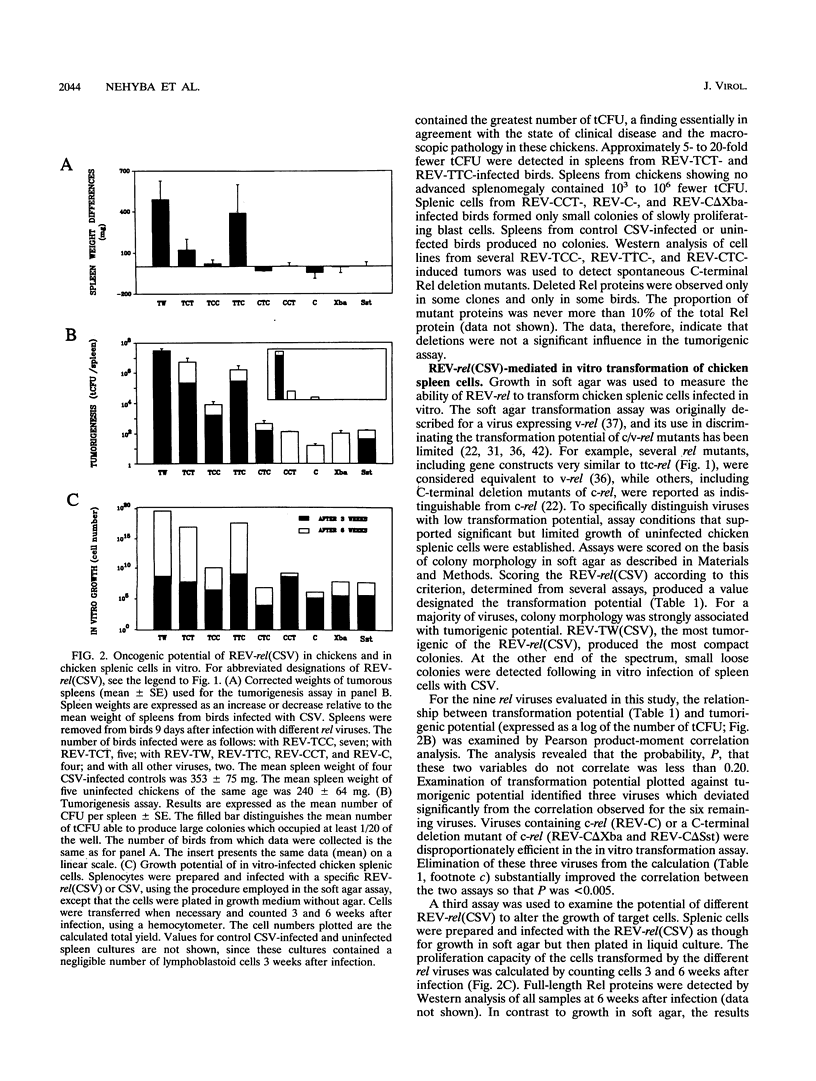
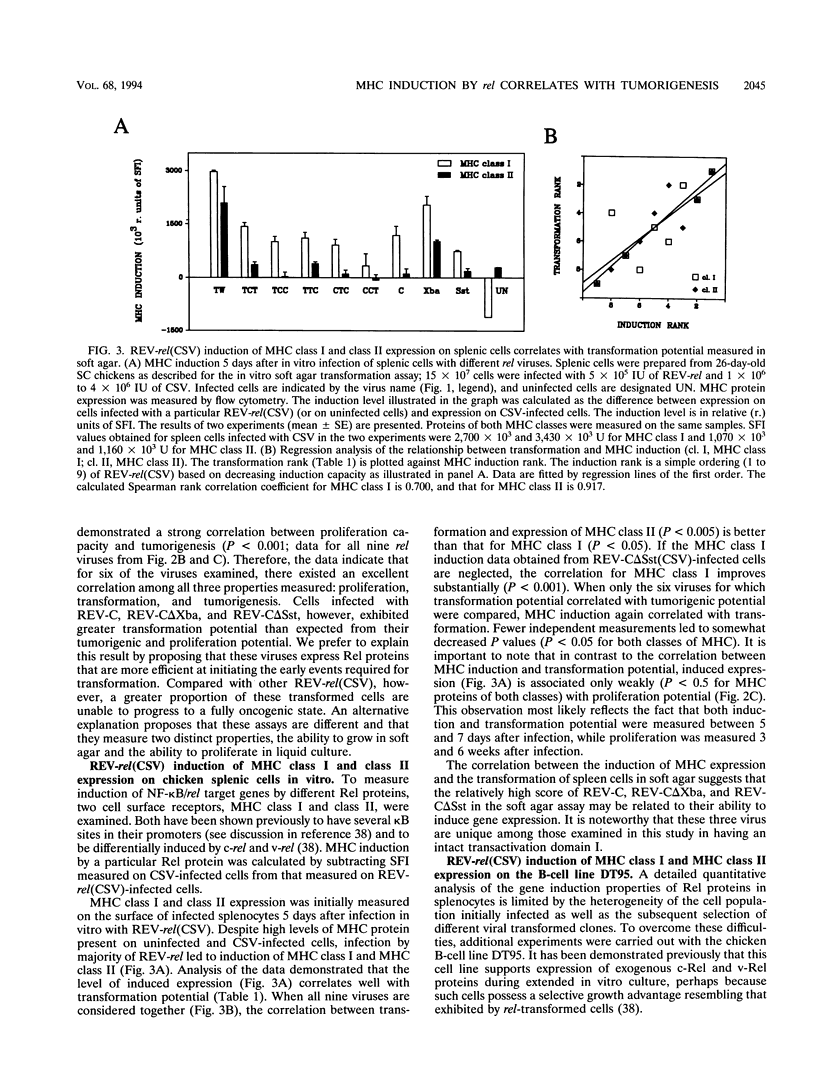
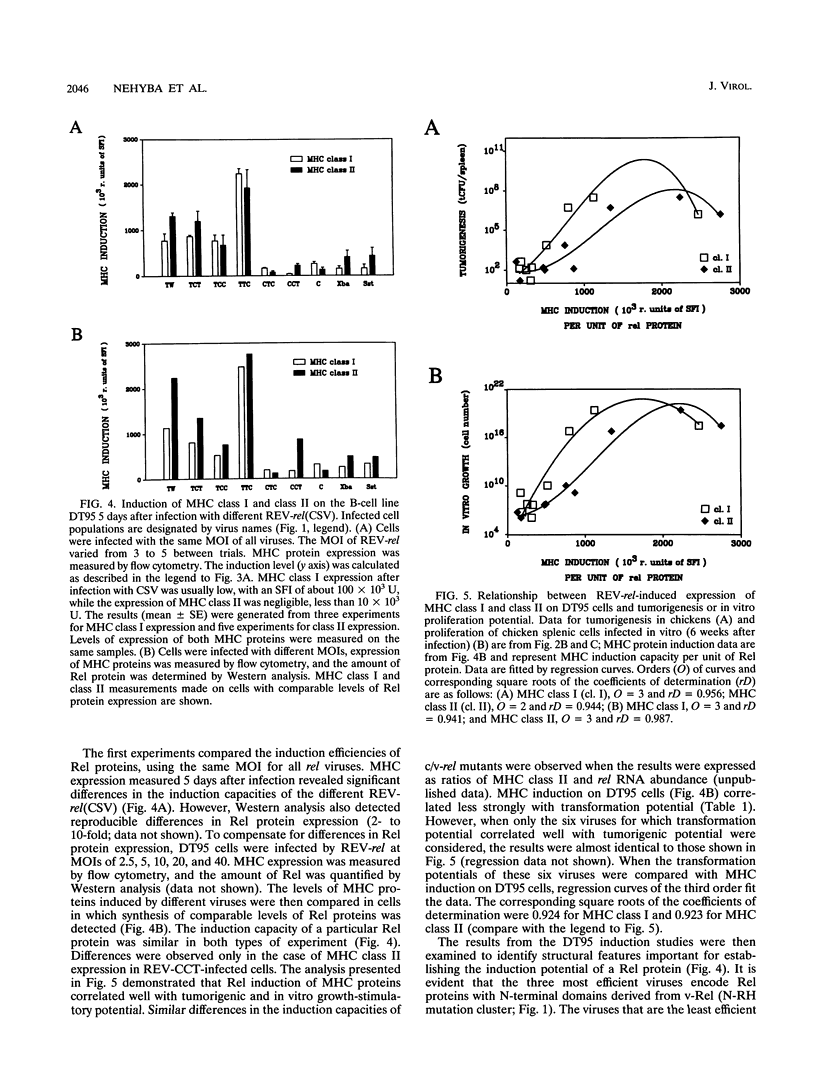
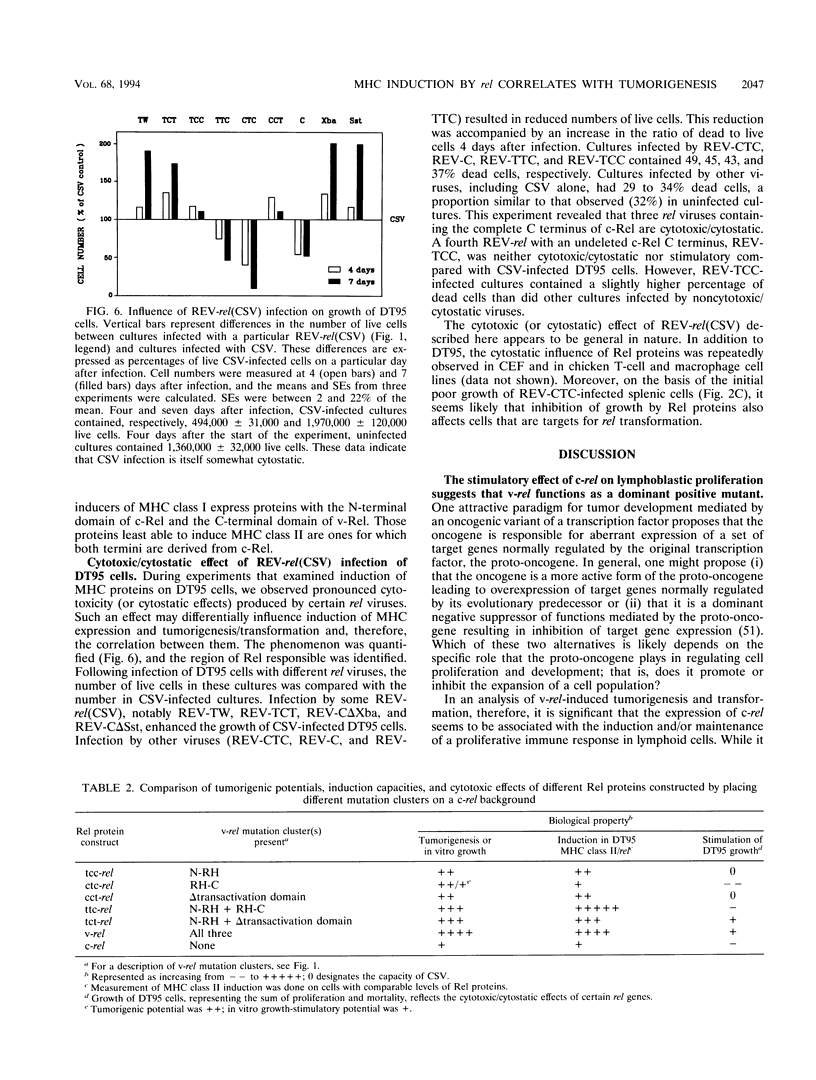
Abstract
v-rel is a viral oncogene that evolved from turkey c-rel, an NF-kappa B-related transcription factor. Numerous structural alterations record the evolutionary selection of v-rel and distinguish it from c-rel. To evaluate the biological significance of these alterations, we constructed a set of five c/v-rel hybrids in which three mutation clusters (c-Rel amino acids 1 to 97,222 to 302, and 328 to 598) were differentially distributed. These constructs, in addition to parental v-rel and c-rel and two C-terminal deletion mutants of c-rel, were expressed from a retroviral vector. An analysis of cells infected with each of the nine viruses revealed that mutations in all three domains contributed to the ability of v-rel to induce two endogenous c-rel target genes, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and class II, in the B-cell line DT95 as well as MHC class II in normal splenocytes. The analysis revealed a strong nonlinear correlation between the ability of a Rel protein to induce expression of MHC proteins and its capacity to produce splenic tumors and establish in vitro transformation. This correlation is consistent with the hypothesis that v-rel transforms by constitutively altering expression of genes regulated by c-rel and in this way simulates events associated with immune response-linked proliferation of cells of hematopoietic origin. Further, the 16 carboxy-terminal amino acids of c-Rel were identified as a domain responsible for producing a cytotoxic and/or cytostatic effect in DT95. Because this effect is likely to differentially influence induction of MHC expression and tumorigenesis/transformation, it may represent one factor that contributes to the nonlinearity of their correlation.
Full text
PDF







Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baba T. W., Giroir B. P., Humphries E. H. Cell lines derived from avian lymphomas exhibit two distinct phenotypes. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):139–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90312-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A. The inducible transcription activator NF-kappa B: regulation by distinct protein subunits. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Apr 16;1072(1):63–80. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Bogerd H., Doerre S., Stein B., Greene W. C. The 65-kDa subunit of human NF-kappa B functions as a potent transcriptional activator and a target for v-Rel-mediated repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1875–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Walker W. H., Doerre S., Sista P., Molitor J. A., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene encodes a kappa B enhancer binding protein that inhibits NF-kappa B function. Cell. 1990 Nov 16;63(4):803–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90146-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth C. F., Ewert D. L., Olson W. C., Humphries E. H. Reticuloendotheliosis virus REV-T(REV-A)-induced neoplasia: development of tumors within the T-lymphoid and myeloid lineages. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6054–6062. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6054-6062.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth C. F., Humphries E. H. A nonimmunosuppressive helper virus allows high efficiency induction of B cell lymphomas by reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):89–108. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.89. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barth C. F., Humphries E. H. Expression of v-rel induces mature B-cell lines that reflect the diversity of avian immunoglobulin heavy- and light-chain rearrangements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5358–5368. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Ruben S. M., Scheinman R. I., Haskill S., Rosen C. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr I kappa B interacts with the nuclear localization sequences of the subunits of NF-kappa B: a mechanism for cytoplasmic retention. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1899–1913. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat G. V., Temin H. M. Mutational analysis of v-rel, the oncogene of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T. Oncogene. 1990 May;5(5):625–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehmelt G., Walker A., Kabrun N., Mellitzer G., Beug H., Zenke M., Enrietto P. J. Hormone-regulated v-rel estrogen receptor fusion protein: reversible induction of cell transformation and cellular gene expression. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4641–4652. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05566.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bose H. R., Jr The Rel family: models for transcriptional regulation and oncogenic transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Sep 14;1114(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(92)90002-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Franzoso G., Azarenko V., Park S., Kanno T., Brown K., Siebenlist U. The oncoprotein Bcl-3 directly transactivates through kappa B motifs via association with DNA-binding p50B homodimers. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90401-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bressler P., Brown K., Timmer W., Bours V., Siebenlist U., Fauci A. S. Mutational analysis of the p50 subunit of NF-kappa B and inhibition of NF-kappa B activity by trans-dominant p50 mutants. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):288–293. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.288-293.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell E., Mathieson B., Young H. A., Keller J., Ihle J. N., Rice N. R. Detection of c-rel-related transcripts in mouse hematopoietic tissues, fractionated lymphocyte populations, and cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1304–1309. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brownell E., Mittereder N., Rice N. R. A human rel proto-oncogene cDNA containing an Alu fragment as a potential coding exon. Oncogene. 1989 Jul;4(7):935–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P., Morley K. L., Hoekstra M. F., Hunter T., Verma I. M. The mouse c-rel protein has an N-terminal regulatory domain and a C-terminal transcriptional transactivation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5473–5485. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capobianco A. J., Simmons D. L., Gilmore T. D. Cloning and expression of a chicken c-rel cDNA: unlike p59v-rel, p68c-rel is a cytoplasmic protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):257–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Mak T. W., O'Rear J. J., Temin H. M. Characterization of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T DNA and isolation of a novel variant of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T by molecular cloning. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):800–811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.800-811.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Temin H. M. Substitution of 5' helper virus sequences into non-rel portion of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T suppresses transformation of chicken spleen cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90410-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crone M., Simonsen M., Skjødt K., Linnet K., Olsson L. Mouse monoclonal antibodies to class I and class II antigens of the chicken MHC. Evidence for at least two class I products of the B complex. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(2):181–187. doi: 10.1007/BF00364870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N., Bargmann W., Lim M. Y., Bose H., Jr Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus-transformed lymphoid cells contain multiple pp59v-rel complexes. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):584–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.584-591.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diehl J. A., McKinsey T. A., Hannink M. Differential pp40I kappa B-beta inhibition of DNA binding by rel proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1769–1778. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerre S., Sista P., Sun S. C., Ballard D. W., Greene W. C. The c-rel protooncogene product represses NF-kappa B p65-mediated transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of type 1 human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1023–1027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garry R. F., Bose H. R., Jr Secretion of a virus-regulated factor by clonal variants of reticuloendotheliosis virus-transformed hematopoietic cells. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90167-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garson K., Percival H., Kang C. Y. The N-terminal env-derived amino acids of v-rel are required for full transforming activity. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90464-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P., Tan T. H., Rice N. R., Sica A., Young H. A. The interleukin 2 CD28-responsive complex contains at least three members of the NF kappa B family: c-Rel, p50, and p65. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1696–1700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Gifford A. M., Riviere L. R., Tempst P., Nolan G. P., Baltimore D. Cloning of the p50 DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B: homology to rel and dorsal. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1019–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90276-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D. Role of rel family genes in normal and malignant lymphoid cell growth. Cancer Surv. 1992;15:69–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T. D., Temin H. M. v-rel oncoproteins in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm transform chicken spleen cells. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):703–714. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.703-714.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grilli M., Chiu J. J., Lenardo M. J. NF-kappa B and Rel: participants in a multiform transcriptional regulatory system. Int Rev Cytol. 1993;143:1–62. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61873-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumont R. J., Gerondakis S. Structure of a mammalian c-rel protein deduced from the nucleotide sequence of murine cDNA clones. Oncogene Res. 1989;4(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gélinas C., Temin H. M. The v-rel oncogene encodes a cell-specific transcriptional activator of certain promoters. Oncogene. 1988 Oct;3(4):349–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Temin H. M. Transactivation of gene expression by nuclear and cytoplasmic rel proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4323–4336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoelzer J. D., Franklin R. B., Bose H. R., Jr Transformation by reticuloendotheliosis virus: development of a focus assay and isolation of a nontransforming virus. Virology. 1979 Feb;93(1):20–30. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrdlicková R., Nehyba J., Humphries E. H. In vivo evolution of c-rel oncogenic potential. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2371–2382. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2371-2382.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hrdlicková R., Nehyba J., Humphries E. H. v-rel induces expression of three avian immunoregulatory surface receptors more efficiently than c-rel. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):308–319. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.308-319.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Kerr L. D., Ransone L. J., Bengal E., Hunter T., Verma I. M. c-rel activates but v-rel suppresses transcription from kappa B sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3715–3719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamens J., Richardson P., Mosialos G., Brent R., Gilmore T. Oncogenic transformation by vrel requires an amino-terminal activation domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2840–2847. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao K. R., Hopwood N. D. Expression of a mRNA related to c-rel and dorsal in early Xenopus laevis embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2697–2701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr L. D., Inoue J., Davis N., Link E., Baeuerle P. A., Bose H. R., Jr, Verma I. M. The rel-associated pp40 protein prevents DNA binding of Rel and NF-kappa B: relationship with I kappa B beta and regulation by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1464–1476. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar S., Rabson A. B., Gélinas C. The RxxRxRxxC motif conserved in all Rel/kappa B proteins is essential for the DNA-binding activity and redox regulation of the v-Rel oncoprotein. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;12(7):3094–3106. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.7.3094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewin B. Oncogenic conversion by regulatory changes in transcription factors. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90640-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logeat F., Israël N., Ten R., Blank V., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P., Israël A. Inhibition of transcription factors belonging to the rel/NF-kappa B family by a transdominant negative mutant. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1827–1832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucibello F. C., Müller R. Transcription factor encoding oncogenes. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol. 1992;119:225–257. doi: 10.1007/3540551921_8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell P. C., Kumar S., Rabson A. B., Gélinas C. Transcriptional activity of rel family proteins. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):163–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore B. E., Bose H. R., Jr Expression of the c-rel and c-myc proto-oncogenes in avian tissues. Oncogene. 1989 Jul;4(7):845–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison L. E., Boehmelt G., Enrietto P. J. Mutations in the rel-homology domain alter the biochemical properties of v-rel and render it transformation defective in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Oncogene. 1992 Jun;7(6):1137–1147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosialos G., Gilmore T. D. v-Rel and c-Rel are differentially affected by mutations at a consensus protein kinase recognition sequence. Oncogene. 1993 Mar;8(3):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosialos G., Hamer P., Capobianco A. J., Laursen R. A., Gilmore T. D. A protein kinase-A recognition sequence is structurally linked to transformation by p59v-rel and cytoplasmic retention of p68c-rel. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):5867–5877. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.5867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama K., Shimizu H., Mitomo K., Watanabe T., Okamoto S., Yamamoto K. A lymphoid cell-specific nuclear factor containing c-Rel-like proteins preferentially interacts with interleukin-6 kappa B-related motifs whose activities are repressed in lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1736–1746. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson P. M., Gilmore T. D. vRel is an inactive member of the Rel family of transcriptional activating proteins. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3122–3130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3122-3130.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar S., Gilmore T. D. Transformation by the vRel oncoprotein requires sequences carboxy-terminal to the Rel homology domain. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2245–2252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Baeuerle P. A. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3805–3817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. C., Witte O. N. A recombinant murine retrovirus expressing v-rel is cytopathic. Virology. 1988 Jul;165(1):182–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90671-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sica A., Tan T. H., Rice N., Kretzschmar M., Ghosh P., Young H. A. The c-rel protooncogene product c-Rel but not NF-kappa B binds to the intronic region of the human interferon-gamma gene at a site related to an interferon-stimulable response element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1740–1744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. M., Rice N. R., Hiebsch R. R., Bose H. R., Jr, Gilden R. V. Nucleotide sequence of v-rel: the oncogene of reticuloendotheliosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6229–6233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward R. Dorsal, an embryonic polarity gene in Drosophila, is homologous to the vertebrate proto-oncogene, c-rel. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):692–694. doi: 10.1126/science.3118464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Bissell M. J. Quantitative immunocytochemical assay for infectious avian retroviruses. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2481–2485. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sylla B. S., Temin H. M. Activation of oncogenicity of the c-rel proto-oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4709–4716. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Huang G. P., Sica A., Ghosh P., Young H. A., Longo D. L., Rice N. R. Kappa B site-dependent activation of the interleukin-2 receptor alpha-chain gene promoter by human c-Rel. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):4067–4075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.4067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Dobrzanski P., Mohn K. L., Cressman D. E., Hsu J. C., Bravo R., Taub R. Rapid induction in regenerating liver of RL/IF-1 (an I kappa B that inhibits NF-kappa B, RelB-p50, and c-Rel-p50) and PHF, a novel kappa B site-binding complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;12(6):2898–2908. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.6.2898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turnbull P. C., Snoeyenbos G. H. Experimental salmonellosis in the chicken. 2. Fate of a temperature-sensitive filamentous mutant. Avian Dis. 1974 Apr-Jun;18(2):178–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner A. J., Small M. B., Hay N. Myc-mediated apoptosis is blocked by ectopic expression of Bcl-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2432–2440. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. H., Stein B., Ganchi P. A., Hoffman J. A., Kaufman P. A., Ballard D. W., Hannink M., Greene W. C. The v-rel oncogene: insights into the mechanism of transcriptional activation, repression, and transformation. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5018–5029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5018-5029.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Eggleton K., Temin H. M. Nucleic acid sequences of the oncogene v-rel in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T and its cellular homolog, the proto-oncogene c-rel. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):172–182. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.172-182.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X., Prorock C., Ishikawa H., Maldonado E., Ito Y., Gélinas C. Functional interaction of the v-Rel and c-Rel oncoproteins with the TATA-binding protein and association with transcription factor IIB. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6733–6741. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


