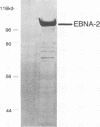
Abstract
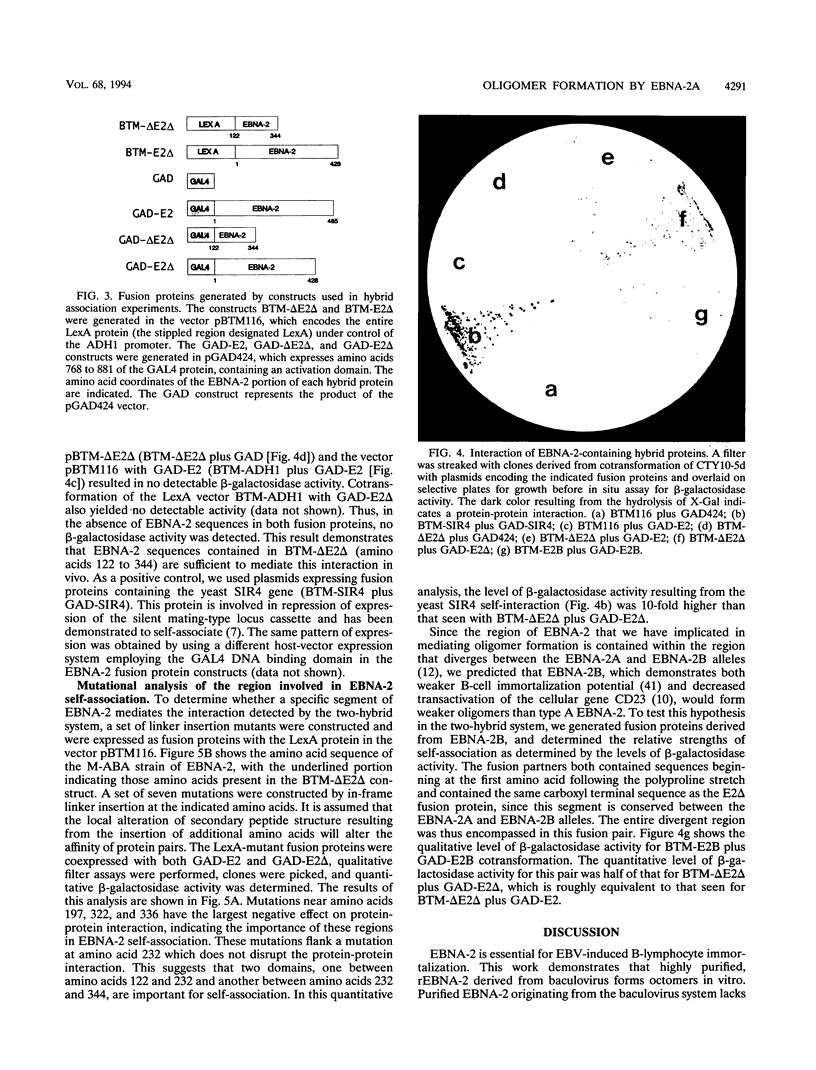
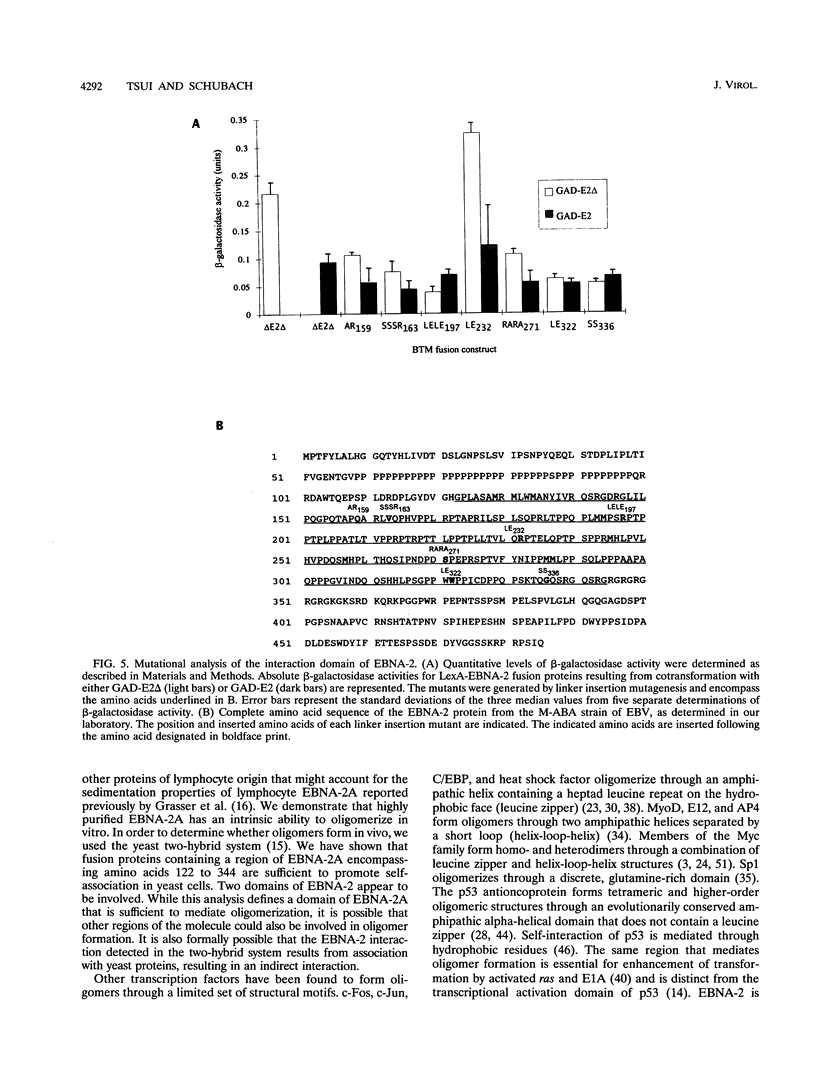
Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 (EBNA-2) has been shown to be indispensable for immortalization of latently infected B lymphocytes, and it has been shown that EBNA-2 exists in a high-molecular-weight complex in these cells. In order to study the components of this protein machinery, we have purified baculovirus-expressed EBNA-2 from insect cells to greater than 95% homogeneity. We have shown by both gel filtration and sucrose gradient analysis that the purified material corresponds to a multimer containing eight EBNA-2 subunits. This multimeric complex is stable in 1.0 M NaCl, suggesting that the self-association is quite strong in vitro. By expressing portions of the EBNA-2 open reading frame to generate fusion proteins in yeast cells, we have used the two-hybrid system to demonstrate that this self-association occurs in vivo and is mediated at least in part by a domain of EBNA-2 encompassing amino acids 122 to 344. Mutational analysis of the self-association function suggests that two subdomains that flank amino acid 232 may each play a role in EBNA-2 protein-protein interaction.
Full text
PDF


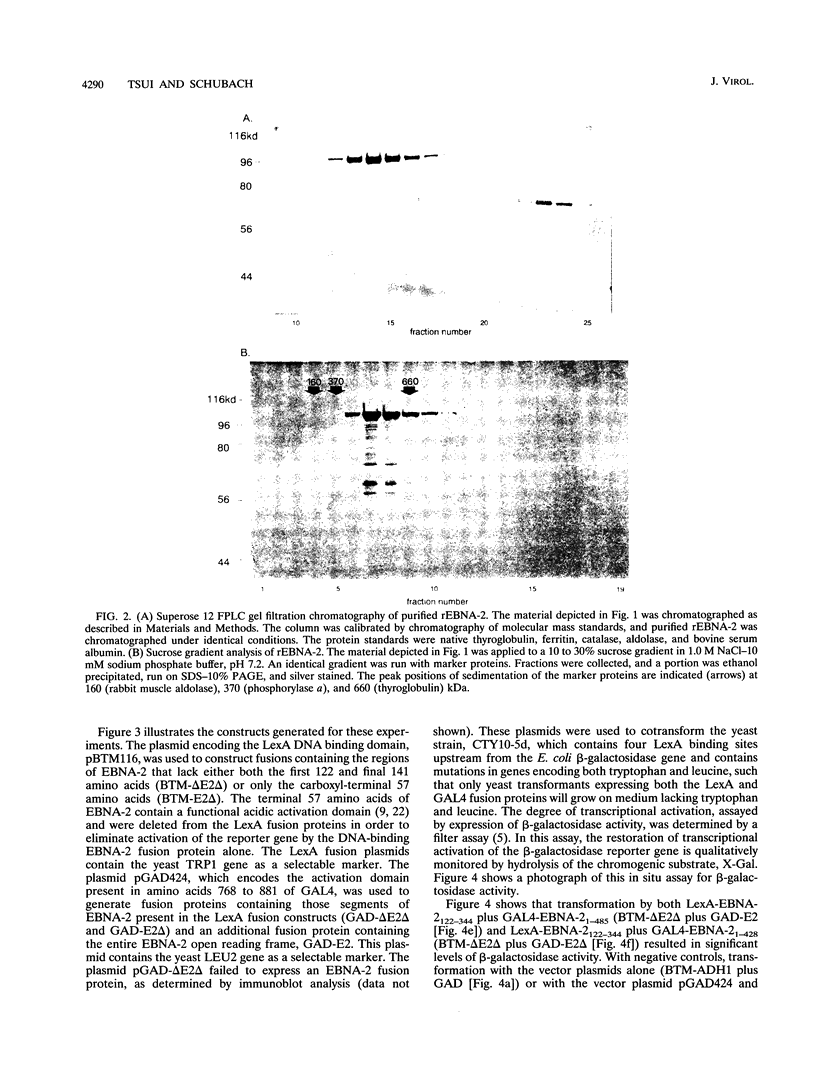


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbot S. D., Rowe M., Cadwallader K., Ricksten A., Gordon J., Wang F., Rymo L., Rickinson A. B. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 induces expression of the virus-encoded latent membrane protein. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2126–2134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2126-2134.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeden L., Nasmyth K. Regulation of the yeast HO gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:643–650. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calender A., Billaud M., Aubry J. P., Banchereau J., Vuillaume M., Lenoir G. M. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induces expression of B-cell activation markers on in vitro infection of EBV-negative B-lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8060–8064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien C. T., Bartel P. L., Sternglanz R., Fields S. The two-hybrid system: a method to identify and clone genes for proteins that interact with a protein of interest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9578–9582. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 domain essential for transformation is a direct transcriptional activator. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5880–5885. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5880-5885.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Wang F., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 mutations define essential domains for transformation and transactivation. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2545–2554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2545-2554.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Wang F., Mannick J., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 is a key determinant of lymphocyte transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9558–9562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Zimber U., Rousselet G., Pavlish O., Banchereau J., Tursz T., Bornkamm G., Lenoir G. M. Stable transfection of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) nuclear antigen 2 in lymphoma cells containing the EBV P3HR1 genome induces expression of B-cell activation molecules CD21 and CD23. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1002–1013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1002-1013.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dambaugh T., Hennessy K., Chamnankit L., Kieff E. U2 region of Epstein-Barr virus DNA may encode Epstein-Barr nuclear antigen 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7632–7636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grässer F. A., Haiss P., Göttel S., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Biochemical characterization of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2A. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3779–3788. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3779-3788.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Genetic analysis of immortalizing functions of Epstein-Barr virus in human B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):393–397. doi: 10.1038/340393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanto D. W., Gajl-Peczalska K. J., Frizzera G., Arthur D. C., Balfour H. H., Jr, McClain K., Simmons R. L., Najarian J. S. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) induced polyclonal and monoclonal B-cell lymphoproliferative diseases occurring after renal transplantation. Clinical, pathologic, and virologic findings and implications for therapy. Ann Surg. 1983 Sep;198(3):356–369. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198309000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W., Diehl V. Relation of Burkitt's tumor-associated herpes-ytpe virus to infectious mononucleosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Jan;59(1):94–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J., Donald K. A., Griffiths D. E., Donald G. DMSO-enhanced whole cell yeast transformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5791–5791. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath G. C., Schubach W. H. Identification of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivation domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Feb 26;191(1):196–200. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. Transcriptional regulation by dimerization: two sides to an incestuous relationship. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):9–11. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90207-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato G. J., Lee W. M., Chen L. L., Dang C. V. Max: functional domains and interaction with c-Myc. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):81–92. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan L., Gill G., Ptashne M. Separation of DNA binding from the transcription-activating function of a eukaryotic regulatory protein. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):699–704. doi: 10.1126/science.3080805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles D. M., Inghirami G., Ubriaco A., Dalla-Favera R. Molecular genetic analysis of three AIDS-associated neoplasms of uncertain lineage demonstrates their B-cell derivation and the possible pathogenetic role of the Epstein-Barr virus. Blood. 1989 Feb 15;73(3):792–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knutson J. C. The level of c-fgr RNA is increased by EBNA-2, an Epstein-Barr virus gene required for B-cell immortalization. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2530–2536. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2530-2536.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraiss S., Quaiser A., Oren M., Montenarh M. Oligomerization of oncoprotein p53. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4737–4744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4737-4744.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascal E., Tjian R. Different activation domains of Sp1 govern formation of multimers and mediate transcriptional synergism. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1646–1656. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope J. H., Horne M. K., Scott W. Transformation of foetal human keukocytes in vitro by filtrates of a human leukaemic cell line containing herpes-like virus. Int J Cancer. 1968 Nov 15;3(6):857–866. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910030619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabindran S. K., Haroun R. I., Clos J., Wisniewski J., Wu C. Regulation of heat shock factor trimer formation: role of a conserved leucine zipper. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):230–234. doi: 10.1126/science.8421783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M., Gradoville L., Heston L., Miller G. Non-immortalizing P3J-HR-1 Epstein-Barr virus: a deletion mutant of its transforming parent, Jijoye. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):834–844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.834-844.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed M., Wang Y., Mayr G., Anderson M. E., Schwedes J. F., Tegtmeyer P. p53 domains: suppression, transformation, and transactivation. Gene Expr. 1993;3(1):95–107. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickinson A. B., Young L. S., Rowe M. Influence of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen EBNA 2 on the growth phenotype of virus-transformed B cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1310-1317.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W. H., Horvath G., Spoth B., Hearing J. C. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 in insect cells from a baculovirus vector. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):428–431. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90792-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenger J. E., Mayr G. A., Mann K., Tegtmeyer P. Formation of stable p53 homotetramers and multiples of tetramers. Mol Carcinog. 1992;5(2):102–106. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940050204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J. C., Atkinson T., Smith M., Pawson T. Identification of functional regions in the transforming protein of Fujinami sarcoma virus by in-phase insertion mutagenesis. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):549–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90385-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Brain R., Addison C., Rudge K., Remm M., Grimaldi M., Keenan E., Jenkins J. R. A C-terminal alpha-helix plus basic region motif is the major structural determinant of p53 tetramerization. Oncogene. 1992 Aug;7(8):1513–1523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C. D., Rowe M., Rickinson A. B., Wang D., Birkenbach M., Kikutani H., Kishimoto T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 specifically induces expression of the B-cell activation antigen CD23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3452–3456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C., Sample C., Rowe M., Liebowitz D., Murray R., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2309–2318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2309-2318.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Tsang S. F., Kurilla M. G., Cohen J. I., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivates latent membrane protein LMP1. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3407–3416. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3407-3416.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Kingston R. E. Nucleosome core displacement in vitro via a metastable transcription factor-nucleosome complex. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1780–1784. doi: 10.1126/science.1465613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos A. S., Gyuris J., Brent R. Mxi1, a protein that specifically interacts with Max to bind Myc-Max recognition sites. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90662-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber-Strobl U., Kremmer E., Grässer F., Marschall G., Laux G., Bornkamm G. W. The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 interacts with an EBNA2 responsive cis-element of the terminal protein 1 gene promoter. EMBO J. 1993 Jan;12(1):167–175. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05642.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimber-Strobl U., Suentzenich K. O., Laux G., Eick D., Cordier M., Calender A., Billaud M., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W. Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 activates transcription of the terminal protein gene. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):415–423. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.415-423.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de-Thé G., Geser A., Day N. E., Tukei P. M., Williams E. H., Beri D. P., Smith P. G., Dean A. G., Bronkamm G. W., Feorino P. Epidemiological evidence for causal relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and Burkitt's lymphoma from Ugandan prospective study. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):756–761. doi: 10.1038/274756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]