Abstract
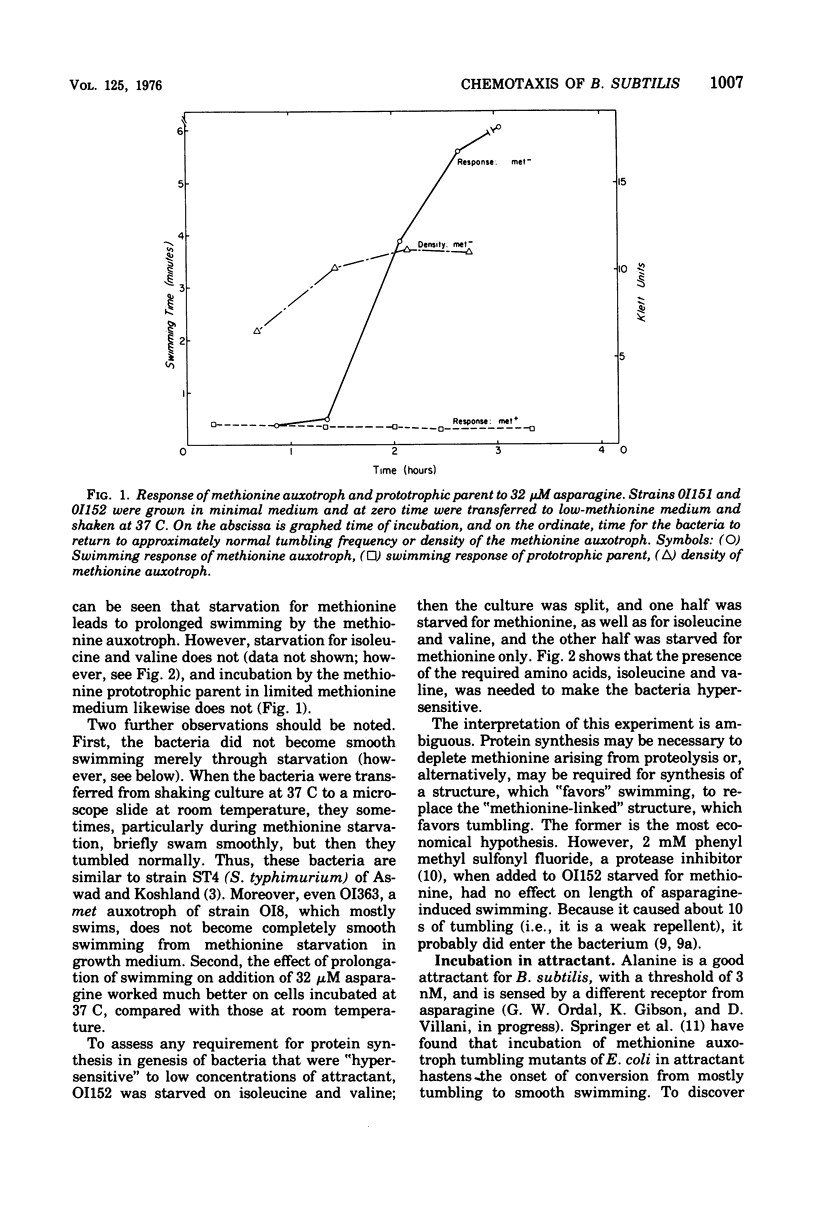
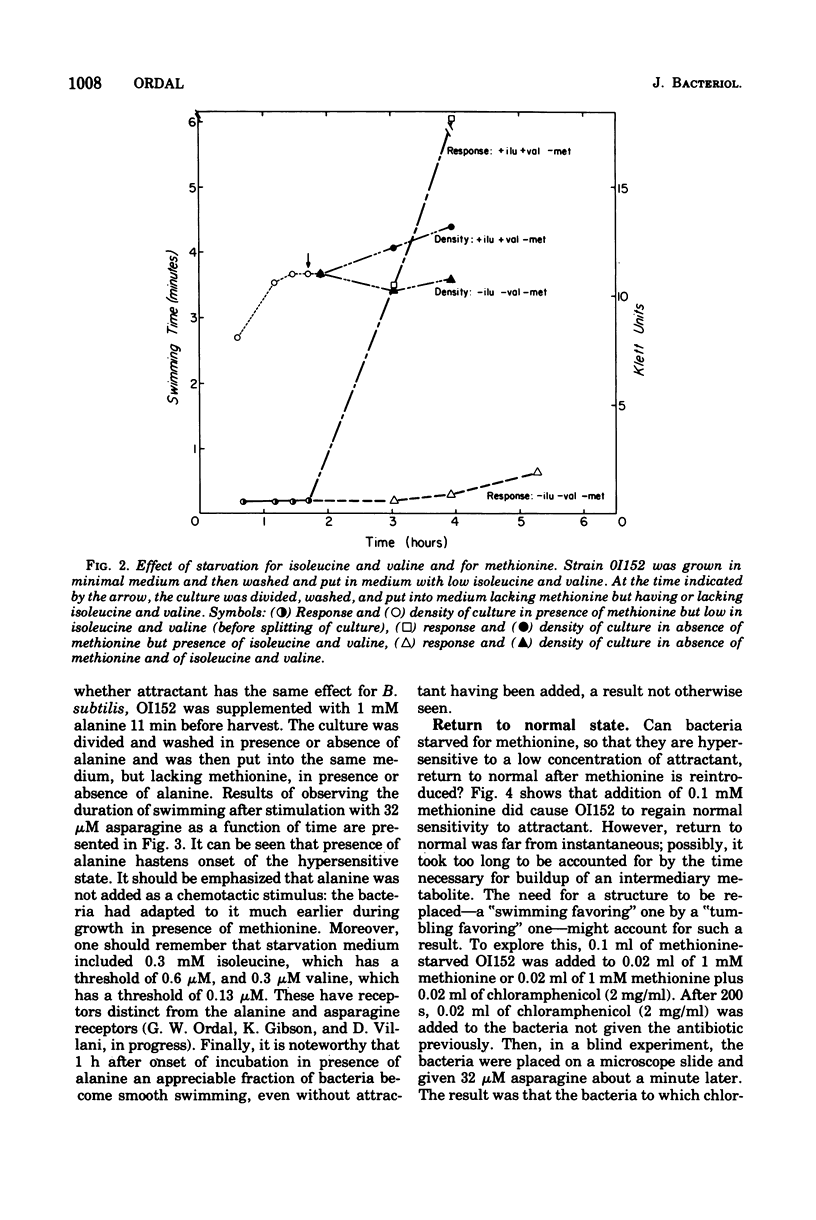
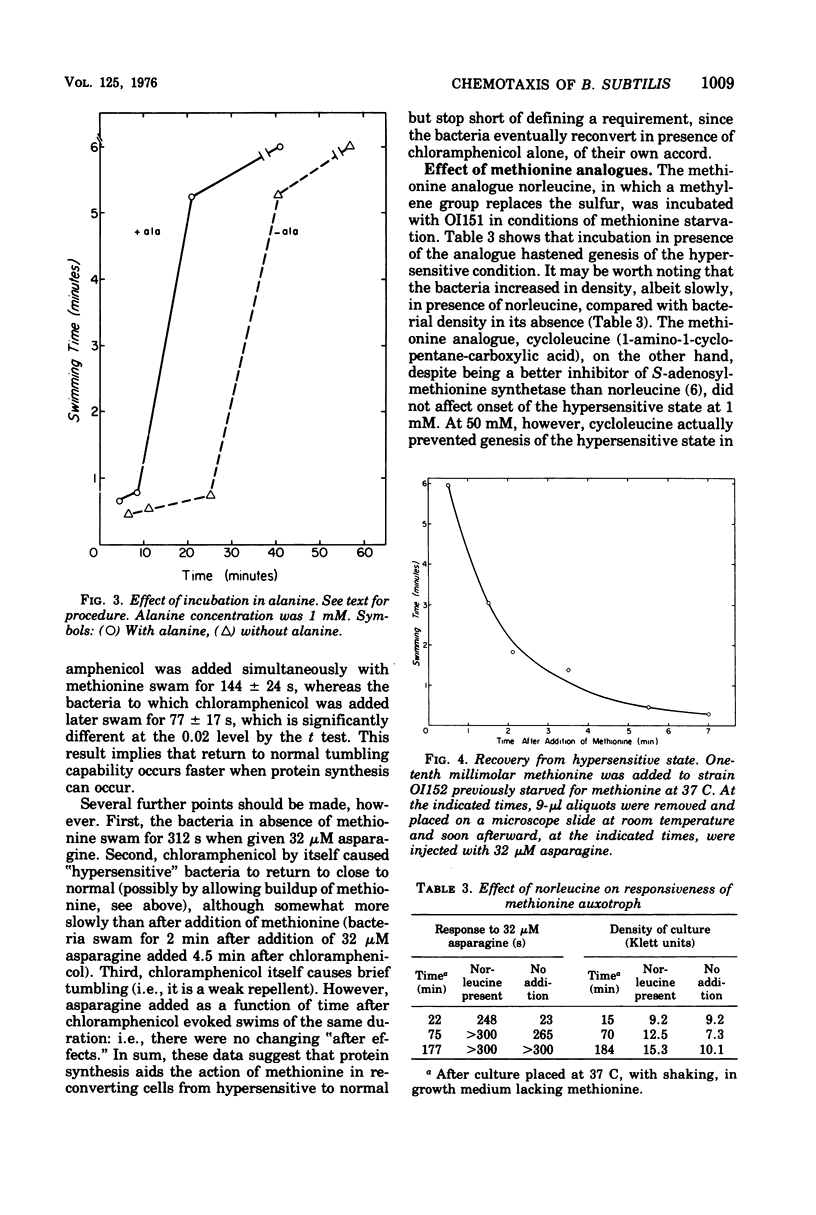
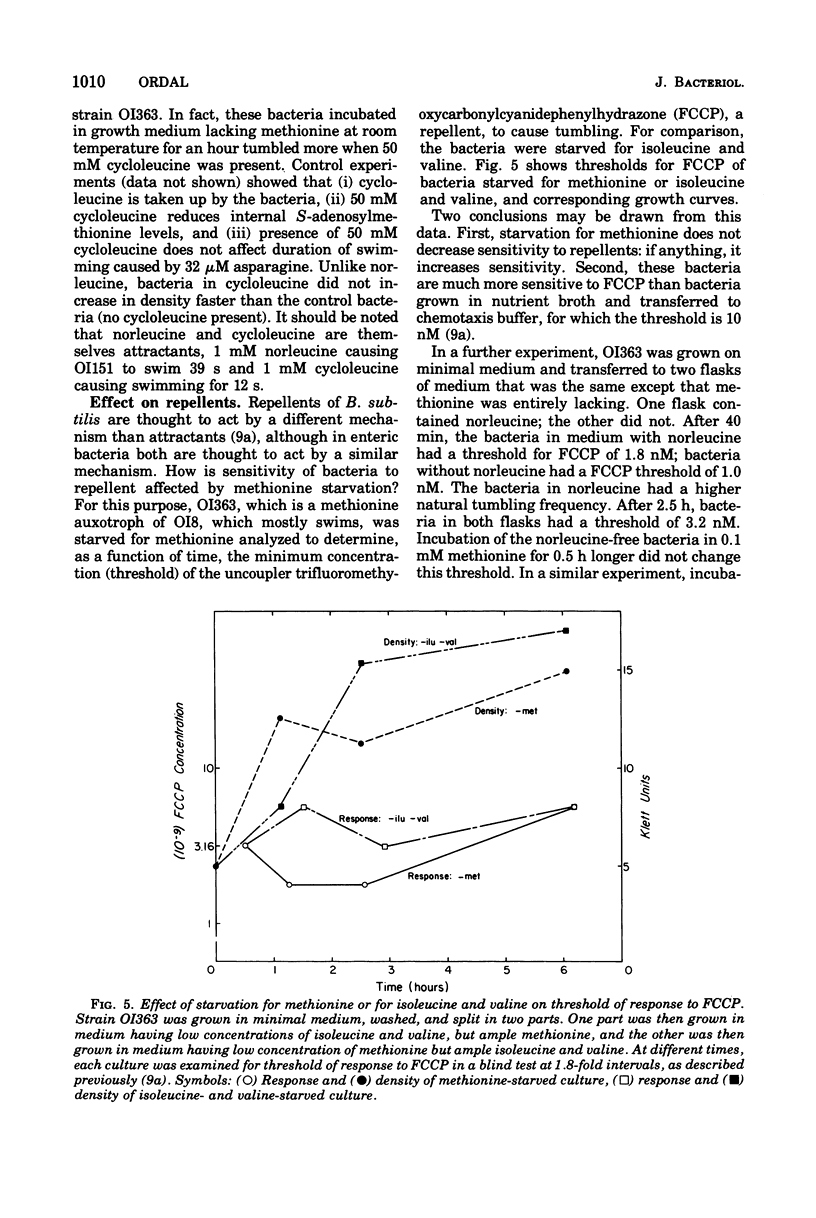
Bacillus subtilis, like Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium, carries out chemotaxis by modulating the relative frequency of smooth swimming and tumbling. Like these enteric bacteria, methionine auxotrophs starved for methionine show an abnormally long-period of smooth swimming after addition of attractant. This "hypersensitive" state requires an hour of starvation for its genesis, which can be hastened by including alanine, a strong attractant, in starvation medium. Susceptibility to repellent, which causes transient tumbling when added, if anything, increases slightly by starvation for methionine. The results are interpreted by postulating the existence of a methionine-derived structure that hastens recovery of attractant-stimulated bacteria back to normal.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler J., Dahl M. M. A method for measuring the motility of bacteria and for comparing random and non-random motility. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Feb;46(2):161–173. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-2-161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. B. An S-adenosylmethionine requirement for chemotaxis in Escherichia coli. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Nov;18(11):1695–1701. doi: 10.1139/m72-263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswad D. W., Koshland D. E., Jr Evidence for an S-adenosylmethionine requirement in the chemotactic behavior of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 15;97(2):207–223. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80035-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aswad D., Koshland D. E., Jr Role of methionine in bacterial chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):640–645. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.640-645.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg H. C., Brown D. A. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli analysed by three-dimensional tracking. Nature. 1972 Oct 27;239(5374):500–504. doi: 10.1038/239500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lombardini J. B., Coulter A. W., Talalay P. Analogues of methionine as substrates and inhibitors of the methionine adenosyltransferase reaction. Deductions concerning the conformation of methionine. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Sep;6(5):481–499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab R. M., Koshland D. E., Jr The gradient-sensing mechanism in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2509–2512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordal G. W., Adler J. Isolation and complementation of mutants in galactose taxis and transport. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):509–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.509-516.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordal G. W., Goldman D. J. Chemotactic repellents of Bacillus subtilis. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jan 5;100(1):103–108. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordal G. W., Goldman D. J. Chemotaxis away from uncouplers of oxidative phosphorylation in Bacillus subtilis. Science. 1975 Sep 5;189(4205):802–805. doi: 10.1126/science.808854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orrego C., Kerjan P., Manca de Nadra M. C., Szulmajster J. Ribonucleic acid polymerase in a thermosensitive sporulation mutant (ts-4) of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):636–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.636-647.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Kort E. N., Larsen S. H., Ordal G. W., Reader R. W., Adler J. Role of methionine in bacterial chemotaxis: requirement for tumbling and involvement in information processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4640–4644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


