Abstract
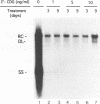
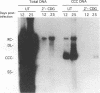
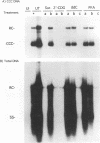
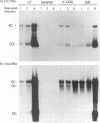
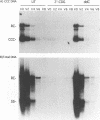
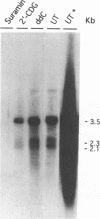
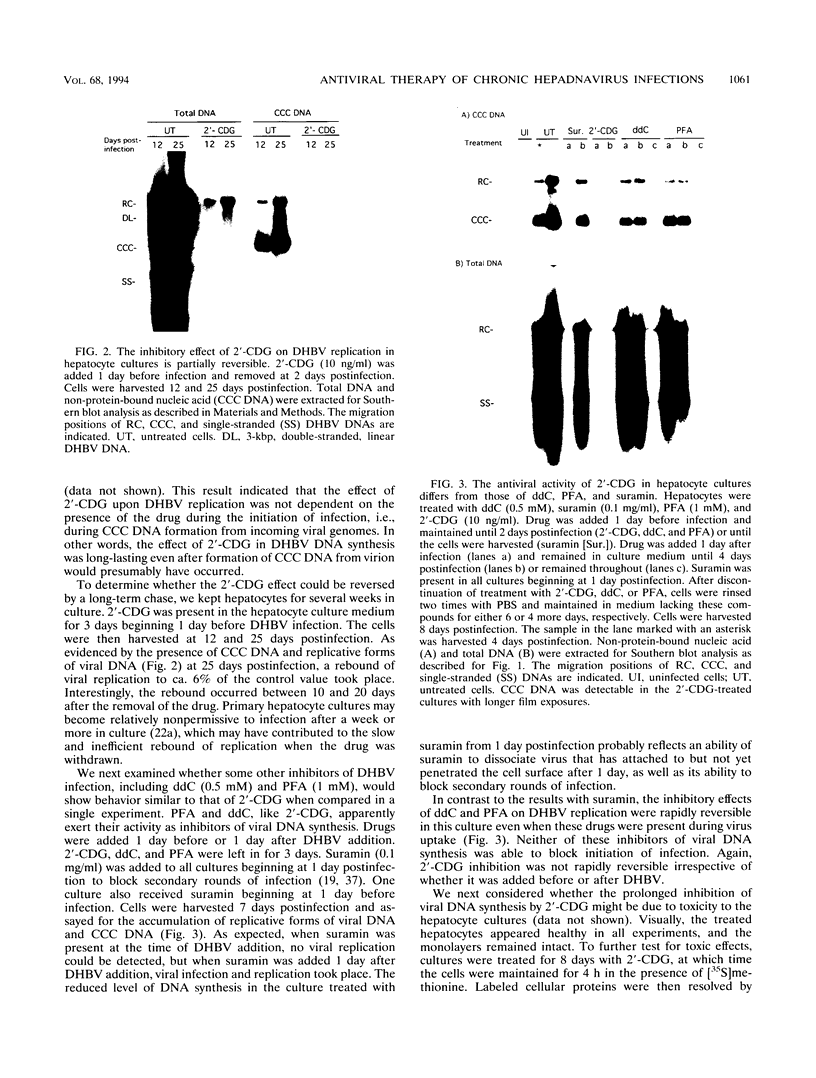
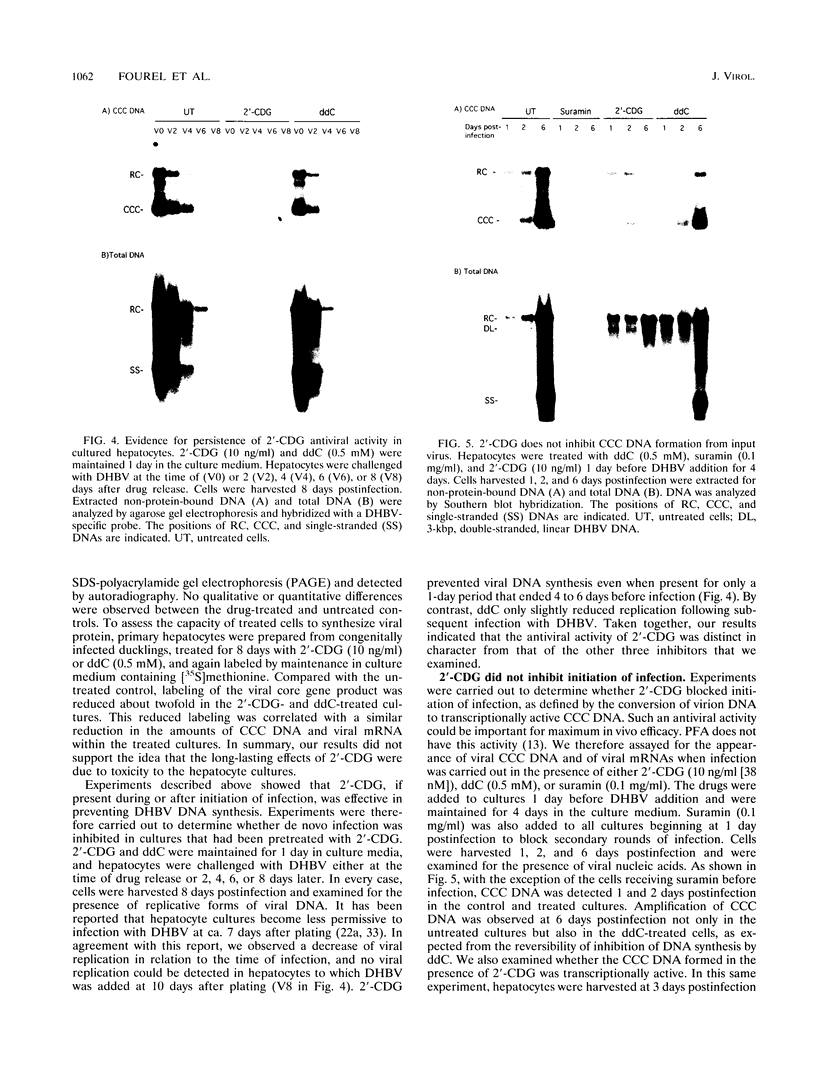
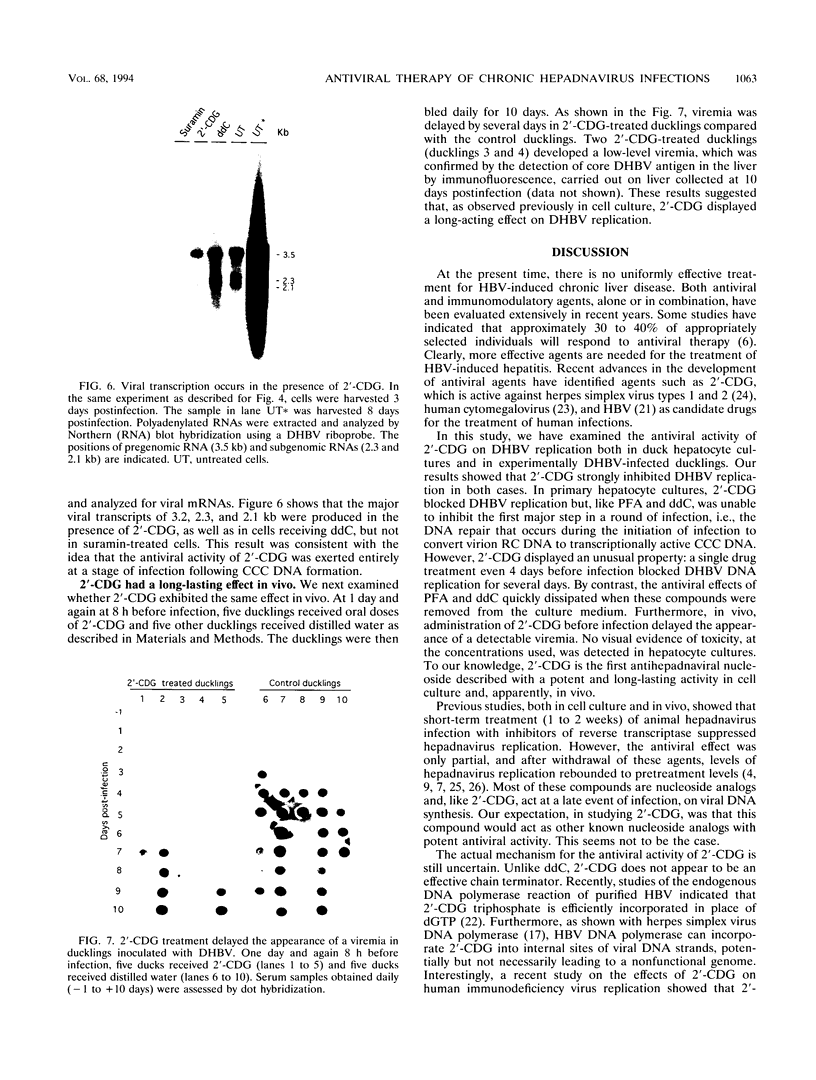
The carbocyclic analog of 2'-deoxyguanosine (2'-CDG) is a strong inhibitor of hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA synthesis in HepG2 cells (P.M. Price, R. Banerjee, and G. Acs, Proc. Natl. Acad. USA 86:8543-8544, 1989). We now report that 2'-CDG inhibited duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) DNA synthesis in primary cultures of duck hepatocytes and in experimentally infected ducks. Like foscarnet (phosphonoformic acid [PFA]) and 2'-,3'-dideoxycytidine (ddC), 2'-CDG blocked viral DNA replication in primary hepatocyte cultures when present during an infection but failed to inhibit the DNA repair reaction that occurs during the initiation of infection to convert virion relaxed circular DNA to covalently closed circular DNA, the template for viral mRNA transcription. Moreover, as for PFA and ddC, viral RNA synthesis was detected when infection was initiated in the presence 2'-CDG. In another respect, however, 2'-CDG exhibited antiviral activity unlike that of ddC or PFA: a single 1-day treatment of hepatocytes with 2'-CDG blocked initiation of viral DNA synthesis for at least 8 days, irrespective of whether DHBV infection was carried out at the time of drug treatment or several days later. Furthermore, orally administered 2'-CDG was long-acting against DHBV in experimentally infected ducklings. Virus replication was delayed by up to 4 days in ducklings infected after administration of 2'-CDG. These observations of long-lasting efficacy in vitro and in vivo even after oral administration suggest that this inhibitor or a nucleoside with similar pharmacological properties may be ideal for reducing virus replication in patients with chronic HBV infection.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blumberg B. S., Gerstley B. J., Hungerford D. A., London W. T., Sutnick A. I. A serum antigen (Australia antigen) in Down's syndrome, leukemia, and hepatitis. Ann Intern Med. 1967 May;66(5):924–931. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-66-5-924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civitico G., Wang Y. Y., Luscombe C., Bishop N., Tachedjian G., Gust I., Locarnini S. Antiviral strategies in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: II. Inhibition of duck hepatitis B virus in vitro using conventional antiviral agents and supercoiled-DNA active compounds. J Med Virol. 1990 Jun;31(2):90–97. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890310205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourel I., Gripon P., Hantz O., Cova L., Lambert V., Jacquet C., Watanabe K., Fox J., Guillouzo C., Trepo C. Prolonged duck hepatitis B virus replication in duck hepatocytes cocultivated with rat epithelial cells: a useful system for antiviral testing. Hepatology. 1989 Aug;10(2):186–191. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fourel I., Li J., Hantz O., Jacquet C., Fox J. J., Trépo C. Effects of 2'-fluorinated arabinosyl-pyrimidine nucleosides on duck hepatitis B virus DNA level in serum and liver of chronically infected ducks. J Med Virol. 1992 Jun;37(2):122–126. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890370209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoofnagle J. H., Shafritz D. A., Popper H. Chronic type B hepatitis and the "healthy" HBsAg carrier state. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):758–763. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassianides C., Hoofnagle J. H., Miller R. H., Doo E., Ford H., Broder S., Mitsuya H. Inhibition of duck hepatitis B virus replication by 2',3'-dideoxycytidine. A potent inhibitor of reverse transcriptase. Gastroenterology. 1989 Nov;97(5):1275–1280. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(89)91699-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampertico P., Malter J. S., Gerber M. A. Development and application of an in vitro model for screening anti-hepatitis B virus therapeutics. Hepatology. 1991 Mar;13(3):422–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Luo W. X., Suzuki S., Robins M. J., Tyrrell D. L. In vitro and in vivo comparison of the abilities of purine and pyrimidine 2',3'-dideoxynucleosides to inhibit duck hepadnavirus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989 Mar;33(3):336–339. doi: 10.1128/aac.33.3.336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lien J. M., Petcu D. J., Aldrich C. E., Mason W. S. Initiation and termination of duck hepatitis B virus DNA synthesis during virus maturation. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3832–3840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3832-3840.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Oshiro L. S., Regnery D. C., Scullard G. H., Robinson W. S. A virus in Beechey ground squirrels that is related to hepatitis B virus of humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2941–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Seal G., Summers J. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.829-836.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthes E., Langen P., von Janta-Lipinski M., Will H., Schröder H. C., Merz H., Weiler B. E., Müller W. E. Potent inhibition of hepatitis B virus production in vitro by modified pyrimidine nucleosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Oct;34(10):1986–1990. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.10.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagahata T., Ueda K., Tsurimoto T., Chisaka O., Matsubara K. Anti-hepatitis B virus activities of purine derivatives of oxetanocin A. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1989 Apr;42(4):644–646. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.42.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker W. B., Shaddix S. C., Allan P. W., Arnett G., Rose L. M., Shannon W. M., Shealy Y. F., Montgomery J. A., Secrist J. A., 3rd, Bennett L. L., Jr Incorporation of the carbocyclic analog of 2'-deoxyguanosine into the DNA of herpes simplex virus and of HEp-2 cells infected with herpes simplex virus. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Feb;41(2):245–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker W. B., White E. L., Shaddix S. C., Ross L. J., Shannon W. M., Secrist J. A., 3rd Interference with HIV-1 reverse transcriptase-catalyzed DNA chain elongation by the 5'-triphosphate of the carbocyclic analog of 2'-deoxyguanosine. Antiviral Res. 1992 Oct 1;19(4):325–332. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(92)90013-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petcu D. J., Aldrich C. E., Coates L., Taylor J. M., Mason W. S. Suramin inhibits in vitro infection by duck hepatitis B virus, Rous sarcoma virus, and hepatitis delta virus. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):385–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Shafritz D. A., Hoofnagle J. H. Relation of the hepatitis B virus carrier state to hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):764–772. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. M., Banerjee R., Acs G. Inhibition of the replication of hepatitis B virus by the carbocyclic analogue of 2'-deoxyguanosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8541–8544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P. M., Banerjee R., Jeffrey A. M., Acs G. The mechanism of inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by the carbocyclic analog of 2'-deoxyguanosine. Hepatology. 1992 Jul;16(1):8–12. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. Infection and uptake of duck hepatitis B virus by duck hepatocytes maintained in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):564–572. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shealy Y. F., O'Dell C. A., Shannon W. M., Arnett G. Synthesis and antiviral activity of carbocyclic analogues of 2'-deoxyribofuranosides of 2-amino-6-substituted-purines and of 2-amino-6-substituted-8-azapurines. J Med Chem. 1984 Nov;27(11):1416–1421. doi: 10.1021/jm00377a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherker A. H., Hirota K., Omata M., Okuda K. Foscarnet decreases serum and liver duck hepatitis B virus DNA in chronically infected ducks. Gastroenterology. 1986 Oct;91(4):818–824. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90681-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smee D. F., Knight S. S., Duke A. E., Robinson W. S., Matthews T. R., Marion P. L. Activities of arabinosyladenine monophosphate and 9-(1,3-dihydroxy-2-propoxymethyl)guanine against ground squirrel hepatitis virus in vivo as determined by reduction in serum virion-associated DNA polymerase. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Feb;27(2):277–279. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Kaleta E. F., Will H. Isolation and characterization of a hepatitis B virus endemic in herons. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3832–3839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3832-3839.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smith P. M., Horwich A. L. Hepadnavirus envelope proteins regulate covalently closed circular DNA amplification. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2819–2824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2819-2824.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smith P. M., Huang M. J., Yu M. S. Morphogenetic and regulatory effects of mutations in the envelope proteins of an avian hepadnavirus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1310-1317.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smolec J. M., Snyder R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pourcel C., Summers J. Formation of the pool of covalently closed circular viral DNA in hepadnavirus-infected cells. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90602-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. In vitro experimental infection of primary duck hepatocyte cultures with duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.17-25.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G. H., Seeger C. The reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B virus acts as a protein primer for viral DNA synthesis. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):663–670. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90599-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Coates L., Aldrich C. E., Summers J., Mason W. S. In hepatocytes infected with duck hepatitis B virus, the template for viral RNA synthesis is amplified by an intracellular pathway. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90206-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Konno K., Chonan E., Mochizuki S., Kojima K., Shigeta S., de Clercq E. Comparative activities of several nucleoside analogs against duck hepatitis B virus in vitro. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Jul;34(7):1326–1330. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.7.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]