Abstract
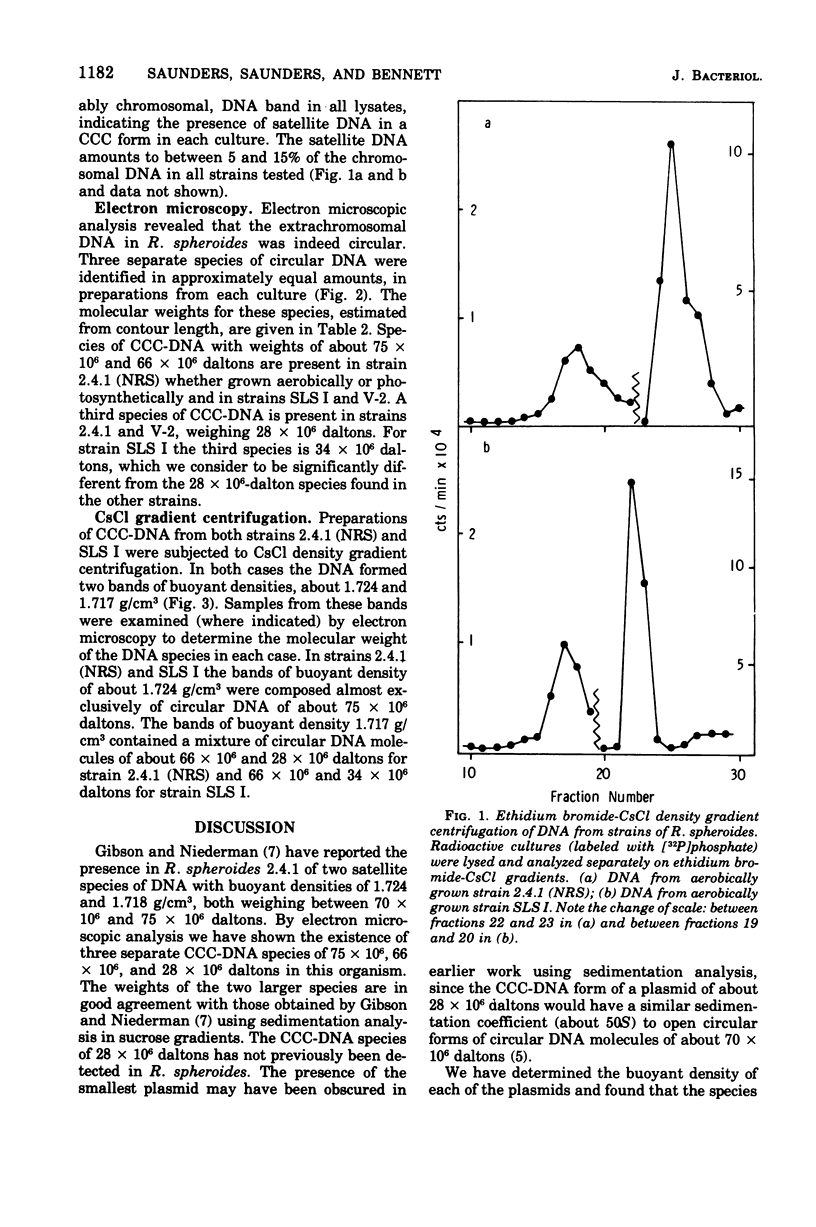
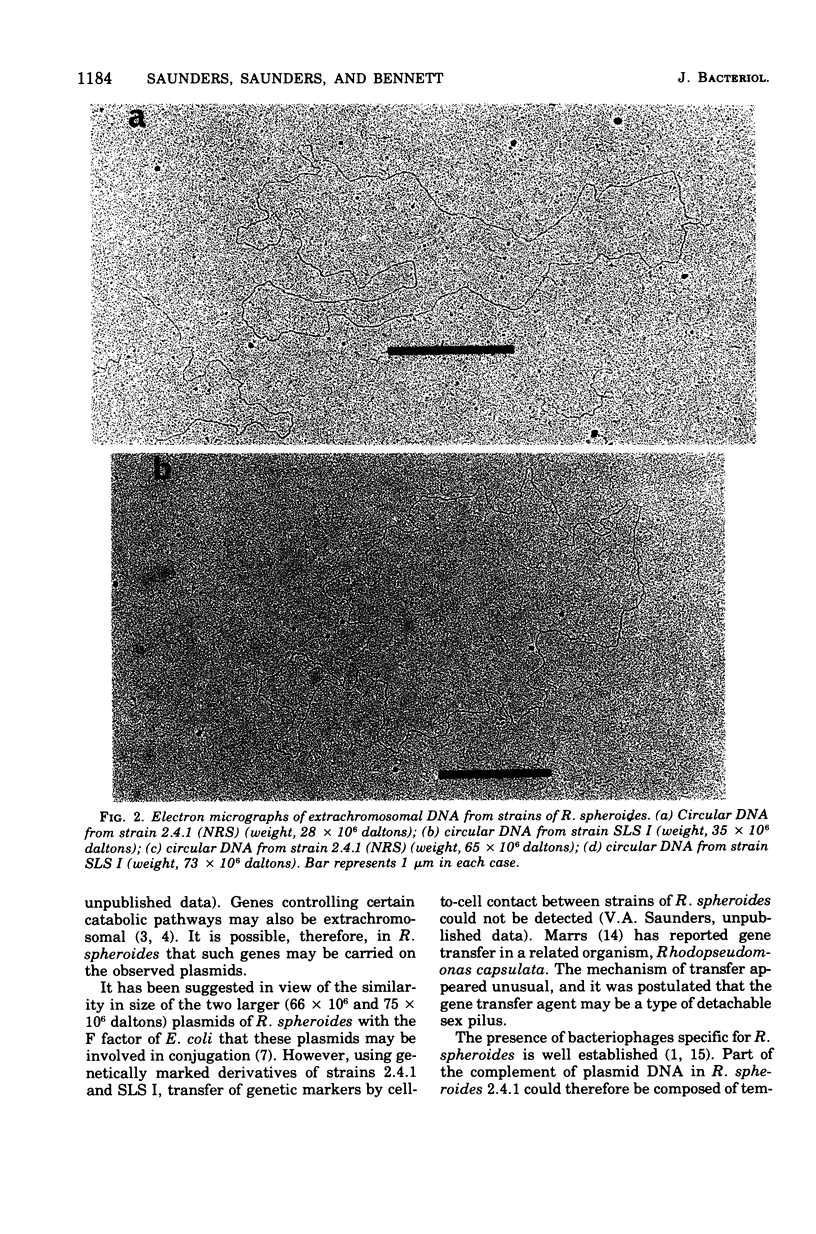
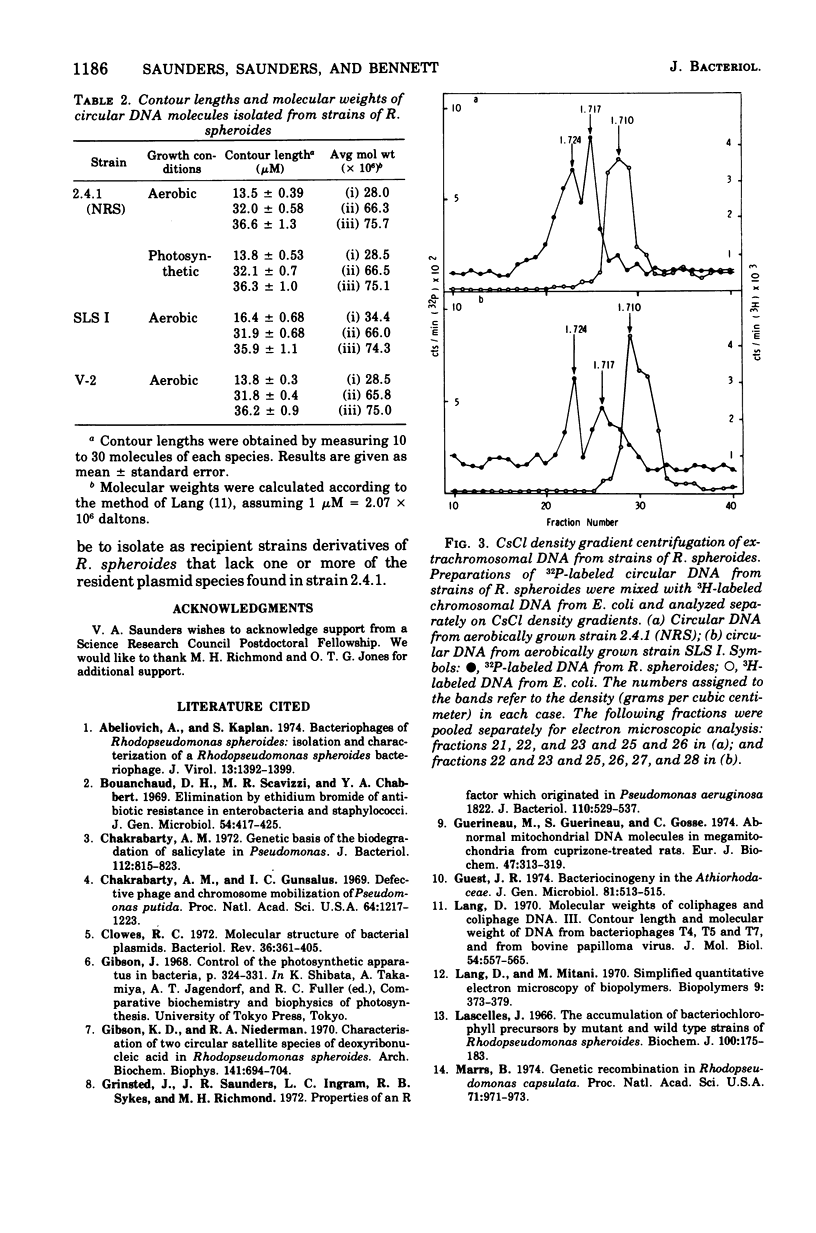
Three covalently closed circular species of extrachromosomal deoxyribonucleic acid have been identified by electron microscopic analysis in strains of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. The weights of these plasmids, as determined from contour length, are about 75 X 10(6), 66 X 10(6), and 28 X 10(6) daltons for both aerobically grown and photosynthetically grown R. spheroides strain 2.4.1 (NRS) and for the photosynthetically incompetent strain V-2 (obtained by N-methyl-N-nitro-N'nitrosoguanidine mutagenesis) and 74 X 10(6), 66 X 10(6) and 34 X 10(6) daltons for a second photosynthetically incompetent strain, SLS I (obtained by incubating strain 2.4.1 [NRS] in medium containing sodium lauryl sulfate). Buoyant densities uere found to be 1.717 g/cm3 (58% guanine plus cytosine) for the plasmids of 66 X 10(6), 28 X 10(6), and 34 X 10(6) daltons in weight and 1.724 g/cm3 (65% guanine plus cytosine) for those weighing about 75 X 10(6) daltons. Possible functions of these plasmids are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeliovich A., Kaplan S. Bacteriophages of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides: isolation and characterization of a Rhodopseudomonas spheroides bacteriophage. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1392–1399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1392-1399.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouanchaud D. H., Scavizzi M. R., Chabbert Y. A. Elimination by ethidium bromide of antibiotic resistance in enterobacteria and staphylococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1968 Dec;54(3):417–425. doi: 10.1099/00221287-54-3-417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M. Genetic basis of the biodegradation of salicylate in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):815–823. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.815-823.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarty A. M., Gunsalus I. C. Defective phage and chromosome mobilization in Pseudomonas putida. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Dec;64(4):1217–1223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.4.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes R. C. Molecular structure of bacterial plasmids. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Sep;36(3):361–405. doi: 10.1128/br.36.3.361-405.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson K. D., Niederman R. A. Characterization of two circular satellite species of deoxyribonucleic acid in Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Dec;141(2):694–704. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90190-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerineau M., Guerineau S., Gosse C. Abnormal mitochondrial DNA molecules in megamitochondria from cuprizone-treated rats. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Sep 1;47(2):313–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guest J. R. Bacteriocinogeny in the Athiorhodaceae. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Apr;81(2):513–515. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-2-513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D., Mitani M. Simplified quantitative electron microscopy of biopolymers. Biopolymers. 1970;9(3):373–379. doi: 10.1002/bip.1970.360090310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang D. Molecular weights of coliphages and coliphage DNA. 3. Contour length and molecular weight of DNA from bacteriophages T4, T5 and T7, and from bovine papilloma virus. J Mol Biol. 1970 Dec 28;54(3):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles J. The accumulation of bacteriochlorophyll precursors by mutant and wild-type strains of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochem J. 1966 Jul;100(1):175–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1000175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs B. Genetic recombination in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):971–973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mural R. J., Friedman D. I. Isolation and characterization of a temperate bacteriophage specific for Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1288–1292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1288-1292.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick R. P. Extrachromosomal inheritance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Jun;33(2):210–263. doi: 10.1128/br.33.2.210-263.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHILDKRAUT C. L., MARMUR J., DOTY P. Determination of the base composition of deoxyribonucleic acid from its buoyant density in CsCl. J Mol Biol. 1962 Jun;4:430–443. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80100-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R. A requirement for sodium in the growth of Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. J Gen Microbiol. 1960 Jun;22:778–785. doi: 10.1099/00221287-22-3-778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SISTROM W. R., CLAYTON R. K. STUDIES ON A MUTANT OF RHODOPSEUDOMONAS SPHEROIDES UNABLE TO GROW PHOTOSYNTHETICALLY. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Jul 29;88:61–73. doi: 10.1016/0926-6577(64)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders J. R., Grinsted J. Properties of RP4, an R factor which originated in Pseudomonas aeruginosa S8. J Bacteriol. 1972 Nov;112(2):690–696. doi: 10.1128/jb.112.2.690-696.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders V. A., Jones O. T. Oxidative phosphorylation and effects of aerobic conditions on Rhodopseudomonas viridis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 28;305(3):581–589. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(73)90077-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders V. A., Jones O. T. Properties of the cytochrome a-like material developed in the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas spheroides when grown aerobically. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Mar 26;333(3):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(74)90128-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonstein S. A., Baldwin J. N. Nature of the elimination of the penicillinase plasmid from Staphylococcus aureus by surface-active agents. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jul;111(1):152–155. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.1.152-155.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starlinger P., Saedler H. Insertion mutations in microorganisms. Biochimie. 1972;54(2):177–185. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(72)80102-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suyama Y., Gibson J. Satellite DNA in photosynthetic bacteria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Aug 23;24(4):549–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomoeda M., Inuzuka M., Kubo N., Nakamura S. Effective elimination of drug resistance and sex factors in Escherichia coli by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):1078–1089. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.1078-1089.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinograd J., Lebowitz J., Radloff R., Watson R., Laipis P. The twisted circular form of polyoma viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 May;53(5):1104–1111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.5.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T., FUKASAWA T. Episome-mediated transfer of drug resistance in Enterobacteriaceae. II. Elimination of resistance factors with acridine dyes. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81:679–683. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.679-683.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whale F. R., Jones O. T. The cytochrome system of heterotrophically-grown Rhodopseudomonas spheroides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 3;223(1):146–157. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willetts N. The genetics of transmissible plasmids. Annu Rev Genet. 1972;6:257–268. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.06.120172.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]