Abstract
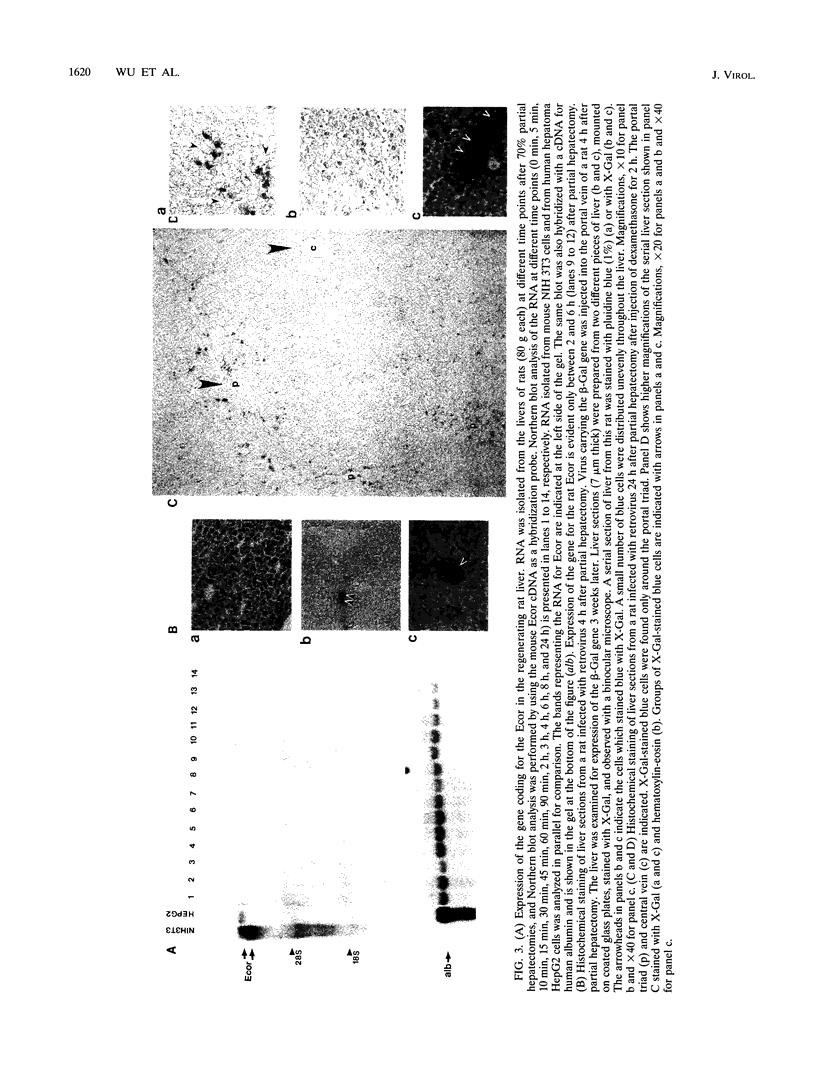
The infectibility of the regenerating rat liver by ecotropic retroviruses was studied relative to the expression of the gene coding for the ecotropic retrovirus receptor (Ecor) that functions as a cationic amino acid transporter. It is known that the gene for the receptor is expressed in primary hepatocytes and hepatoma cells but is absent in adult liver cells. Isolation of a 2.85-kb cDNA for the rat Ecor suggested that the rat viral receptor is 97% homologous to the mouse viral receptor and that it contains the envelope-binding domain that determines the host range of ecotropic murine retroviruses. This explains the efficient infection of rat cells by ecotropic retroviruses. Since cell division is required for liver cells to be infected, we determined the susceptibility of the regenerating rat liver to infection at different time points after partial hepatectomy (0 to 24 h) in relation to the presence of receptor mRNA. Infection of the liver occurred only when the liver was exposed to virus 4 h after partial hepatectomy. This time course of infection paralleled expression of the gene for the Ecor, which was rapidly induced between 2 and 6 h during liver regeneration. However, expression of the dormant receptor gene in quiescent liver cells can be induced by insulin, dexamethasone, and arginine, indicating that cell division is not required for expression of the receptor gene in liver cells. A diet high in carbohydrate (low in protein) significantly increased the concentration of receptor mRNA in liver cells, indicating that hormones play a role in the regulation of expression of this gene in vivo. We conclude that the gene for the viral receptor is expressed in the regenerating and quiescent liver when the urea cycle enzymes are down regulated. The infection of the regenerating rat liver by ecotropic retroviruses at the time point of expression of the receptor gene supports the requirement of expression of this transporter for infection.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton L. M., Kim J. W., Tseng L., Cunningham J. M. Envelope-binding domain in the cationic amino acid transporter determines the host range of ecotropic murine retroviruses. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2091–2096. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2091-2096.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albritton L. M., Tseng L., Scadden D., Cunningham J. M. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale E. G., Chrapkiewicz N. B., Scoble H. A., Metz R. J., Quick D. P., Noble R. L., Donelson J. E., Biemann K., Granner D. K. Rat hepatic cytosolic phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP). Structures of the protein, messenger RNA, and gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10748–10760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beale E. G., Schaefer I. M., Li Q. A. Culture at high density increases phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase messenger RNA in H4IIEC3 hepatoma cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 May;5(5):661–669. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-5-661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brebnor L. D., Balinsky J. B. Changes in activities of urea cycle enzymes in early stages of liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats. Life Sci. 1983 Mar 21;32(12):1391–1400. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90815-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruneau C., Hubert P., Waksman A., Beck J. P., Staedel-Flaig C. Modifications of cellular lipids induce insulin resistance in cultured hepatoma cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 May 18;928(3):297–304. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucher M. L., Swaffield M. N. Regulation of hepatic regeneration in rats by synergistic action of insulin and glucagon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1157–1160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cepko C. L., Roberts B. E., Mulligan R. C. Construction and applications of a highly transmissible murine retrovirus shuttle vector. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90440-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapp D. W., Dumenco L. L., Hatzoglou M., Gerson S. L. Fetal liver hematopoietic stem cells as a target for in utero retroviral gene transfer. Blood. 1991 Aug 15;78(4):1132–1139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs E. I., Albritton L. M., Kim J. W., Cunningham J. M. Identification of a low affinity, high capacity transporter of cationic amino acids in mouse liver. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 5;268(10):7538–7544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Closs E. I., Borel Rinkes I. H., Bader A., Yarmush M. L., Cunningham J. M. Retroviral infection and expression of cationic amino acid transporters in rodent hepatocytes. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2097–2102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2097-2102.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compere S. J., Baldacci P., Sharpe A. H., Thompson T., Land H., Jaenisch R. The ras and myc oncogenes cooperate in tumor induction in many tissues when introduced into midgestation mouse embryos by retroviral vectors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2224–2228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of concanavalin A and wheat germ agglutinin with the insulin receptor of fat cells and liver. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 25;248(10):3528–3534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. The gene family encoding the mouse ribosomal protein L32 contains a uniquely expressed intron-containing gene and an unmutated processed gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrikant J. I. The kinetics of cellular proliferation in regenerating liver. J Cell Biol. 1968 Mar;36(3):551–565. doi: 10.1083/jcb.36.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fausto N., Brandt J. T., Kesner L. Possible interactions between the urea cycle and synthesis of pyrimidines and polyamines in regenerating liver. Cancer Res. 1975 Feb;35(2):397–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris G. M., Clark J. B. Early changes in plasma and hepatic free amino acids in partially hepatectomised rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jun 26;273(1):73–79. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(72)90192-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry N., Duplessis O., Houssin D., Danos O., Heard J. M. Retroviral-mediated gene transfer into hepatocytes in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8377–8381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd J. C., Jr, Fajans S. S., Conn J. W., Knopf R. F., Rull J. Stimulation of insulin secretion by amino acids. J Clin Invest. 1966 Sep;45(9):1487–1502. doi: 10.1172/JCI105456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRISHAM J. W. A morphologic study of deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis and cell proliferation in regenerating rat liver; autoradiography with thymidine-H3. Cancer Res. 1962 Aug;22:842–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grompe M., Jones S. N., Loulseged H., Caskey C. T. Retroviral-mediated gene transfer of human ornithine transcarbamylase into primary hepatocytes of spf and spf-ash mice. Hum Gene Ther. 1992 Feb;3(1):35–44. doi: 10.1089/hum.1992.3.1-35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harel J., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Cell cycle dependence of synthesis of unintegrated viral DNA in mouse cells newly infected with murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):202–207. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzoglou M., Bosch F., Park E. A., Hanson R. W. Hormonal control of interacting promoters introduced into cells by retroviruses. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8416–8425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzoglou M., Lamers W., Bosch F., Wynshaw-Boris A., Clapp D. W., Hanson R. W. Hepatic gene transfer in animals using retroviruses containing the promoter from the gene for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17285–17293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzoglou M., Park E., Wynshaw-Boris A., Kaung H. L., Hanson R. W. Hormonal regulation of chimeric genes containing the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase promoter regulatory region in hepatoma cells infected by murine retroviruses. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17798–17808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R. Retroviruses and embryogenesis: microinjection of Moloney leukemia virus into midgestation mouse embryos. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90399-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaleko M., Garcia J. V., Miller A. D. Persistent gene expression after retroviral gene transfer into liver cells in vivo. Hum Gene Ther. 1991 Spring;2(1):27–32. doi: 10.1089/hum.1991.2.1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay M. A., Li Q., Liu T. J., Leland F., Toman C., Finegold M., Woo S. L. Hepatic gene therapy: persistent expression of human alpha 1-antitrypsin in mice after direct gene delivery in vivo. Hum Gene Ther. 1992 Dec;3(6):641–647. doi: 10.1089/hum.1992.3.6-641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. W., Closs E. I., Albritton L. M., Cunningham J. M. Transport of cationic amino acids by the mouse ecotropic retrovirus receptor. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):725–728. doi: 10.1038/352725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. R., Mogg A. E., Burke J. F., Caskey C. T. Histochemical staining of clonal mammalian cell lines expressing E. coli beta galactosidase indicates heterogeneous expression of the bacterial gene. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 May;13(3):253–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01535207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod C. L., Finley K., Kakuda D., Kozak C. A., Wilkinson M. F. Activated T cells express a novel gene on chromosome 8 that is closely related to the murine ecotropic retroviral receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3663–3674. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalopoulos G. K. Liver regeneration: molecular mechanisms of growth control. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):176–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. G., Adam M. A., Miller A. D. Gene transfer by retrovirus vectors occurs only in cells that are actively replicating at the time of infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4239–4242. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohn K. L., Laz T. M., Melby A. E., Taub R. Immediate-early gene expression differs between regenerating liver, insulin-stimulated H-35 cells, and mitogen-stimulated Balb/c 3T3 cells. Liver-specific induction patterns of gene 33, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, and the jun, fos, and egr families. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21914–21921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moorman A. F., de Boer P. A., Charles R., Lamers W. H. Diet- and hormone-induced reversal of the carbamoylphosphate synthetase mRNA gradient in the rat liver lobulus. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80494-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris S. M., Jr Regulation of enzymes of urea and arginine synthesis. Annu Rev Nutr. 1992;12:81–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.12.070192.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C. The basic science of gene therapy. Science. 1993 May 14;260(5110):926–932. doi: 10.1126/science.8493530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabes H. M., Wirsching R., Tuczek H. V., Iseler G. Analysis of cell cycle compartments of hepatocytes after partial hepatecomy. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1976 Nov;9(6):517–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1976.tb01301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmons B., Günzburg W. H. Targeting of retroviral vectors for gene therapy. Hum Gene Ther. 1993 Apr;4(2):129–141. doi: 10.1089/hum.1993.4.2-129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G., Schmid W., Strange C. M., Röwekamp W., Schütz G. Isolation of cDNA clones coding for rat tyrosine aminotransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7205–7208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz W. A., Gebhardt R., Mecke D. Dexamethasone restores hormonal inducibility of ornithine decarboxylase in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;146(3):549–553. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08686.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springett G. M., Moen R. C., Anderson S., Blaese R. M., Anderson W. F. Infection efficiency of T lymphocytes with amphotropic retroviral vectors is cell cycle dependent. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3865–3869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3865-3869.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuhlmann H., Cone R., Mulligan R. C., Jaenisch R. Introduction of a selectable gene into different animal tissue by a retrovirus recombinant vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7151–7155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Dechant E., Kavanaugh M., North R. A., Kabat D. Effects of ecotropic murine retroviruses on the dual-function cell surface receptor/basic amino acid transporter. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23617–23624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Kavanaugh M. P., North R. A., Kabat D. Cell-surface receptor for ecotropic murine retroviruses is a basic amino-acid transporter. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):729–731. doi: 10.1038/352729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H., Paul R., Burgeson R. E., Keene D. R., Kabat D. Plasma membrane receptors for ecotropic murine retroviruses require a limiting accessory factor. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6468–6477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6468-6477.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Christensen H. N. Cationic amino acid transport into cultured animal cells. II. Transport system barely perceptible in ordinary hepatocytes, but active in hepatoma cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4450–4457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. A., Eiden M. V. Viral and cellular factors governing hamster cell infection by murine and gibbon ape leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5975–5982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5975-5982.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Yoshimoto E., Meruelo D. Enhanced gene expression of the murine ecotropic retroviral receptor and its human homolog in proliferating cells. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4377–4381. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4377-4381.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Yoshimoto E., Meruelo D. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel human gene homologous to the murine ecotropic retroviral receptor. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):10–17. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90748-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot C. J., van Zonneveld A. J., Mooren P. G., Zonneveld D., van den Dool A., van den Bogaert A. J., Lamers W. H., Moorman A. F., Charles R. Regulation of mRNA levels of rat liver carbamoylphosphate synthetase by glucocorticosteroids and cyclic AMP as estimated with a specific cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 14;124(3):882–888. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]