Abstract
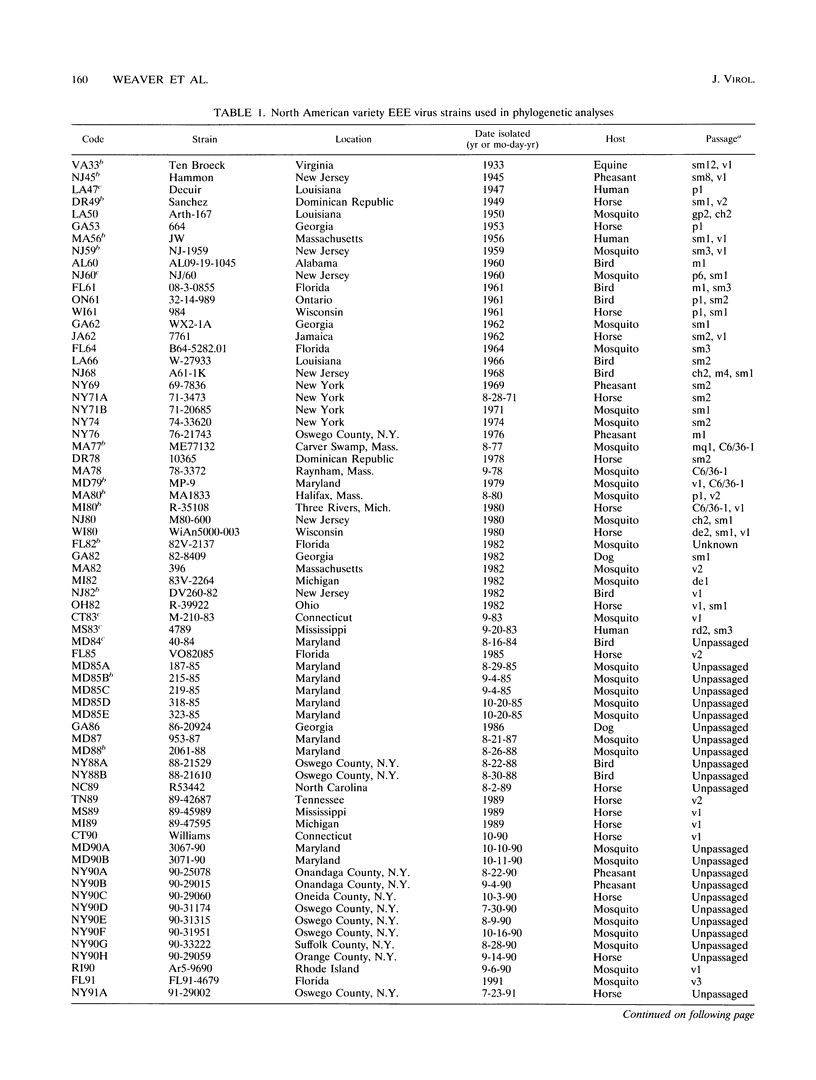
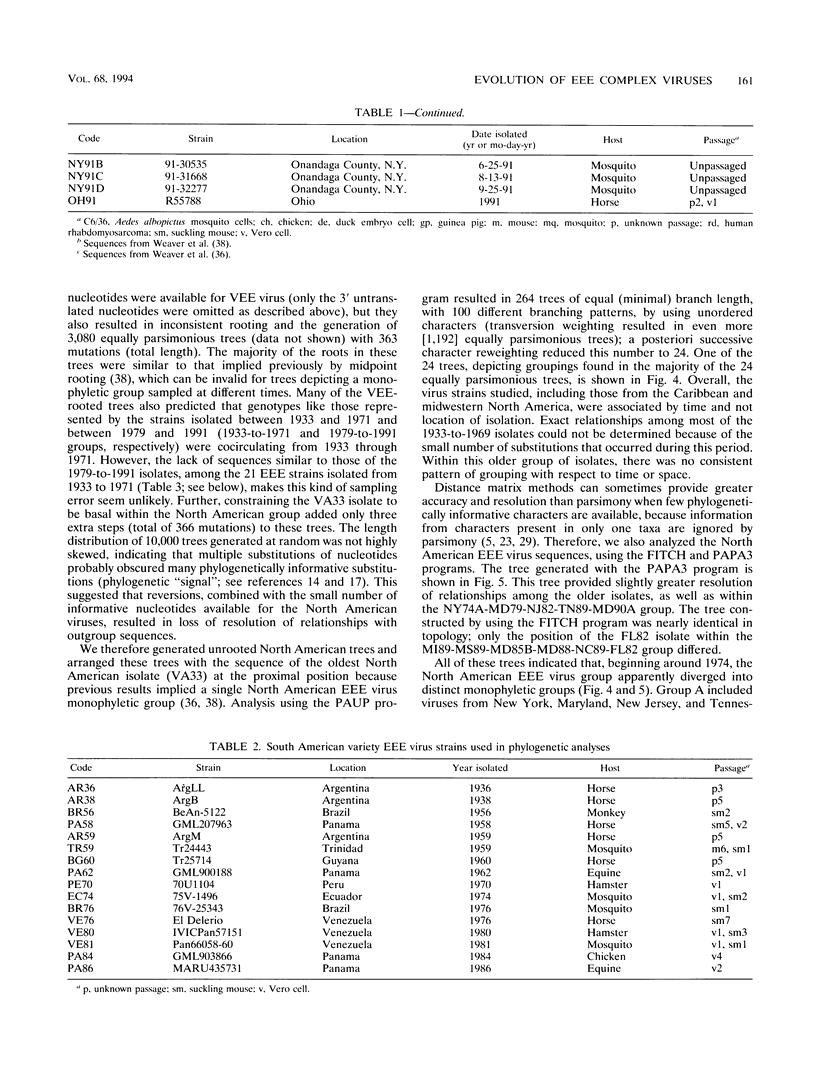
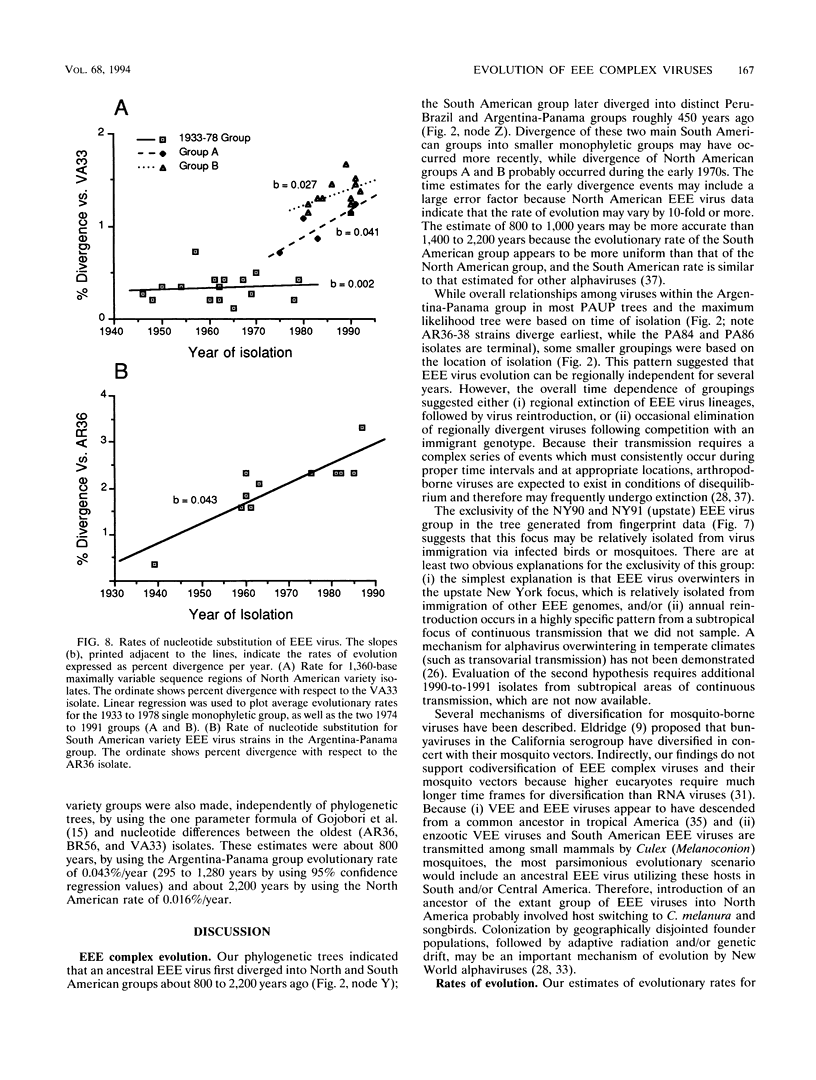
Evolution of viruses in the eastern equine encephalomyelitis (EEE) complex was studied by analyzing RNA sequences and oligonucleotide fingerprints from isolates representing the North and South American antigenic varieties. By using homologous sequences of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus as an outgroup, phylogenetic trees revealed three main EEE virus monophyletic groups. A North American variety group included all isolates from North America and the Caribbean. One South American variety group included isolates from the Amazon basin in Brazil and Peru, while the other included strains from Argentina, Guyana, Ecuador, Panama, Trinidad, and Venezuela. No evidence of heterologous recombination was obtained when three separate regions of the EEE virus genome were analyzed independently. Estimates of the overall rate of EEE virus evolution (nucleotide substitution) were 1.6 x 10(-4) substitution per nucleotide per year for the North American group and 4.3 x 10(-4) for the Argentina-Panama South American group. Evolutionary rate estimates for the North American group increased over 10-fold (from about 2 x 10(-5) to 4 x 10(-4)) concurrent with divergence of two monophyletic groups during the early 1970s. The North and South American antigenic varieties diverged roughly 1,000 years ago, while the two main South American groups diverged about 450 years ago. Analysis of multiple strains isolated from an upstate New York transmission focus during the same years suggested that, in certain locations, EEE virus may be relatively isolated for short time periods.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buonagurio D. A., Nakada S., Parvin J. D., Krystal M., Palese P., Fitch W. M. Evolution of human influenza A viruses over 50 years: rapid, uniform rate of change in NS gene. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):980–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2939560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASALS J. ANTIGENIC VARIANTS OF EASTERN EQUINE ENCEPHALITIS VIRUS. J Exp Med. 1964 Apr 1;119:547–565. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.4.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calisher C. H., Karabatsos N., Foster J. P., Pallansch M., Roehrig J. T. Identification of an antigenic subtype of eastern equine encephalitis virus isolated from a human. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):373–374. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.373-374.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calisher C. H., Shope R. E., Brandt W., Casals J., Karabatsos N., Murphy F. A., Tesh R. B., Wiebe M. E. Proposed antigenic classification of registered arboviruses I. Togaviridae, Alphavirus. Intervirology. 1980;14(5-6):229–232. doi: 10.1159/000149190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F. Nearest neighbor procedure for relating progressively aligned amino acid sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:659–669. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldridge B. F. Evolutionary relationships among California serogroup viruses (Bunyaviridae) and Aedes mosquitoes (Diptera: Culicidae) J Med Entomol. 1990 Sep;27(5):738–749. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/27.5.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fichot O., Girard M. An improved method for sequencing of RNA templates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6162–6162. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gojobori T., Moriyama E. N., Kimura M. Statistical methods for estimating sequence divergence. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:531–550. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn C. S., Lustig S., Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Western equine encephalitis virus is a recombinant virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5997–6001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinney R. M., Johnson B. J., Welch J. B., Tsuchiya K. R., Trent D. W. The full-length nucleotide sequences of the virulent Trinidad donkey strain of Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus and its attenuated vaccine derivative, strain TC-83. Virology. 1989 May;170(1):19–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90347-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins C. S., Sauer J. R., Greenberg R. S., Droege S. Population declines in North American birds that migrate to the neotropics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7658–7662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehrig J. T., Hunt A. R., Chang G. J., Sheik B., Bolin R. A., Tsai T. F., Trent D. W. Identification of monoclonal antibodies capable of differentiating antigenic varieties of eastern equine encephalitis viruses. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1990 Apr;42(4):394–398. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1990.42.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott T. W., Weaver S. C. Eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus: epidemiology and evolution of mosquito transmission. Adv Virus Res. 1989;37:277–328. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60838-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sourdis J., Nei M. Relative efficiencies of the maximum parsimony and distance-matrix methods in obtaining the correct phylogenetic tree. Mol Biol Evol. 1988 May;5(3):298–311. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss J. H., Strauss E. G. Evolution of RNA viruses. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:657–683. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.003301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver S. C., Bellew L. A., Gousset L., Repik P. M., Scott T. W., Holland J. J. Diversity within natural populations of eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus. Virology. 1993 Aug;195(2):700–709. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver S. C., Bellew L. A., Rico-Hesse R. Phylogenetic analysis of alphaviruses in the Venezuelan equine encephalitis complex and identification of the source of epizootic viruses. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):282–290. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90190-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver S. C., Hagenbaugh A., Bellew L. A., Calisher C. H. Genetic characterization of an antigenic subtype of eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus. Arch Virol. 1992;127(1-4):305–314. doi: 10.1007/BF01309592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver S. C., Rico-Hesse R., Scott T. W. Genetic diversity and slow rates of evolution in New World alphaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1992;176:99–117. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-77011-1_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver S. C., Scott T. W., Rico-Hesse R. Molecular evolution of eastern equine encephalomyelitis virus in North America. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):774–784. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90618-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S. The Distribution of Gene Frequencies in Populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1937 Jun;23(6):307–320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.23.6.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


