Abstract
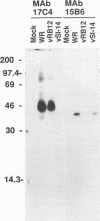
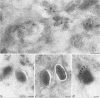
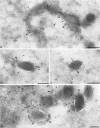
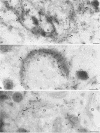
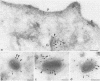
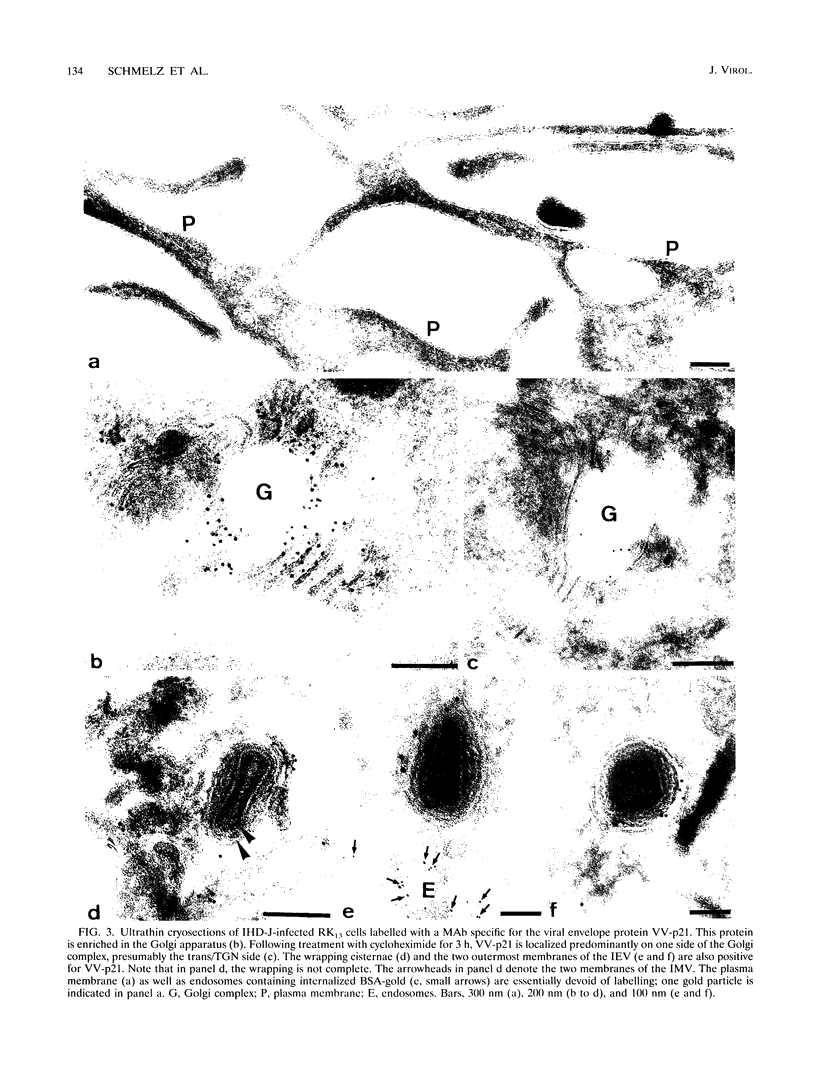
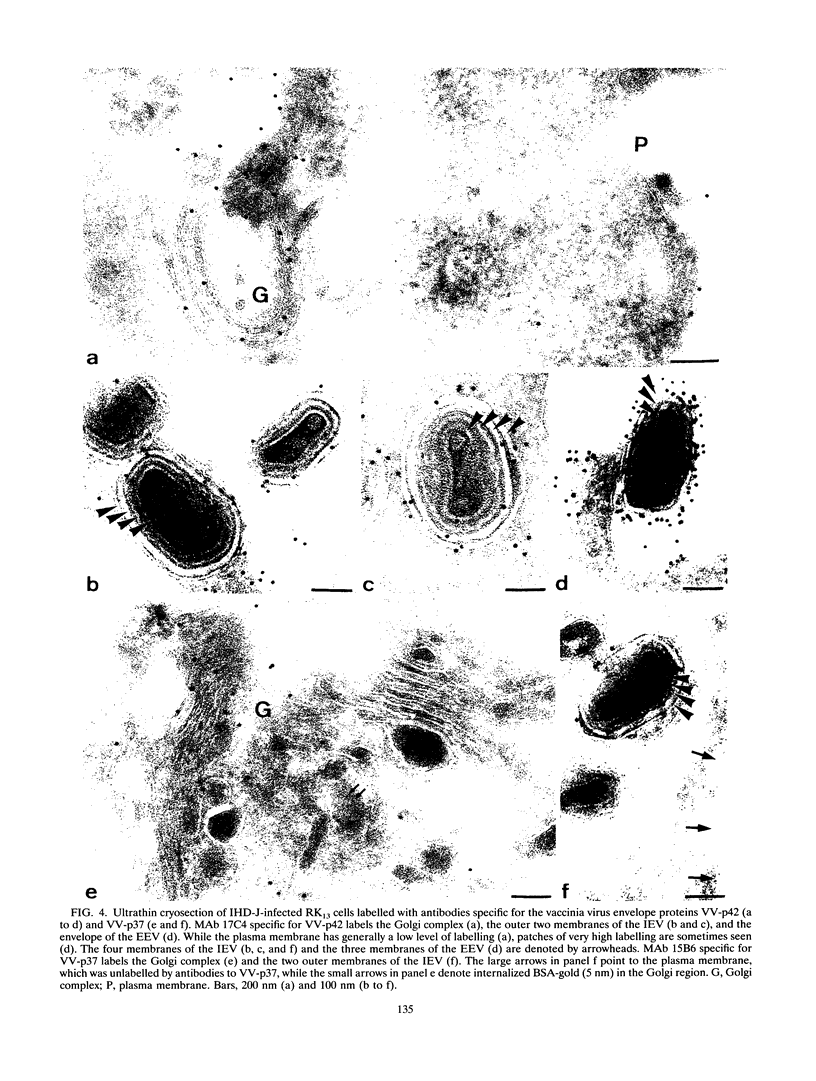
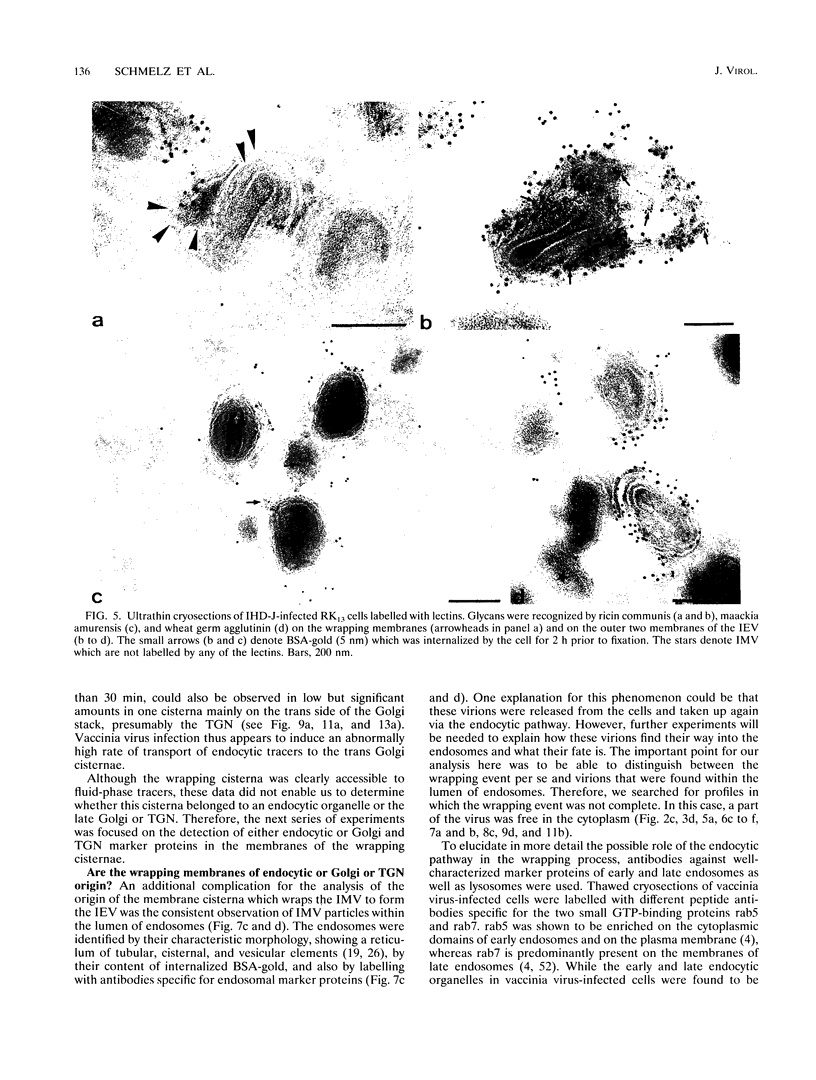
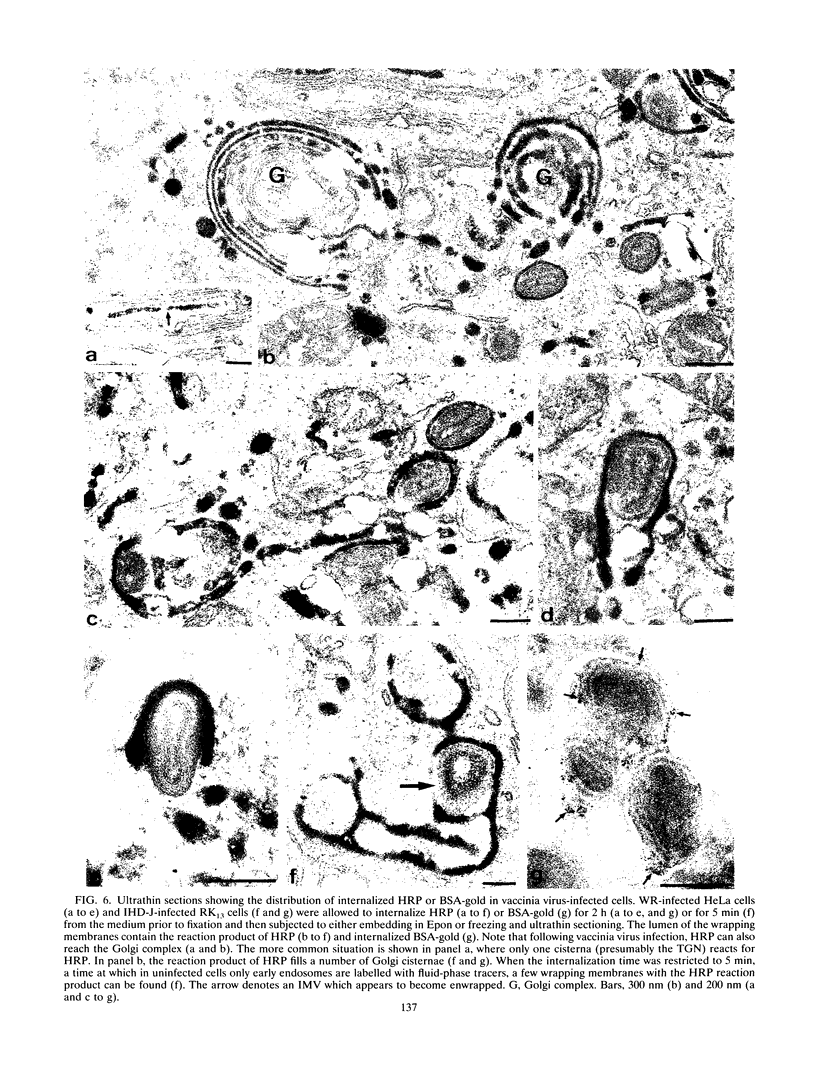
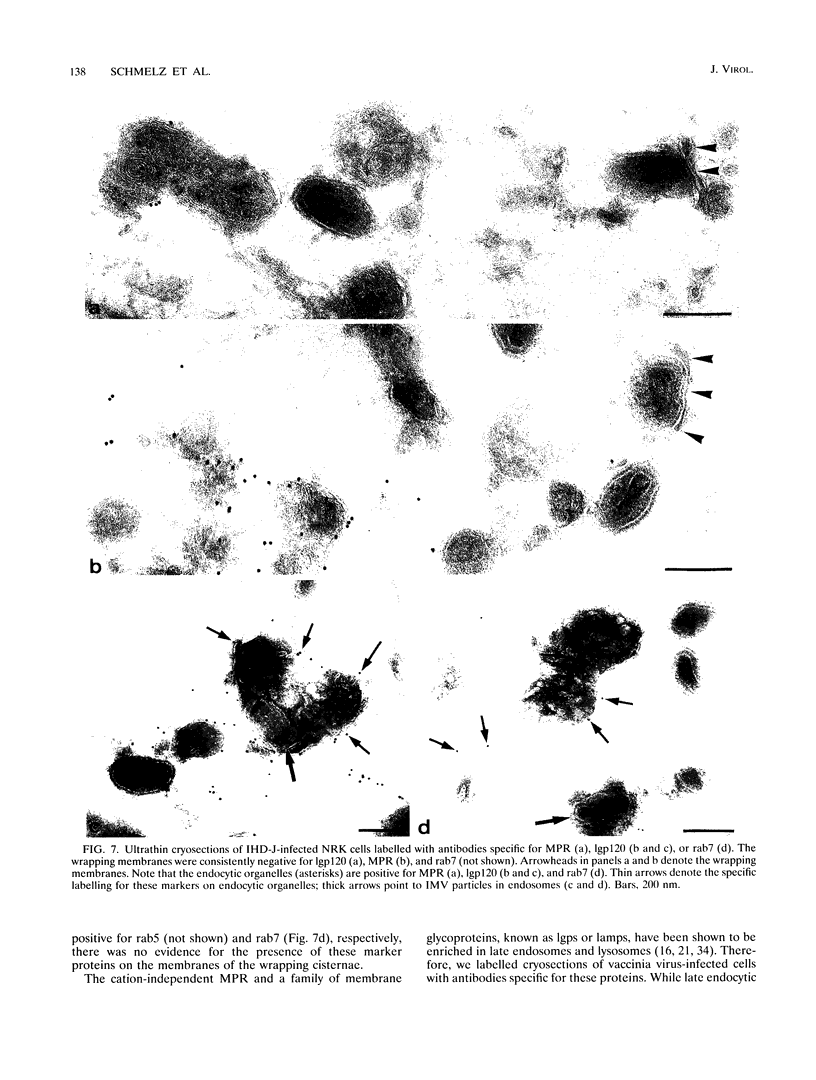
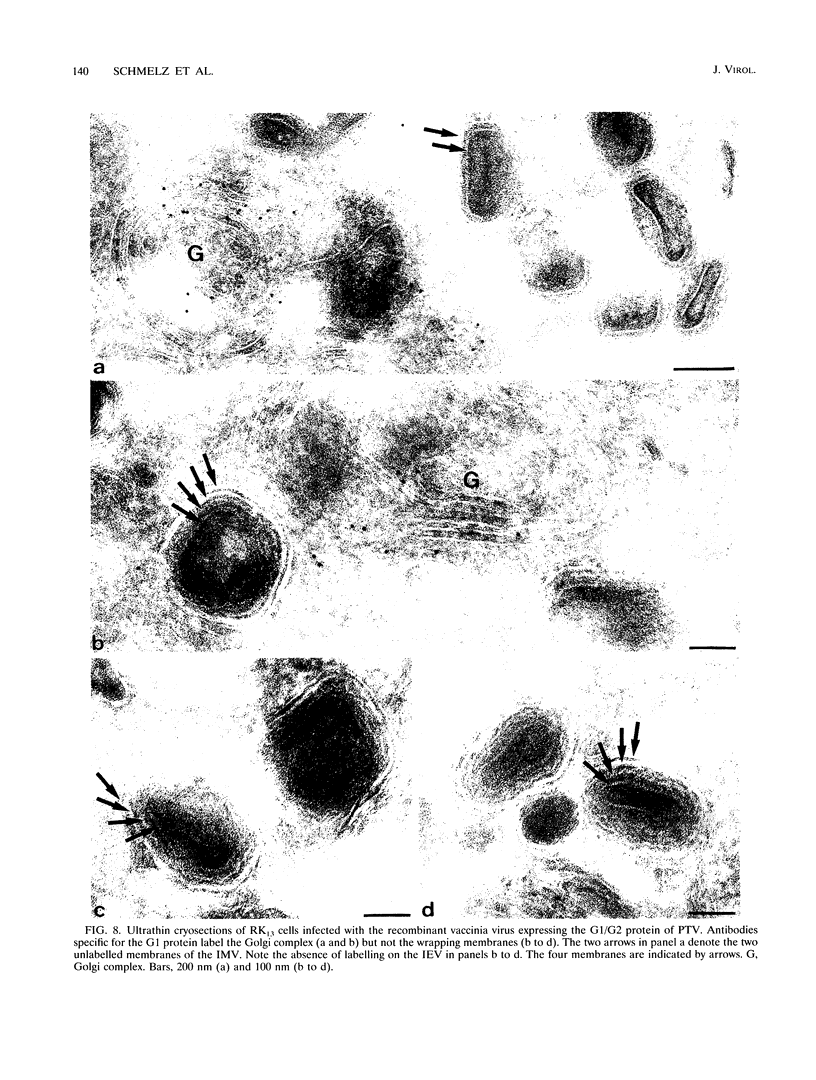
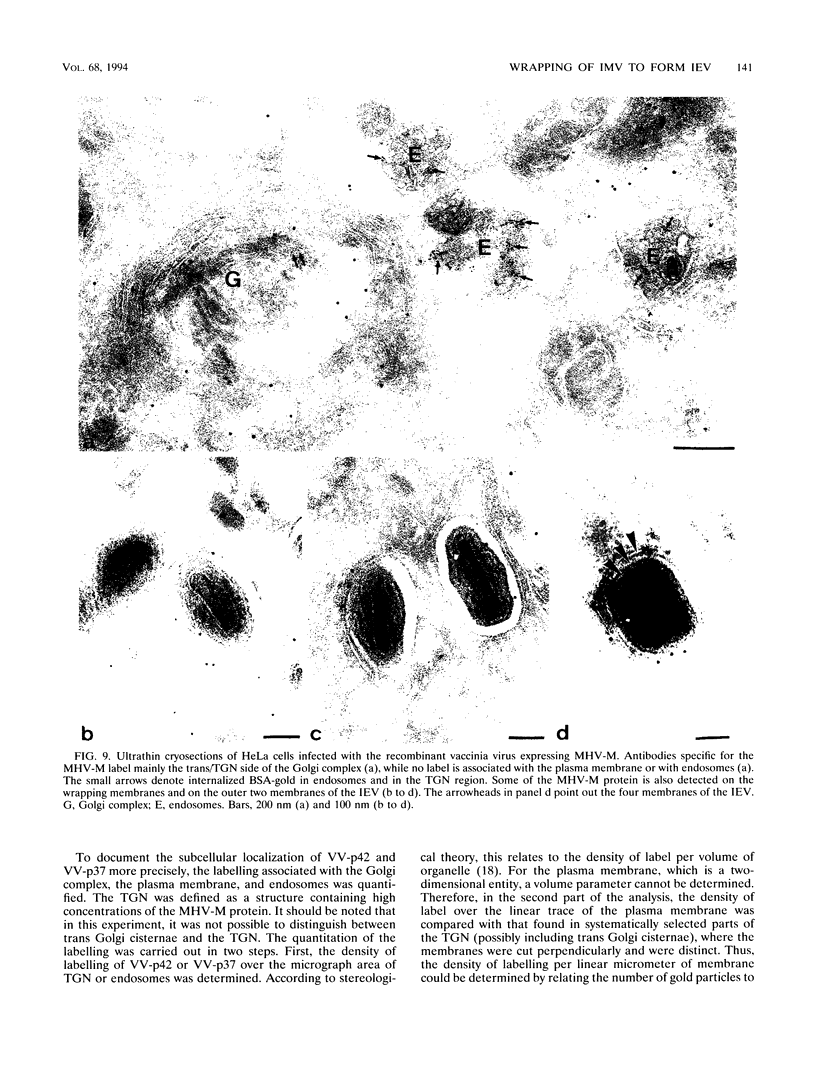
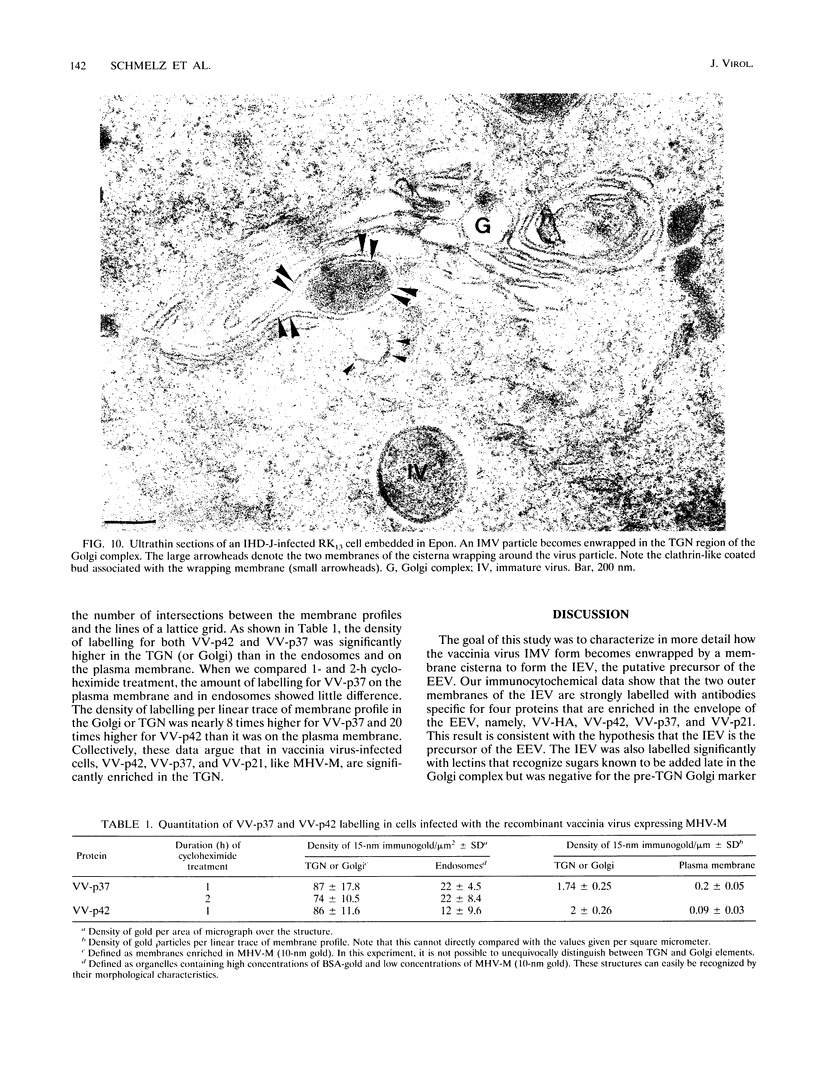
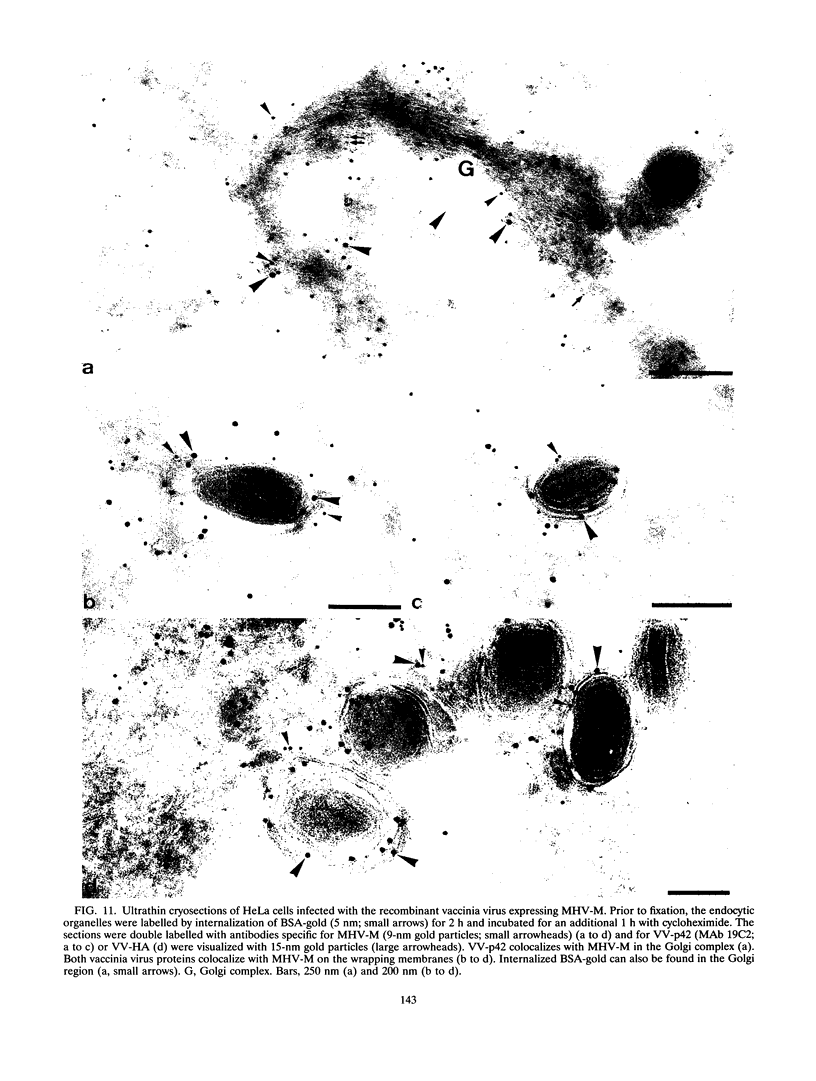
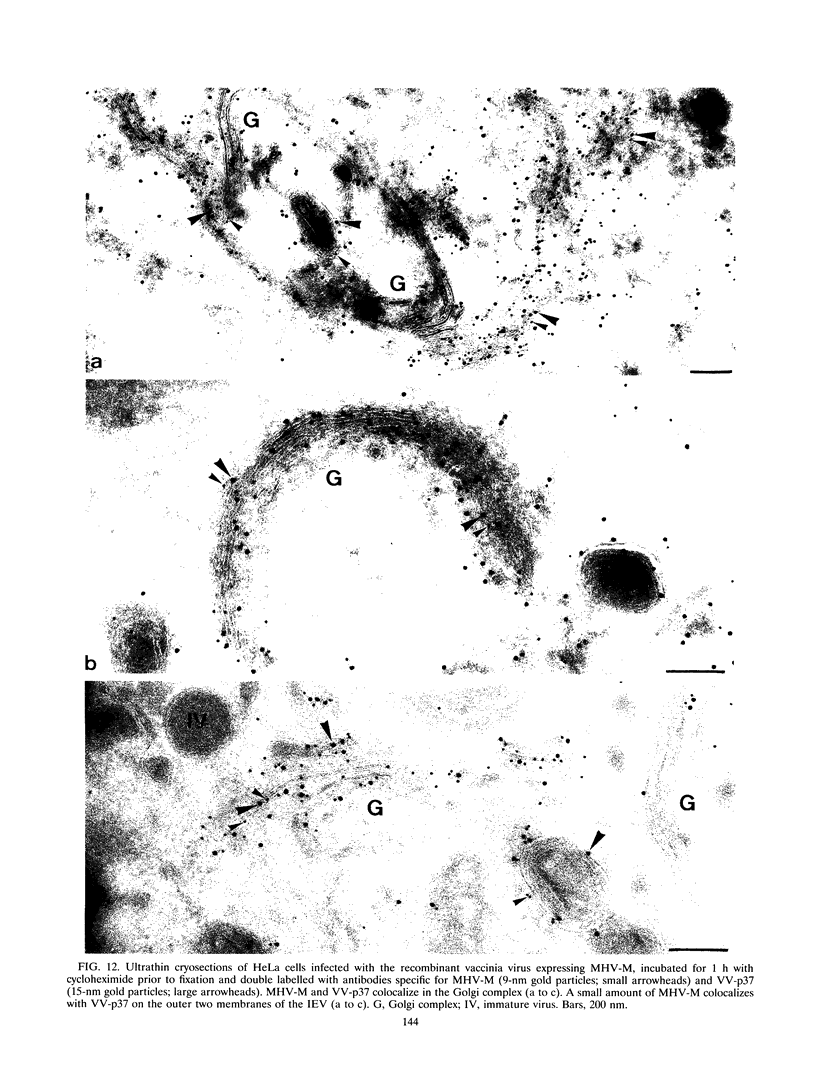
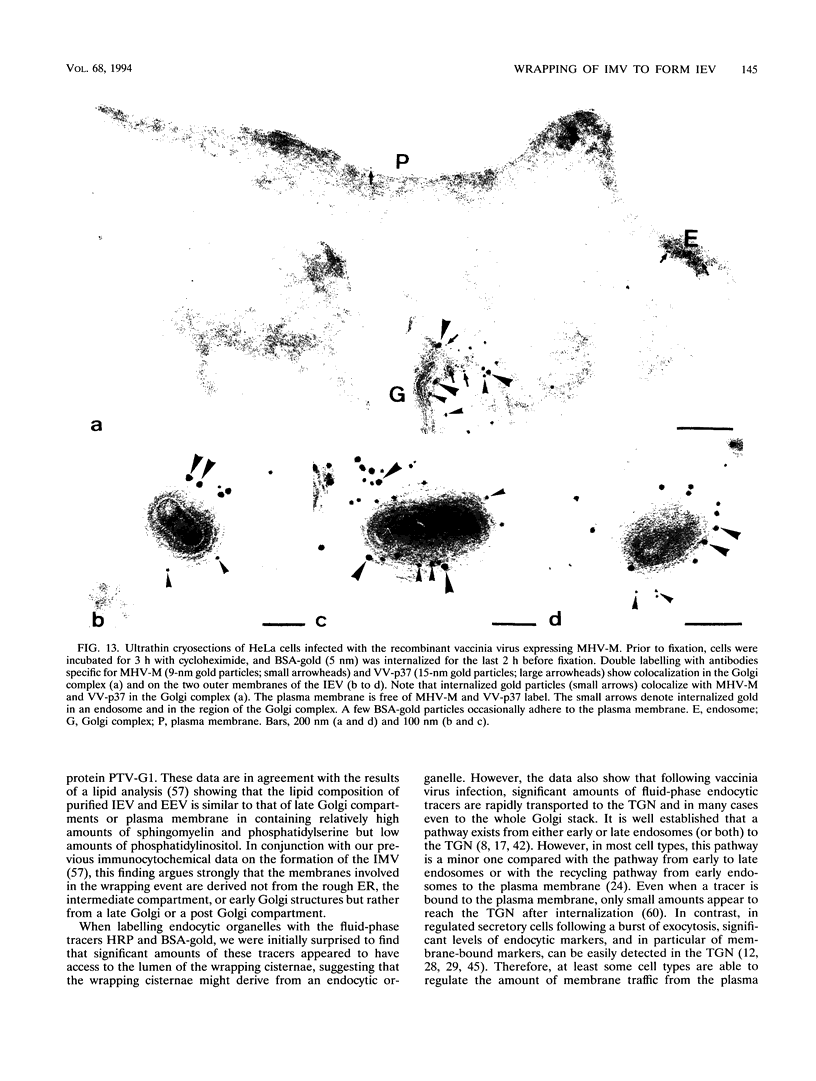
During the assembly of vaccinia virus, the intracellular mature virus becomes enwrapped by a cellular cisterna to form the intracellular enveloped virus (IEV), the precursor of the extracellular enveloped virus (EEV). In this study, we have characterized the origin of this wrapping cisterna by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry using lectins, antibodies against endocytic organelles, and recombinant vaccinia viruses expressing proteins which behave as Golgi resident proteins. No labelling for endocytic marker proteins could be detected on the wrapping membrane. However, the wrapping membrane labelled significantly for a trans Golgi network (TGN) marker protein. The recycling pathway from endosomes to the TGN appears to be greatly increased following vaccinia virus infection, since significant amounts of endocytic fluid-phase tracers were found in the lumen of the TGN, Golgi complex, and the wrapping cisternae. Using immunoelectron microscopy, we localized the vaccinia virus membrane proteins VV-p37, VV-p42, VV-p21, and VV-hemagglutinin (VV-HA) in large amounts in the wrapping cisternae, in the outer membranes of the IEV, and in the outermost membrane of the EEV. The bulk of the cellular VV-p37, VV-p21, and VV-p42 were in the TGN, whereas VV-HA was also found in large amounts on the plasma membrane and in endosomes. Collectively, these data argue that the TGN becomes enriched in vaccinia virus membrane proteins that facilitate the wrapping event responsible for the formation of the IEV.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. G., Pathak R. K. Vesicles and cisternae in the trans Golgi apparatus of human fibroblasts are acidic compartments. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasco R., Moss B. Extracellular vaccinia virus formation and cell-to-cell virus transmission are prevented by deletion of the gene encoding the 37,000-Dalton outer envelope protein. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5910–5920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5910-5920.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucci C., Parton R. G., Mather I. H., Stunnenberg H., Simons K., Hoflack B., Zerial M. The small GTPase rab5 functions as a regulatory factor in the early endocytic pathway. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):715–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90306-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Parton R. G., Hauri H. P., Simons K., Zerial M. Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and endocytic compartments. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90369-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. Y., Matsuoka Y., Compans R. W. Assembly and polarized release of Punta Toro virus and effects of brefeldin A. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1427–1439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1427-1439.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S. Y., Matsuoka Y., Compans R. W. Golgi complex localization of the Punta Toro virus G2 protein requires its association with the G1 protein. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):351–365. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90148-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan J. R., Kornfeld S. Intracellular movement of two mannose 6-phosphate receptors: return to the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):617–628. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan S. A., Smith G. L. Identification and characterization of an extracellular envelope glycoprotein affecting vaccinia virus egress. J Virol. 1992 Mar;66(3):1610–1621. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.3.1610-1621.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelstad M., Howard S. T., Smith G. L. A constitutively expressed vaccinia gene encodes a 42-kDa glycoprotein related to complement control factors that forms part of the extracellular virus envelope. Virology. 1992 Jun;188(2):801–810. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90535-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G. Multiple pathways of exocytosis, endocytosis, and membrane recycling: validation of a Golgi route. Fed Proc. 1983 May 15;42(8):2407–2413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Shubin R. A., Sussman M. A., Casteel N., Stohlman S. A. Monoclonal antibodies to the matrix (E1) glycoprotein of mouse hepatitis virus protect mice from encephalitis. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):162–167. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90415-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Fernandez M. P., Moss B. Transfer of the inducible lac repressor/operator system from Escherichia coli to a vaccinia virus expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2549–2553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galfrè G., Milstein C. Preparation of monoclonal antibodies: strategies and procedures. Methods Enzymol. 1981;73(Pt B):3–46. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(81)73054-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geuze H. J., Stoorvogel W., Strous G. J., Slot J. W., Bleekemolen J. E., Mellman I. Sorting of mannose 6-phosphate receptors and lysosomal membrane proteins in endocytic vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2491–2501. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goda Y., Pfeffer S. R. Selective recycling of the mannose 6-phosphate/IGF-II receptor to the trans Golgi network in vitro. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):309–320. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Back R., Marsh M. A quantitative analysis of the endocytic pathway in baby hamster kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2703–2720. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Gruenberg J. The arguments for pre-existing early and late endosomes. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;1(1):5–9. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90047-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Hoflack B., Simons K., Mellman I., Kornfeld S. The mannose 6-phosphate receptor and the biogenesis of lysosomes. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):329–341. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Pfeiffer S., Simons K., Matlin K. Exit of newly synthesized membrane proteins from the trans cisterna of the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):949–964. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Rottier P. Cell biology of viruses that assemble along the biosynthetic pathway. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;3(5):367–381. doi: 10.1016/1043-4682(92)90022-N. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Warren G., Stuhlfauth I., Jockusch B. M. The role of clathrin-coated vesicles in acrosome formation. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;26(1):52–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J., Griffiths G., Howell K. E. Characterization of the early endosome and putative endocytic carrier vesicles in vivo and with an assay of vesicle fusion in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1301–1316. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauri H. P., Schweizer A. The endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):600–608. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90078-Q. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog V., Farquhar M. G. Luminal membrane retrieved after exocytosis reaches most golgi cisternae in secretory cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):5073–5077. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.5073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog V., Reggio H. Pathways of endocytosis from luminal plasma membrane in rat exocrine pancreas. Eur J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;21(2):141–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiller G., Weber K. Golgi-derived membranes that contain an acylated viral polypeptide are used for vaccinia virus envelopment. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):651–659. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.651-659.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichihashi Y., Dales S. Biogenesis of poxviruses: interrelationship between hemagglutinin production and polykaryocytosis. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):533–543. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90057-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs S. N., Wolffe E. J., Payne L. G., Moss B. Characterization of a vaccinia virus-encoded 42-kilodalton class I membrane glycoprotein component of the extracellular virus envelope. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7217–7224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7217-7224.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killisch I., Steinlein P., Römisch K., Hollinshead R., Beug H., Griffiths G. Characterization of early and late endocytic compartments of the transferrin cycle. Transferrin receptor antibody blocks erythroid differentiation by trapping the receptor in the early endosome. J Cell Sci. 1992 Sep;103(Pt 1):211–232. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S., Mellman I. The biogenesis of lysosomes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:483–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis V., Green S. A., Marsh M., Vihko P., Helenius A., Mellman I. Glycoproteins of the lysosomal membrane. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1839–1847. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker J. K., Griffiths G., Horzinek M. C., Rottier P. J. O-glycosylation of the coronavirus M protein. Differential localization of sialyltransferases in N- and O-linked glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14094–14101. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)49683-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker J. K., Rose J. K., Horzinek M. C., Rottier P. J. Membrane assembly of the triple-spanning coronavirus M protein. Individual transmembrane domains show preferred orientation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21911–21918. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)36699-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuoka Y., Ihara T., Bishop D. H., Compans R. W. Intracellular accumulation of Punta Toro virus glycoproteins expressed from cloned cDNA. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90075-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C. Vaccinia virus reexamined: development and release. Virology. 1976 Aug;73(1):43–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Regulation of vaccinia virus transcription. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:661–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Verkerk J. M., Broxterman H. J., van der Marel G. A., van Boom J. H., Ploegh H. L. Recycling glycoproteins do not return to the cis-Golgi. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):79–87. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Amherdt M., Louvard D., Perrelet A. Clathrin-immunoreactive sites in the Golgi apparatus are concentrated at the trans pole in polypeptide hormone-secreting cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5385–5389. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzak A., Winkler H. Exocytotic exposure and recycling of membrane antigens of chromaffin granules: ultrastructural evaluation after immunolabeling. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):510–515. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. G. Characterization of vaccinia virus glycoproteins by monoclonal antibody precipitation. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90313-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. G. Identification of the vaccinia hemagglutinin polypeptide from a cell system yielding large amounts of extracellular enveloped virus. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):147–155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.147-155.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. G., Kristenson K. Mechanism of vaccinia virus release and its specific inhibition by N1-isonicotinoyl-N2-3-methyl-4-chlorobenzoylhydrazine. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):614–622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.614-622.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. Polypeptide composition of extracellular enveloped vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):28–37. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.28-37.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pifat D. Y., Osterling M. C., Smith J. F. Antigenic analysis of Punta Toro virus and identification of protective determinants with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):442–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabinowitz S., Horstmann H., Gordon S., Griffiths G. Immunocytochemical characterization of the endocytic and phagolysosomal compartments in peritoneal macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):95–112. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmutz C., Payne L. G., Gubser J., Wittek R. A mutation in the gene encoding the vaccinia virus 37,000-M(r) protein confers resistance to an inhibitor of virus envelopment and release. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3435–3442. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3435-3442.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shida H., Matsumoto S. Analysis of the hemagglutinin glycoprotein from mutants of vaccinia virus that accumulates on the nuclear envelope. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90424-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shida H. Nucleotide sequence of the vaccinia virus hemagglutinin gene. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):451–462. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90309-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;38(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodeik B., Doms R. W., Ericsson M., Hiller G., Machamer C. E., van 't Hof W., van Meer G., Moss B., Griffiths G. Assembly of vaccinia virus: role of the intermediate compartment between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi stacks. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):521–541. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Hollinshead M., Reis B., Radsak K., Kern H. Progeny vaccinia and human cytomegalovirus particles utilize early endosomal cisternae for their envelopes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;60(1):163–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S., Newman R. A., Domingo D. L., Sauvage C. Transferrin receptors: structure and function. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 15;33(6):925–932. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90447-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe E. J., Isaacs S. N., Moss B. Deletion of the vaccinia virus B5R gene encoding a 42-kilodalton membrane glycoprotein inhibits extracellular virus envelope formation and dissemination. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):4732–4741. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.4732-4741.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Deurs B., Sandvig K., Petersen O. W., Olsnes S., Simons K., Griffiths G. Estimation of the amount of internalized ricin that reaches the trans-Golgi network. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):253–267. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]