Abstract
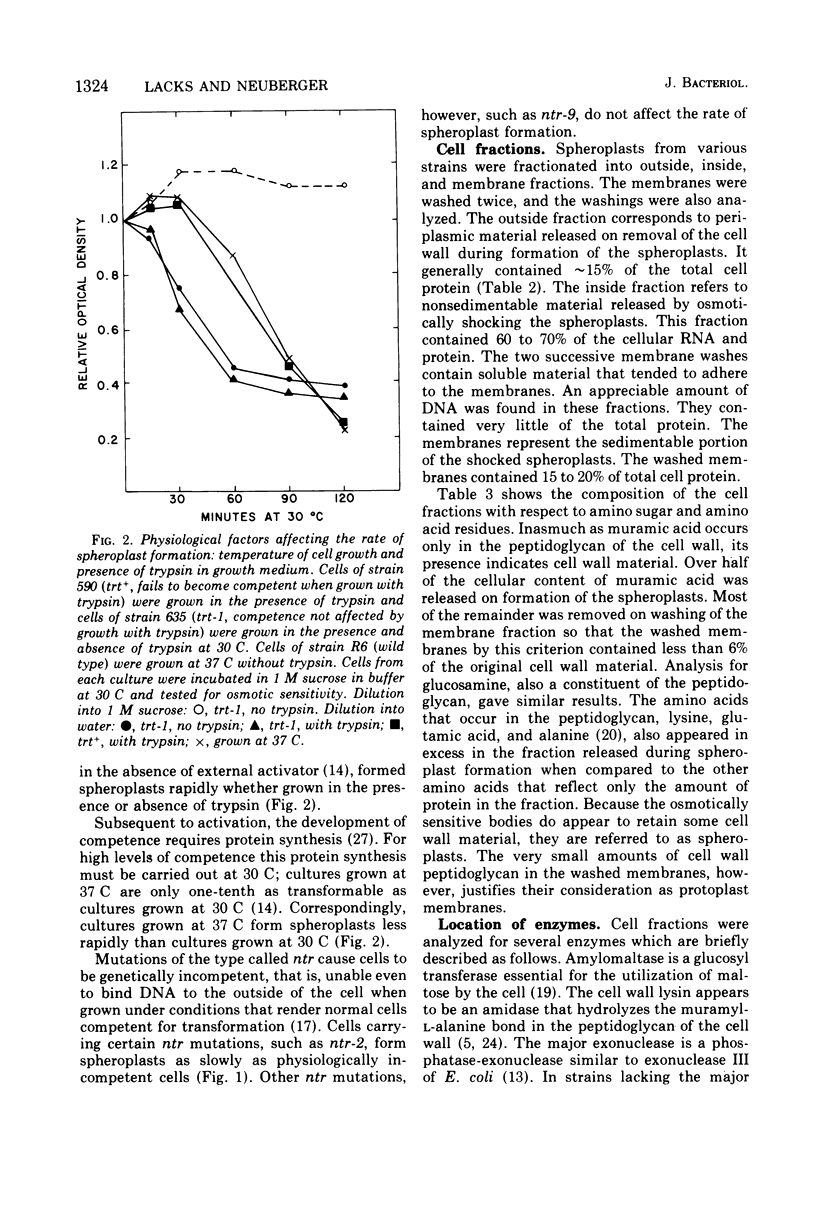
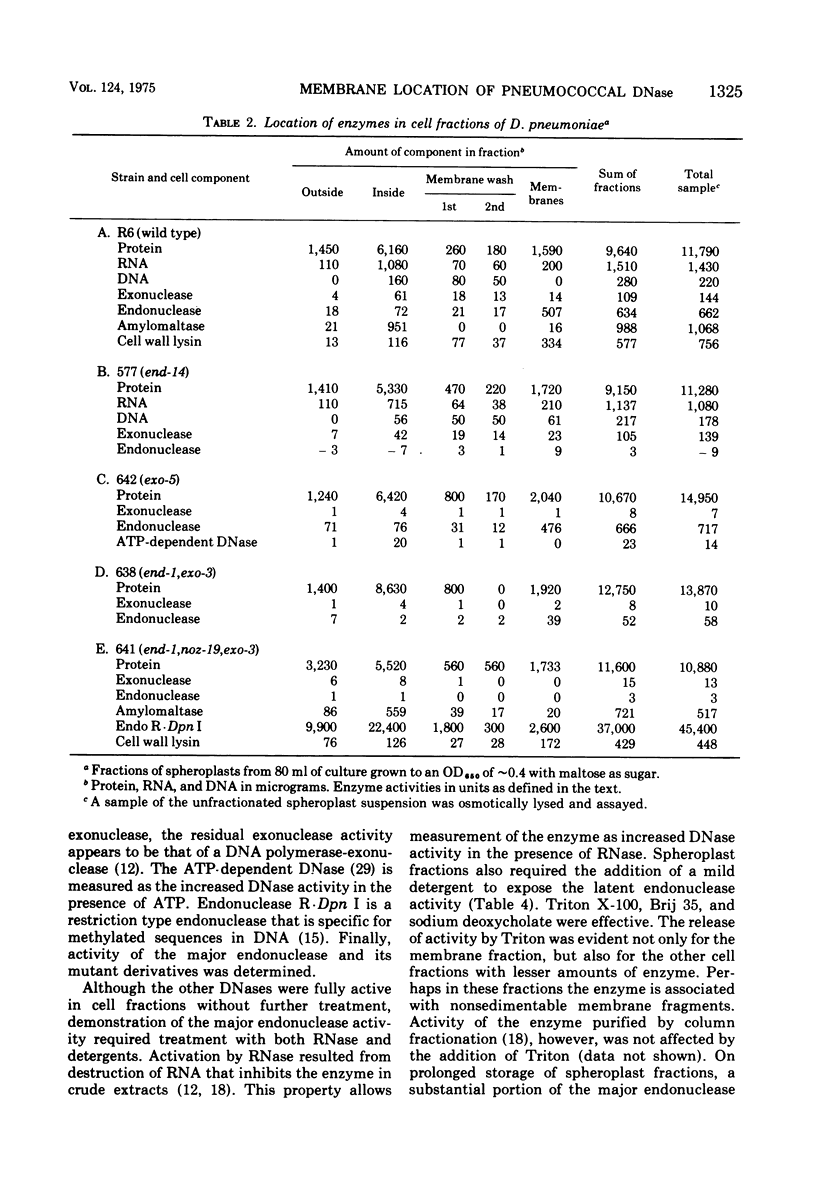
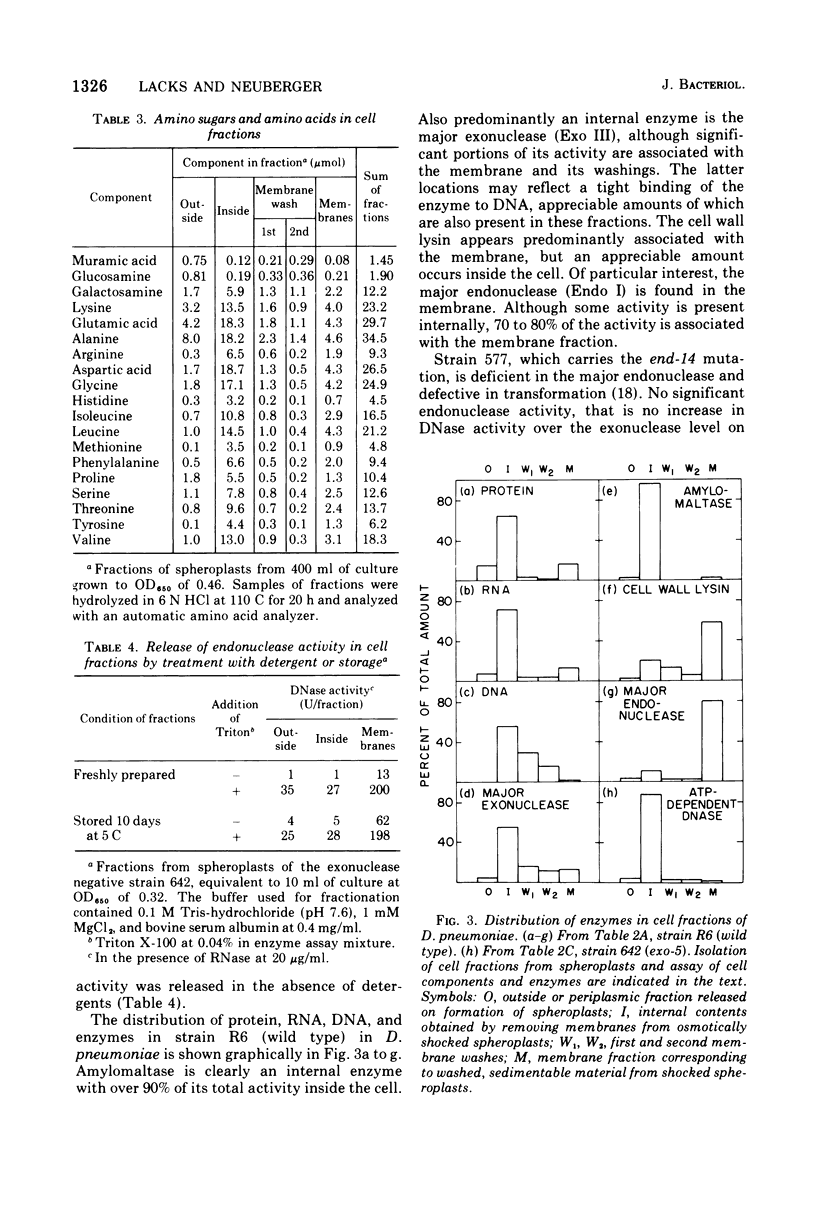
The cellular localization of enzymes in Diplococcus pneumoniae was examined by fractionation of spheroplasts. A deoxyribonuclease implicated in the entry of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) into the cell during genetic transformation was located in the cell membrane. This enzyme, the major endonuclease of the cell (endonuclease I), which is necessary for the conversion of donor DNA to single strands inside the cell and oligonucleotides outside, thus could act at the cell surface. Another enzyme, the cell wall lysin (autolysin), was also found in the membrane fraction. Other enzymes, including amylomaltase, two exonucleases, and adenosine triphosphate-dependent deoxyribonuclease, and a restriction type endonuclease, were located in the cytosol within the cell. None of the enzymes examined were predominantly periplasmic in location. Spheroplasts were obtained spontaneously on incubation of pneumococcal cells in concentrated sugar solutions. The autolytic enzyme appears to be involved in this process. Cells that were physiologically competent to take up DNA formed osmotically sensitive spheroplasts two to three times faster than cells that were not in the competent state. Although some genetically incompetent mutants also formed spheroplasts more slowly, other such mutants formed them at the faster rate.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cordonnier C., Bernardi G. Localization of E. coli endonuclease I. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Sep 8;20(5):555–559. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90434-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidoff-Abelson R., Dubnau D. Kinetic analysis of the products of donor deoxyribonucleate in transformed cells of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):154–162. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.154-162.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard L. V., Gooder H. Specificity of the autolysin of Streptococcus (Diplococcus) pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):796–804. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.796-804.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joenje H., Konings W. N., Venema G. Interactions between exogenous deoxyribonucleic acid and membrane vesicles isolated from Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):784–794. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.784-794.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joenje H., Venema G. Different nuclease activities in competent and noncompetent Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Apr;122(1):25–33. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.1.25-33.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Shockman G. D. Autolytic formation of protoplasts (autoplasts) of Streptococcus faecalis 9790: release of cell wall, autolysin, and formation of stable autoplasts. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):735–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.735-746.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACKS S., HOTCHKISS R. D. Formation of amylomaltase after genetic transformation of pneumococcus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 4;45:155–163. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACKS S. Molecular fate of DNA in genetic transformation of Pneumococcus. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jul;5:119–131. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIU T. Y., GOTSCHLICH E. C. The chemical composition of pneumococcal C-polysaccharide. J Biol Chem. 1963 Jun;238:1928–1934. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Genetic regulation of maltosaccharide utilization in Pneumococcus. Genetics. 1968 Dec;60(4):685–706. doi: 10.1093/genetics/60.4.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B. A deoxyribonuclease of Diplococcus pneumoniae specific for methylated DNA. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4060–4066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B. Competence for deoxyribonucleic acid uptake and deoxyribonuclease action external to cells in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Apr;114(1):152–163. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.1.152-163.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B. Deoxyribonucleases of Pneumococcus. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jul 10;242(13):3108–3120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B., Neuberger M. Identification of a deoxyribonuclease implicated in genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):222–232. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.222-232.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S., Greenberg B., Neuberger M. Role of a deoxyribonuclease in the genetic transformation of Diplococcus pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2305–2309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Integration efficiency and genetic recombination in pneumococcal transformation. Genetics. 1966 Jan;53(1):207–235. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. Mutants of Diplococcus pneumoniae that lack deoxyribonucleases and other activities possibly pertinent to genetic transformation. J Bacteriol. 1970 Feb;101(2):373–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.2.373-383.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan R. R., Kronish D. P., Pianotti R. S., Epstein R. L., Schwartz B. S. Autolytic mechanism for spheroplast formation in Bacillus cereus and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1355–1364. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1355-1364.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A., Guild W. R. Breakage prior to entry of donor DNA in Pneumococcus transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):545–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90226-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosser J. L., Tomasz A. Choline-containing teichoic acid as a structural component of pneumococcal cell wall and its role in sensitivity to lysis by an autolytic enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jan 25;245(2):287–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. E., Bernlohr R. W. Determinaion of muraic acid, ornithine, and diaminopimelic acid during automatic amino aci analysis. Anal Biochem. 1970 Feb;33(2):238–243. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90292-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto H., Tomasz A. Protoplast formation and leakage of intramembrane cell components: induction by the competence activator substance of pneumococci. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):344–353. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.344-353.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. Cellular metabolism in genetic transformation of pneumococci: requirement for protein synthesis during induction of competence. J Bacteriol. 1970 Mar;101(3):860–871. doi: 10.1128/jb.101.3.860-871.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Mosser J. L. On the nature of the pneumococcal activator substance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):58–66. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vovis G. F., Buttin G. An ATP-dependent deoxyribonuclease from diplococcus pneumoniae. I. Partial purification and some biochemical properties. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 12;224(1):29–41. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90617-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


