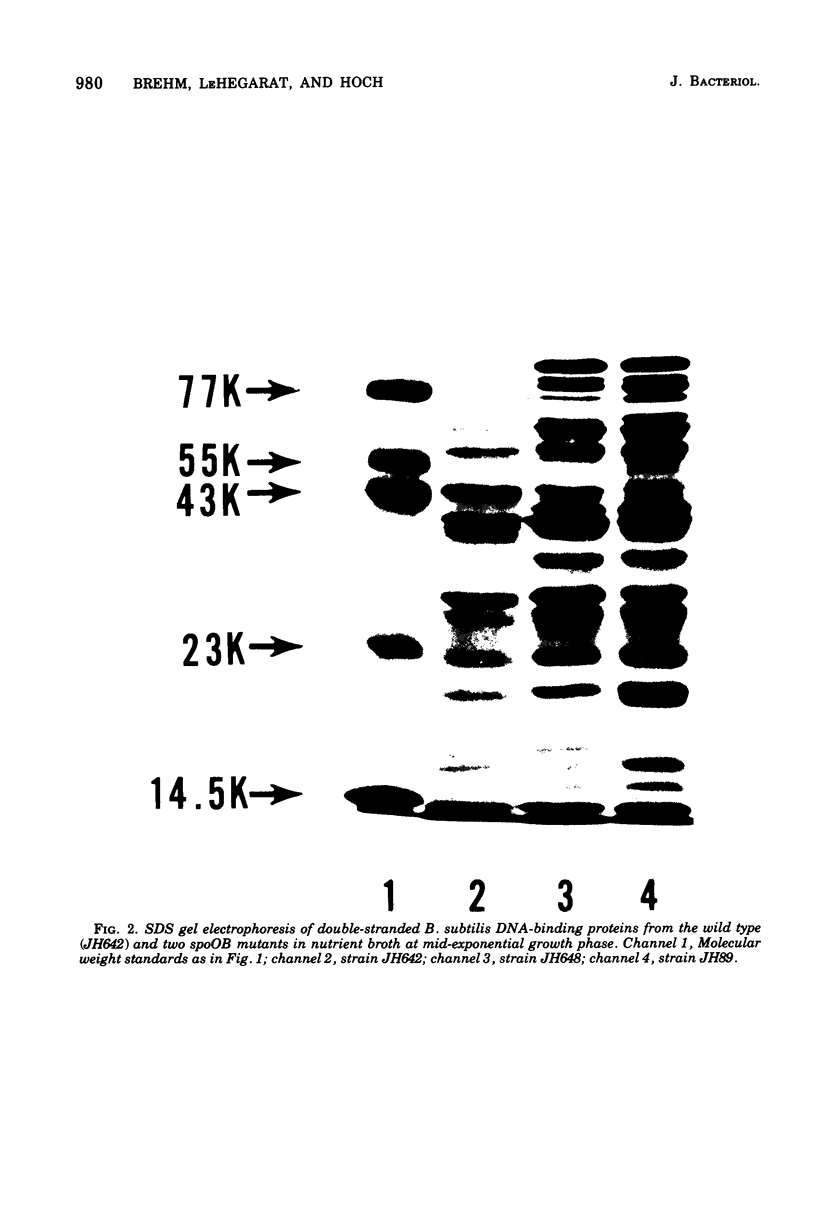
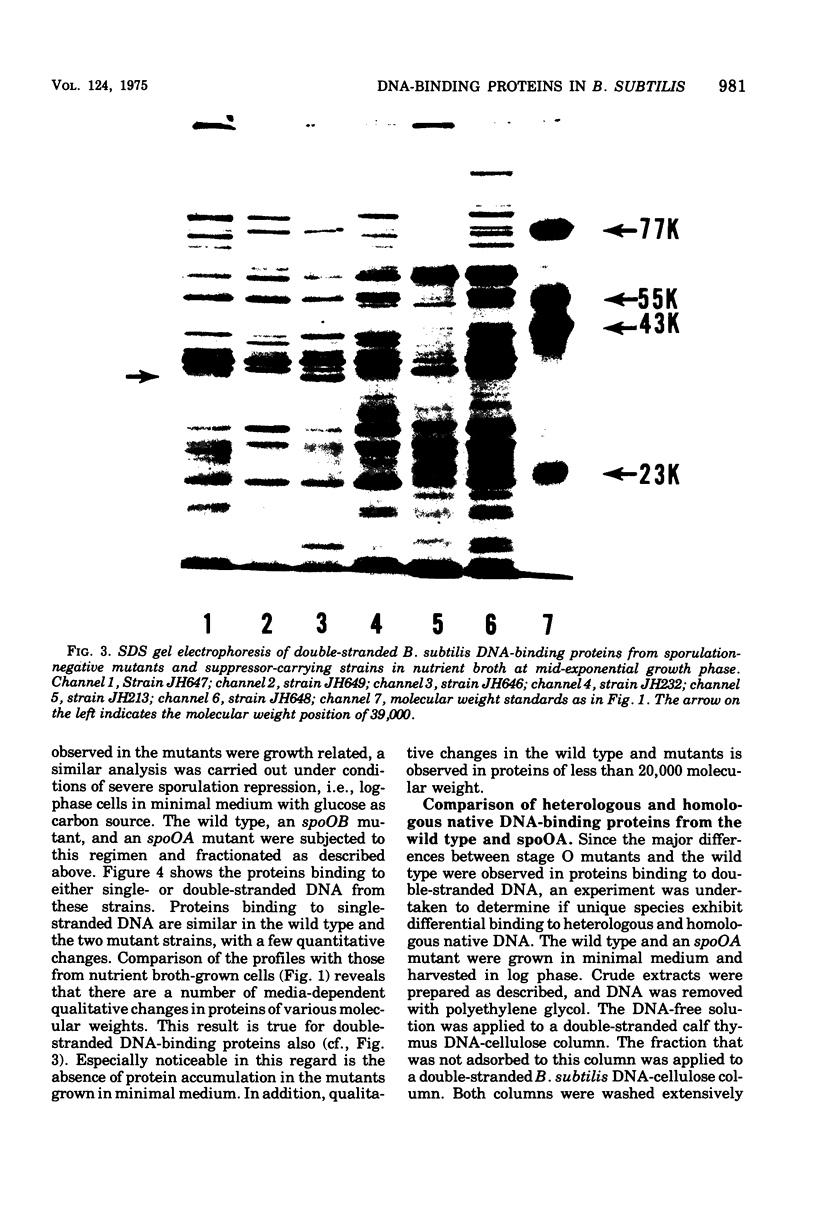
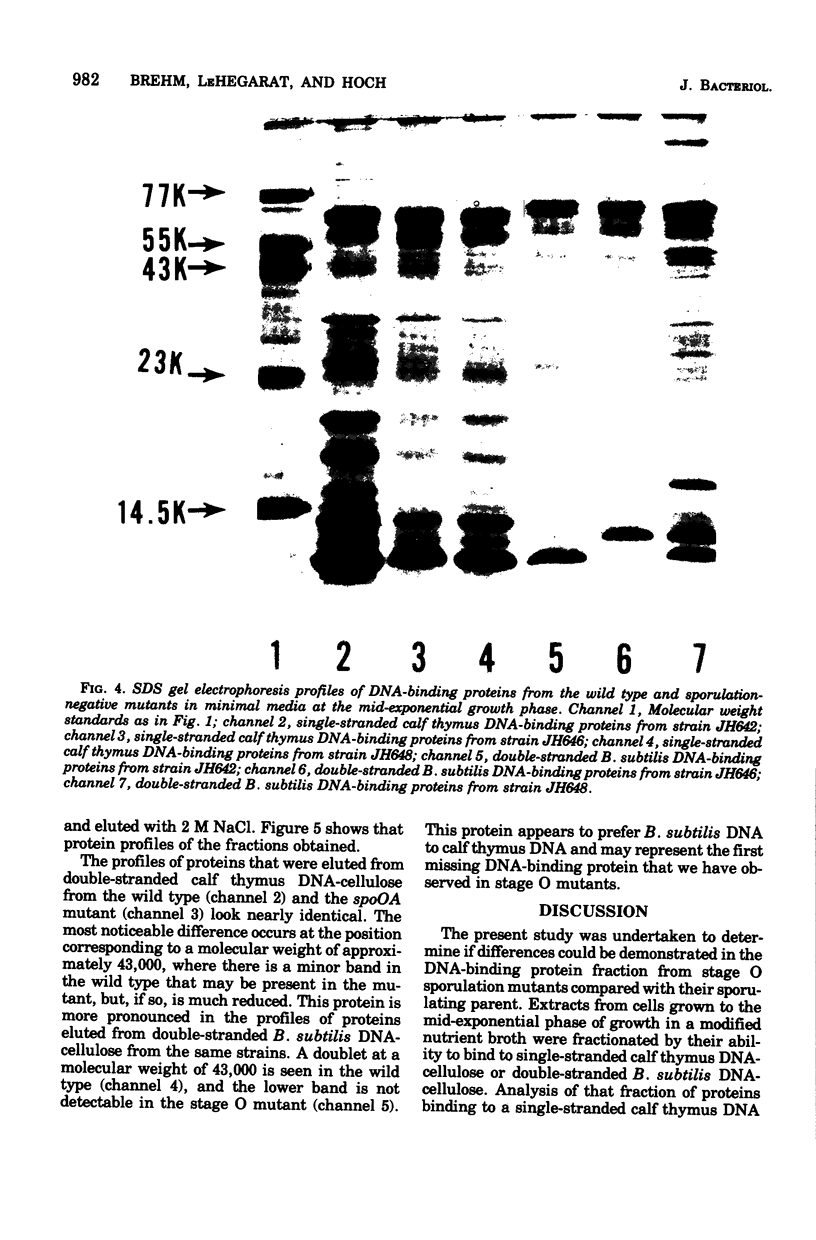
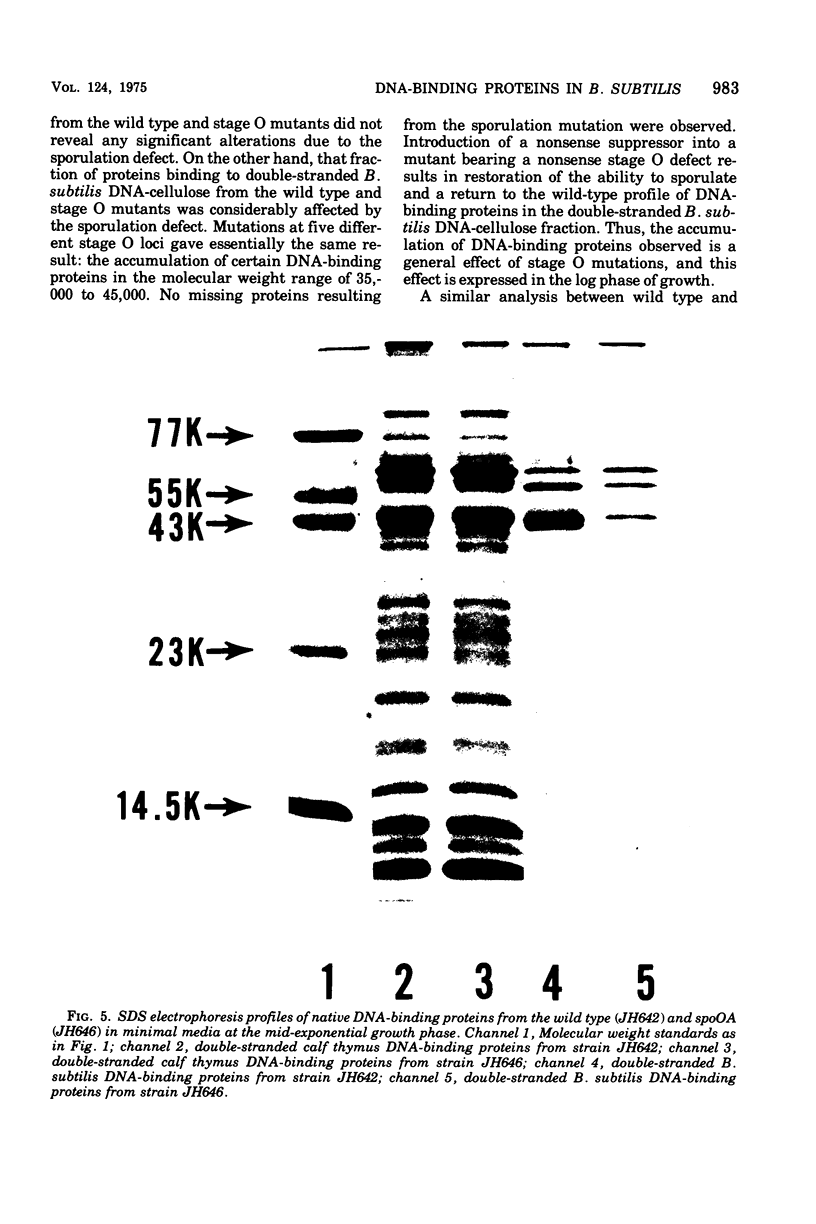
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)-binding proteins have been compared between wild-type Bacillus subtilis and five sporulation mutants blocked at different stage O loci. Extracts from exponentially growing cells have been fractionated for proteins binding to single-stranded calf thymus DNA-cellulose and double-stranded B. subtilis DNA-cellulose. In nutrient broth, stage O mutations cause an accumulation of proteins with affinity for double-stranded DNA. Suppression of the mutation with extragenic suppressors relieves the accumulation. In minimal glucose medium, the stage O mutations also cause accumulation of proteins with affinity for double-stranded DNA, but the species accumulated are different from those of nutrient broth-grown cells. In neither case did stage O mutations affect proteins with affinity for single-stranded DNA. The results suggest that the products of stage O loci are functional and operative during vegetative growth.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brehm S. P., Le Hegarat F., Hoch J. A. Developmental modulation of deoxyribonucleic acid-binding proteins of Bacillus subtilis during sporulation stages. J Bacteriol. 1974 Dec;120(3):1443–1450. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.3.1443-1450.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brehm S. P., Staal S. P., Hoch J. A. Phenotypes of pleiotropic-negative sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):1063–1070. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.1063-1070.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C. P. Suppressor system in Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1397–1402. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1397-1402.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross-Bellard M., Oudet P., Chambon P. Isolation of high-molecular-weight DNA from mammalian cells. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 2;36(1):32–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02881.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J. A., Mathews J. L. Chromosomal location of pleiotropic negative sporulation mutations in Bacillus subtilis. Genetics. 1973 Feb;73(2):215–228. doi: 10.1093/genetics/73.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litman R. M. A deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase from Micrococcus luteus (Micrococcus lysodeikticus) isolated on deoxyribonucleic acid-cellulose. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6222–6233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piggot P. J. Mapping of asporogenous mutations of Bacillus subtilis: a minimum estimate of the number of sporeulation operons. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1241–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1241-1253.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]