Abstract
A method is presented whereby cells of Mycoplasma hominis can be prepared with minimal distortion for electron microscopy. After the addition of glutaraldehyde to broth cultures, incubation is continued for 1 h. The cells are then collected by centrifugation, washed in distilled water, and used for negative-contrast preparations.
Full text
PDF
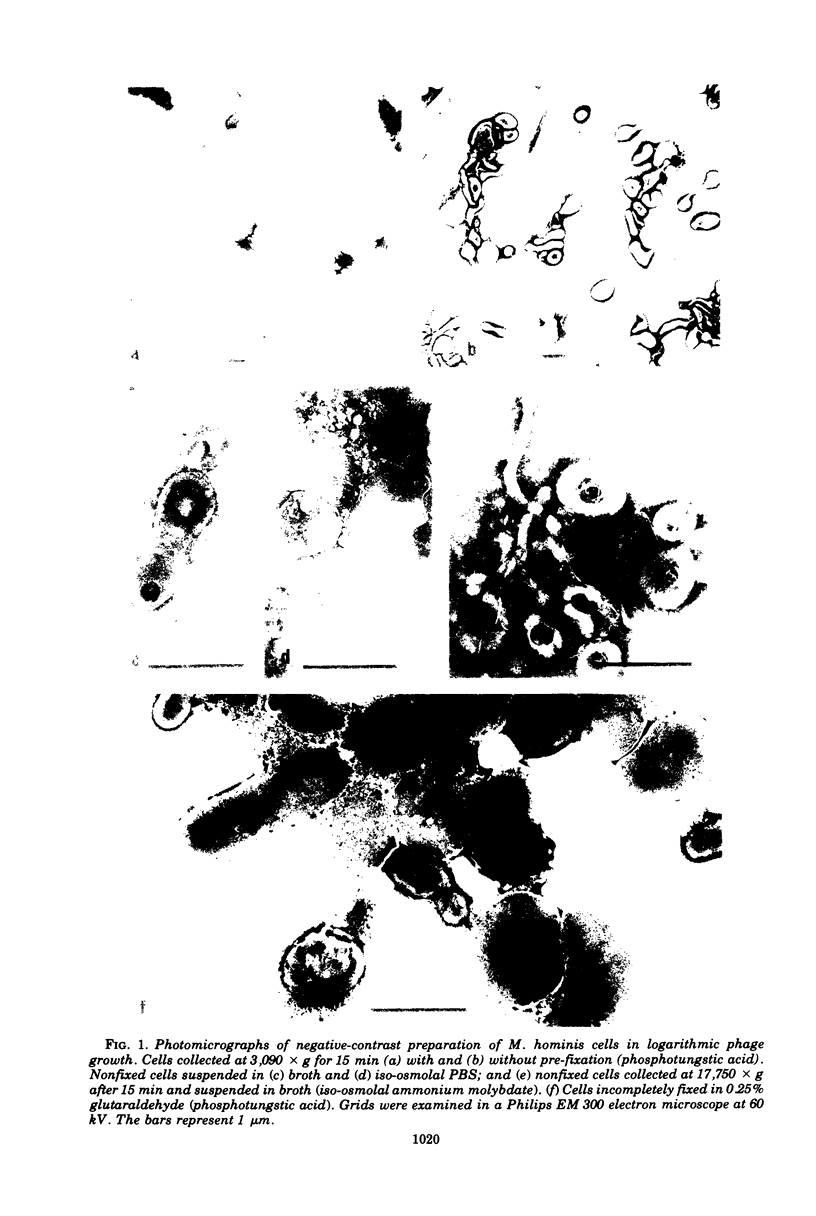


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein-Ziv R. The effect of hypotonic solutions on the morphology of cells of Mycoplasma gallisepticum. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Sep;17(9):1203–1205. doi: 10.1139/m71-192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark H. W. Sedimentation counting and morphology of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1373–1386. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1373-1386.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole R. M., Tully J. G., Popkin T. J., Bové J. M. Morphology, ultrastructure, and bacteriophage infection of the helical mycoplasma-like organism (Spiroplasma citri gen. nov., sp. nov.) cultured from "stubborn" disease of citrus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jul;115(1):367–384. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.1.367-386.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemcke R. M. Osmolar concentration and fixation of mycoplasmas. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1154–1162. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1154-1162.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morowitz H. J., Maniloff J. Analysis of the life cycle of Mycoplasma gallisepticum. J Bacteriol. 1966 Apr;91(4):1638–1644. doi: 10.1128/jb.91.4.1638-1644.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAZIN S., ARGAMAN M. Lysis of Mycoplasma, bacterial protoplasts, spheroplasts and L-forms by various agents. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Jan;30:155–172. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-1-155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuss K. Influence of fixation on gross morphology of Mycoplasma. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):490–492. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.490-492.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J., Gomersall M., Gill P. Mycoplasma hominis: growth, reproduction, and isolation of small viable cells. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):1007–1018. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.1007-1018.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J., Gomersall M., Gill P. Virus-like particles in Mycoplasma hominis. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Dec;18(12):1971–1972. doi: 10.1139/m72-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spears D. M., Provost P. J. A comparison of the osmotic and passive permeability properties of Mycoplasma laidlawii and Mycoplasma hominis. Can J Microbiol. 1967 Feb;13(2):213–225. doi: 10.1139/m67-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolanski B., Maramorosch K. Negatively stained mycoplasmas: fact or artifact? Virology. 1970 Oct;42(2):319–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



