Abstract
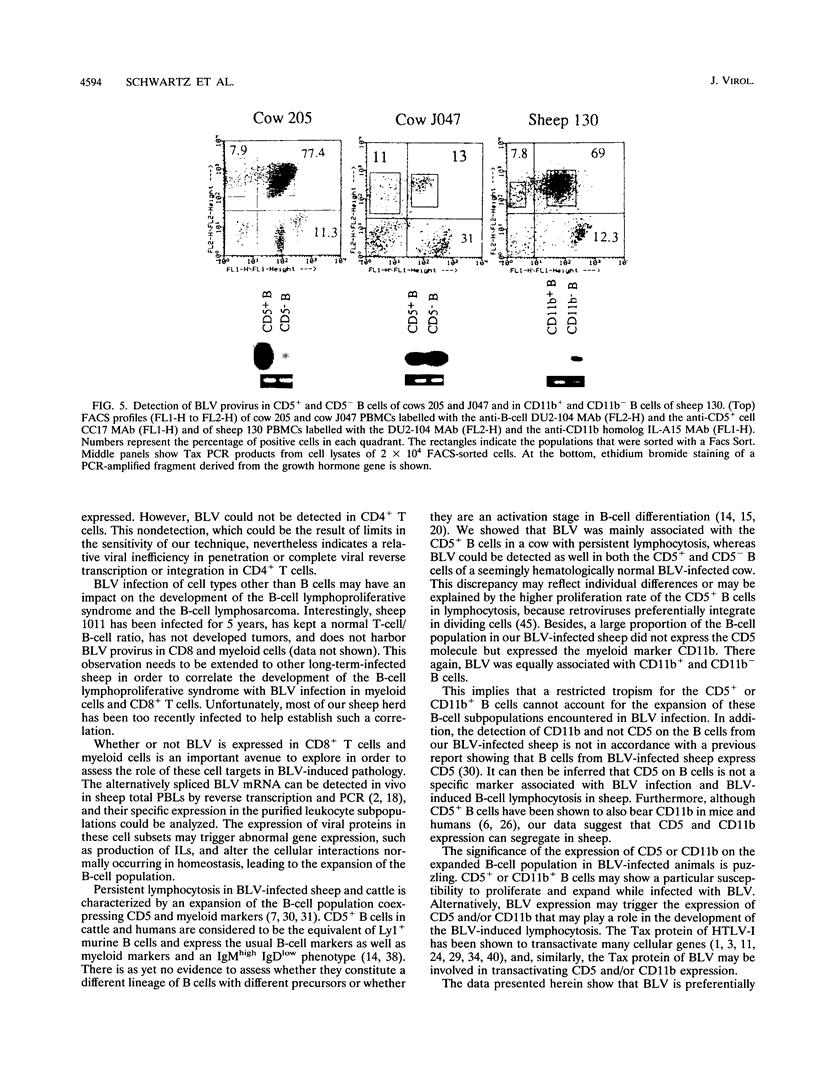
Bovine leukemia virus (BLV), an oncovirus related to human T-cell leukemia virus type I, causes a B-cell lymphoproliferative syndrome in cattle, leading to an inversion of the T-cell/B-cell ratio and, more rarely, to a B-cell lymphosarcoma. Sheep are highly sensitive to BLV experimental infection and develop B-cell pathologies similar to those in cattle in 90% of the cases. BLV tropism for B cells has been well documented, but the infection of other cell populations may also be involved in the BLV-induced lymphoproliferative syndrome. We thus looked for BLV provirus in other leukocyte populations in sheep and cattle by using PCR. We found that while B cells harbor the highest proviral load, CD8+ T cells, monocytes, and granulocytes, but not CD4+ T cells, also bear BLV provirus. As previously described, we found that persistent lymphocytosis in cows is characterized by an expansion of the CD5+ B-cell subpopulation but we did not confirm this observation in sheep in which the expanded B-cell population expressed the CD11b marker. Nevertheless, BLV could be detected both in bovine CD5+ and CD5- B cells and in sheep CD11b+ and CD11b- B cells, indicating that the restricted BLV tropism for a specific B-cell subpopulation cannot explain its expansion encountered in BLV infection. Altogether, this work shows that BLV tropism in leukocytes is wider than previously thought. These results lead the way to further studies of cellular interactions among B cells and other leukocytes that may intervene in the development of the lymphoproliferative syndrome induced by BLV infection.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albrecht H., Shakhov A. N., Jongeneel C. V. trans activation of the tumor necrosis factor alpha promoter by the human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax1 protein. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6191–6193. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6191-6193.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Carpenter S., Christensen J., Storgaard T., Viuff B., Wannemuehler Y., Belousov J., Roth J. A. Identification of alternatively spliced mRNAs encoding potential new regulatory proteins in cattle infected with bovine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):39–52. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.39-52.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Wano Y., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. HTLV-I tax induces cellular proteins that activate the kappa B element in the IL-2 receptor alpha gene. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1652–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burny A., Cleuter Y., Kettmann R., Mammerickx M., Marbaix G., Portetelle D., Van den Broeke A., Willems L., Thomas R. Bovine leukemia: facts and hypotheses derived from the study of an infectious cancer. Adv Vet Sci Comp Med. 1988;32:149–170. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-039232-2.50010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Da Y., Shanks R. D., Stewart J. A., Lewin H. A. Milk and fat yields decline in bovine leukemia virus-infected Holstein cattle with persistent lymphocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6538–6541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De la Hera A., Alvarez-Mon M., Sanchez-Madrid F., Martinez C., Durantez A. Co-expression of Mac-1 and p150,95 on CD5+ B cells. Structural and functional characterization in a human chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jul;18(7):1131–1134. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depelchin A., Letesson J. J., Lostrie-Trussart N., Mammerickx M., Portetelle D., Burny A. Bovine leukemia virus (BLV)-infected B-cells express a marker similar to the CD5 T cell marker. Immunol Lett. 1989 Jan 15;20(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0165-2478(89)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Martarano L. Construction of a recombinant bovine leukemia virus vector for analysis of virus infectivity. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):401–405. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.401-405.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D. trans-acting regulation of bovine leukemia virus mRNA processing. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1115–1119. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1115-1119.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desrosiers R. C., Hansen-Moosa A., Mori K., Bouvier D. P., King N. W., Daniel M. D., Ringler D. J. Macrophage-tropic variants of SIV are associated with specific AIDS-related lesions but are not essential for the development of AIDS. Am J Pathol. 1991 Jul;139(1):29–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duyao M. P., Kessler D. J., Spicer D. B., Sonenshein G. E. Transactivation of the murine c-myc gene by HTLV-1 tax is mediated by NFkB. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 May;8(5):752–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English R. V., Johnson C. M., Gebhard D. H., Tompkins M. B. In vivo lymphocyte tropism of feline immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5175–5186. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5175-5186.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauci A. S. The human immunodeficiency virus: infectivity and mechanisms of pathogenesis. Science. 1988 Feb 5;239(4840):617–622. doi: 10.1126/science.3277274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman A. S., Freeman G., Whitman J., Segil J., Daley J., Levine H., Nadler L. M. Expression and regulation of CD5 on in vitro activated human B cells. Eur J Immunol. 1989 May;19(5):849–855. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman A. S., Freeman G., Whitman J., Segil J., Daley J., Nadler L. M. Studies of in vitro activated CD5+ B cells. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):202–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii M., Sassone-Corsi P., Verma I. M. c-fos promoter trans-activation by the tax1 protein of human T-cell leukemia virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8526–8530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grassmann R., Berchtold S., Radant I., Alt M., Fleckenstein B., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A., Ramstedt U. Role of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 X region proteins in immortalization of primary human lymphocytes in culture. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4570–4575. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4570-4575.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
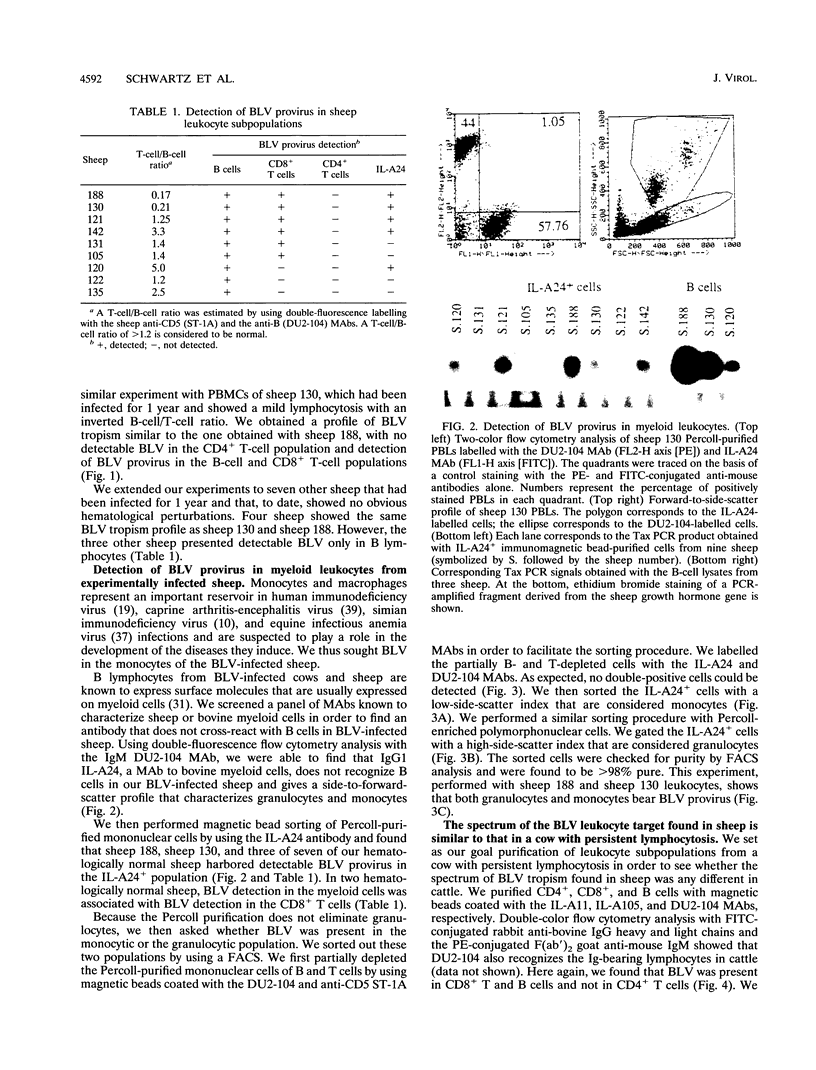
- Haas L., Divers T., Casey J. W. Bovine leukemia virus gene expression in vivo. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6223–6225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6223-6225.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori N., Michaels F., Fargnoli K., Marcon L., Gallo R. C., Franchini G. The human immunodeficiency virus type 2 vpr gene is essential for productive infection of human macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):8080–8084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.8080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa K., Hardy R. R., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Progenitors for Ly-1 B cells are distinct from progenitors for other B cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1554–1568. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heeney J. L., Valli P. J., Jacobs R. M., Valli V. E. Evidence for bovine leukemia virus infection of peripheral blood monocytes and limited antigen expression in bovine lymphoid tissue. Lab Invest. 1992 May;66(5):608–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka M., Inoue J., Yoshida M., Seiki M. Post-transcriptional regulator (rex) of HTLV-1 initiates expression of viral structural proteins but suppresses expression of regulatory proteins. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):519–523. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02840.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman P. M., Dhib-Jalbut S., Mikovits J. A., Robbins D. S., Wolf A. L., Bergey G. K., Lohrey N. C., Weislow O. S., Ruscetti F. W. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I infection of monocytes and microglial cells in primary human cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11784–11788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Seiki M., Taniguchi T., Tsuru S., Yoshida M. Induction of interleukin 2 receptor gene expression by p40x encoded by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2883–2888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamori H., Suzuki N., Siomi H., Nosaka T., Sato A., Sabe H., Hatanaka M., Honjo T. HTLV-1 p27rex stabilizes human interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain mRNA. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4161–4166. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07639.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kantor A. B. The development and repertoire of B-1 cells (CD5 B cells). Immunol Today. 1991 Nov;12(11):389–391. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(91)90136-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh I., Yoshinaka Y., Ikawa Y. Bovine leukemia virus trans-activator p38tax activates heterologous promoters with a common sequence known as a cAMP-responsive element or the binding site of a cellular transcription factor ATF. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):497–503. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03403.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettmann R., Cleuter Y., Mammerickx M., Meunier-Rotival M., Bernardi G., Burny A., Chantrenne H. Genomic integration of bovine leukemia provirus: comparison of persistent lymphocytosis with lymph node tumor form of enzootic. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2577–2581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. J., Kehrl J. H., Burton J., Tendler C. L., Jeang K. T., Danielpour D., Thevenin C., Kim K. Y., Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Transactivation of the transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-beta 1) gene by human T lymphotropic virus type 1 tax: a potential mechanism for the increased production of TGF-beta 1 in adult T cell leukemia. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):121–129. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letesson J. J., Mager A., Mammerickx M., Burny A., Depelchin A. B cells from bovine leukemia virus- (BLV) infected sheep with hematological disorders express the CD5 T cell marker. Leukemia. 1990 May;4(5):377–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letesson J. J., Van den Broecke A., Marbaix-Cleuter Y., Delcommenne M., Mager A., Mammerickx M., Burny A., Depelchin A. FACS analysis of bovine leukemia virus (BLV)-infected cell lines with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to B cells and to monocytes/macrophages. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1991 Jan;27(1-3):207–213. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(91)90102-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin H. A. Disease resistance and immune response genes in cattle: strategies for their detection and evidence of their existence. J Dairy Sci. 1989 May;72(5):1334–1348. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(89)79241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilienbaum A., Duc Dodon M., Alexandre C., Gazzolo L., Paulin D. Effect of human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax protein on activation of the human vimentin gene. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):256–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.256-263.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévy D., Kettmann R., Marchand P., Djilali S., Parodi A. L. Selective tropism of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) for surface immunoglobulin-bearing ovine B lymphocytes. Leukemia. 1987 May;1(5):463–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mammerickx M., Palm R., Portetelle D., Burny A. Experimental transmission of enzootic bovine leukosis to sheep: latency period of the tumoral disease. Leukemia. 1988 Feb;2(2):103–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire K. L., Curtiss V. E., Larson E. L., Haseltine W. A. Influence of human T-cell leukemia virus type I tax and rex on interleukin-2 gene expression. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1590–1599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1590-1599.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Crawford T. B., Henson J. B. Immunofluorescent localization of equine infectious anemia virus in tissue. Am J Pathol. 1971 Feb;62(2):283–294. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naessens J., Williams D. J. Characterization and measurement of CD5+ B cells in normal and Trypanosoma congolense-infected cattle. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Jul;22(7):1713–1718. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Kennedy-Stoskopf S., Sheffer D., Griffin D. E., Clements J. E. Activation of caprine arthritis-encephalitis virus expression during maturation of monocytes to macrophages. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):67–73. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.67-73.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nimer S. D., Gasson J. C., Hu K., Smalberg I., Williams J. L., Chen I. S., Rosenblatt J. D. Activation of the GM-CSF promoter by HTLV-I and -II tax proteins. Oncogene. 1989 Jun;4(6):671–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. H., Edwards A. J., Cruickshank J. K., Rudge P., Dalgleish A. G. In vivo cellular tropism of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5682–5687. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5682-5687.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stott M. L., Thurmond M. C., Dunn S. J., Osburn B. I., Stott J. L. Integrated bovine leukosis proviral DNA in T helper and T cytotoxic/suppressor lymphocytes. J Gen Virol. 1991 Feb;72(Pt 2):307–315. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-2-307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Bruck C., Portetelle D., Burny A., Kettmann R. Expression of a cDNA clone corresponding to the long open reading frame (XBL-I) of the bovine leukemia virus. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willems L., Heremans H., Chen G., Portetelle D., Billiau A., Burny A., Kettmann R. Cooperation between bovine leukaemia virus transactivator protein and Ha-ras oncogene product in cellular transformation. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1577–1581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S. R., Go A. S., Haislip A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 entry into quiescent primary lymphocytes: molecular analysis reveals a labile, latent viral structure. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90802-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]