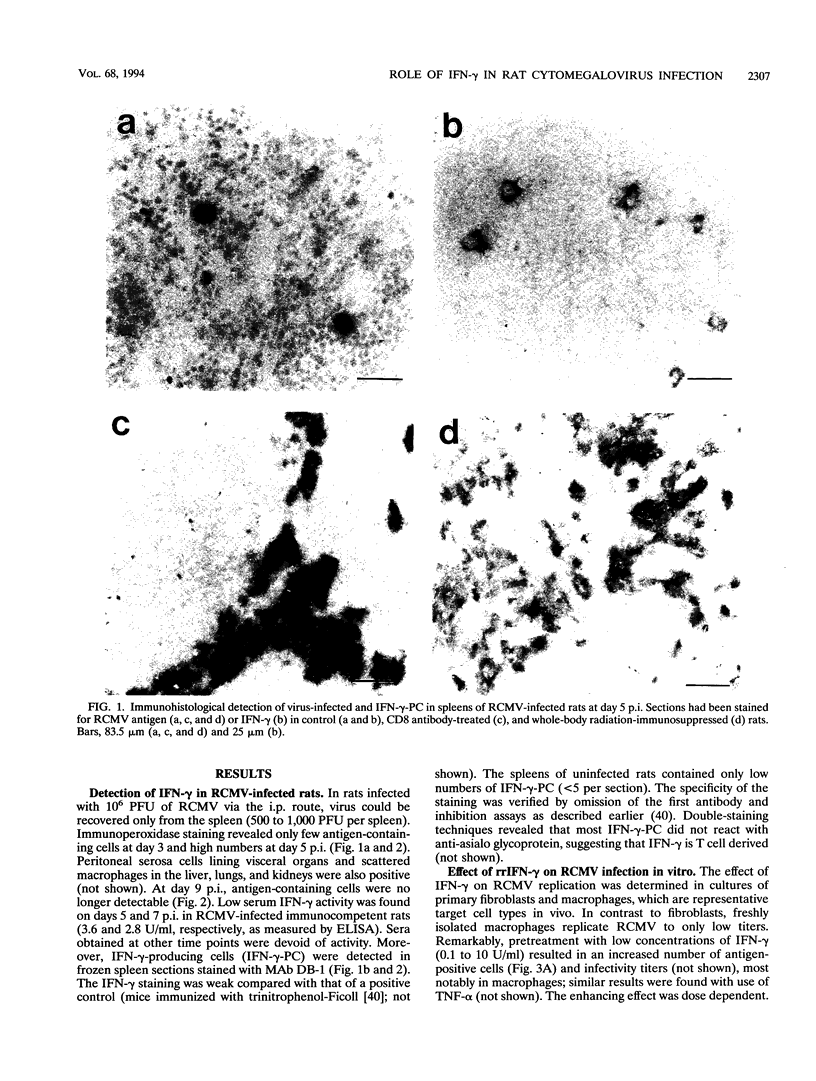
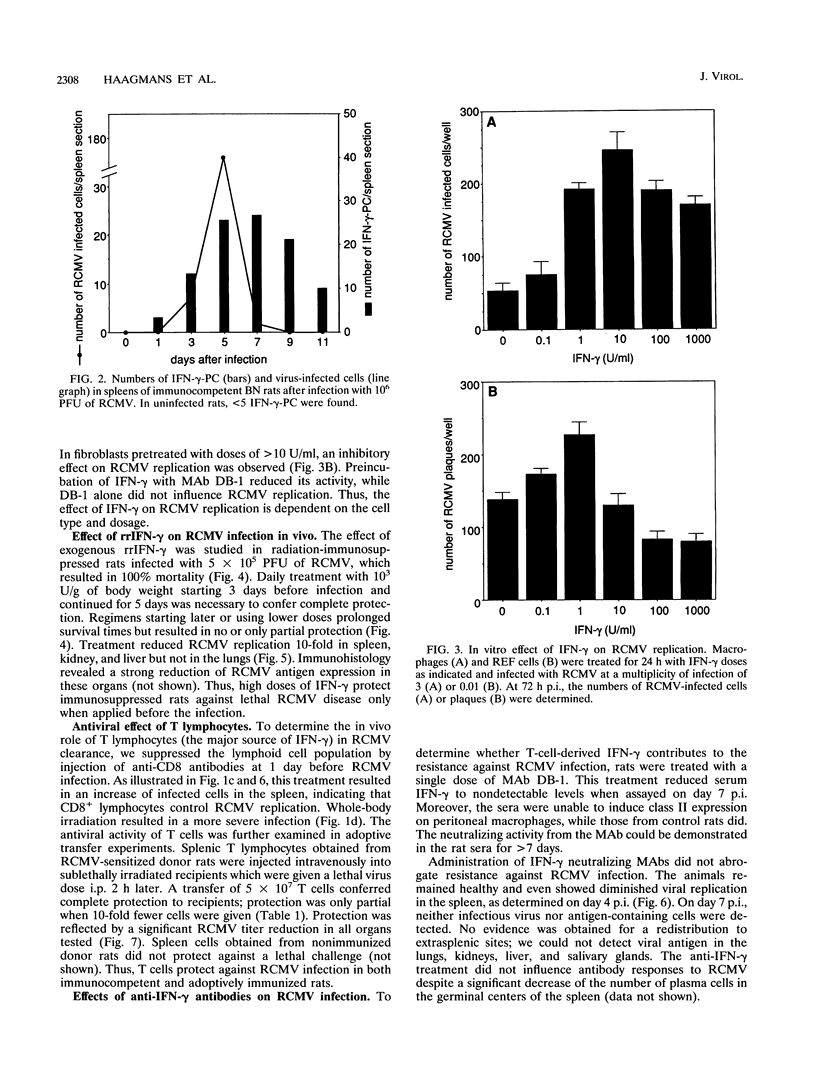
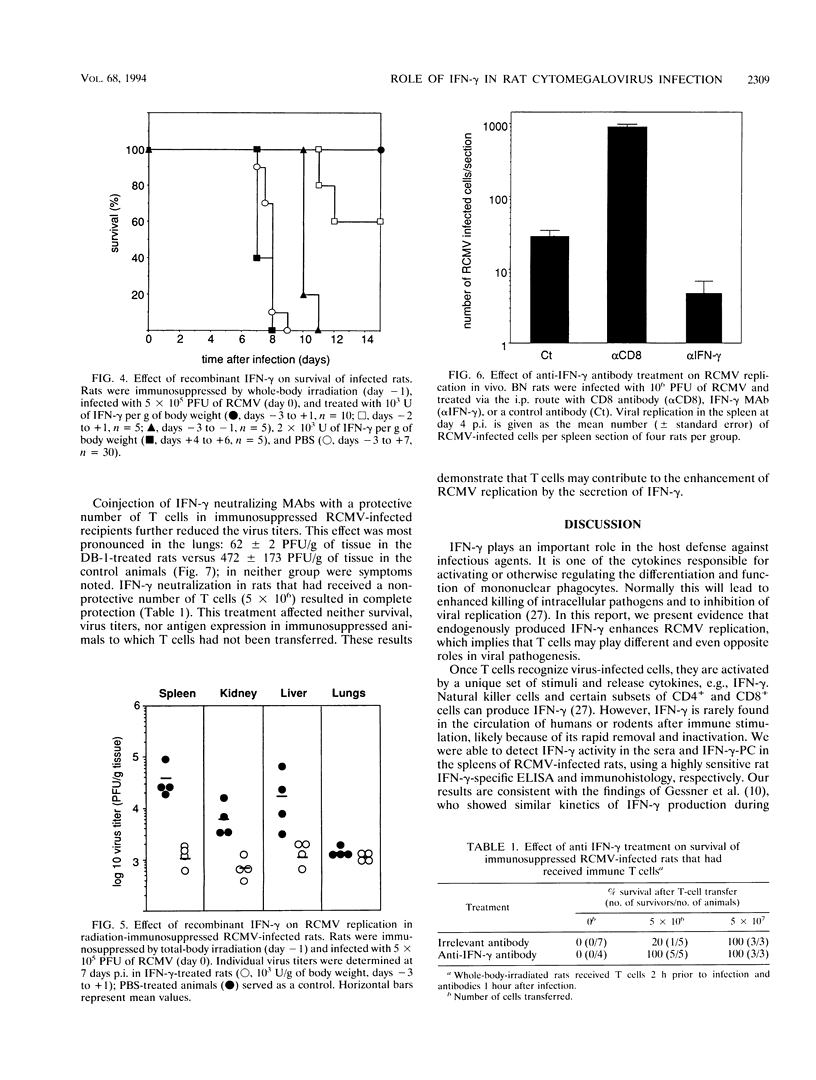
Abstract
The role of gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) in the resolution of rat cytomegalovirus (RCMV) infection was investigated. In the spleen, IFN-gamma-producing cells reached maximum numbers on day 7 after infection. Prophylactic treatment with high doses of recombinant rat IFN-gamma exerted antiviral activity in fibroblasts and protected immunosuppressed rats against a lethal RCMV challenge. Remarkably, in immunocompetent rats, neutralization of endogenous IFN-gamma activity significantly reduced the numbers of RCMV antigen-expressing cells in the spleen, the predominant site of viral replication. Moreover, protection of radiation-immunosuppressed infected rats by transferred immune T cells was enhanced by coinjection of IFN-gamma neutralizing antibodies. The observations were paralleled by in vitro findings: low concentrations of IFN-gamma enhanced viral replication in both macrophages and fibroblasts. These data suggest that IFN-gamma can play different and even opposite roles in the regulation of RCMV replication in vivo; T lymphocytes may contribute to the progression of RCMV infection by secreting IFN-gamma.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alcami J., Paya C. V., Virelizier J. L., Michelson S. Antagonistic modulation of human cytomegalovirus replication by transforming growth factor beta and basic fibroblastic growth factor. J Gen Virol. 1993 Feb;74(Pt 2):269–274. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-2-269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belosevic M., Finbloom D. S., Van Der Meide P. H., Slayter M. V., Nacy C. A. Administration of monoclonal anti-IFN-gamma antibodies in vivo abrogates natural resistance of C3H/HeN mice to infection with Leishmania major. J Immunol. 1989 Jul 1;143(1):266–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruggeman C. A., Meijer H., Dormans P. H., Debie W. M., Grauls G. E., van Boven C. P. Isolation of a cytomegalovirus-like agent from wild rats. Arch Virol. 1982;73(3-4):231–241. doi: 10.1007/BF01318077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton D. K., Pitts-Meek S., Keshav S., Figari I. S., Bradley A., Stewart T. A. Multiple defects of immune cell function in mice with disrupted interferon-gamma genes. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1739–1742. doi: 10.1126/science.8456300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fennie E. H., Lie Y. S., Low M. A., Gribling P., Anderson K. P. Reduced mortality in murine cytomegalovirus infected mice following prophylactic murine interferon-gamma treatment. Antiviral Res. 1988 Nov;10(1-3):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0166-3542(88)90012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong T. A., Mosmann T. R. Alloreactive murine CD8+ T cell clones secrete the Th1 pattern of cytokines. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1744–1752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganser A., Brücher W., Brodt H. R., Busch W., Brandhorst I., Helm E. B., Hoelzer D. Treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma with recombinant gamma-interferon. Onkologie. 1986 Jun;9(3):163–166. doi: 10.1159/000215998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessner A., Drjupin R., Löhler J., Lother H., Lehmann-Grube F. IFN-gamma production in tissues of mice during acute infection with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3160–3165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haagmans B. L., Stals F. S., van der Meide P. H., Bruggeman C. A., Horzinek M. C., Schijns V. E. Tumor necrosis factor alpha promotes replication and pathogenicity of rat cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2297–2304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2297-2304.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallahan D. E., Spriggs D. R., Beckett M. A., Kufe D. W., Weichselbaum R. R. Increased tumor necrosis factor alpha mRNA after cellular exposure to ionizing radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10104–10107. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heagy W., Groopman J., Schindler J., Finberg R. Use of IFN-gamma in patients with AIDS. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(6):584–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Hendriks W., Althage A., Hemmi S., Bluethmann H., Kamijo R., Vilcek J., Zinkernagel R. M., Aguet M. Immune response in mice that lack the interferon-gamma receptor. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1742–1745. doi: 10.1126/science.8456301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibanez C. E., Schrier R., Ghazal P., Wiley C., Nelson J. A. Human cytomegalovirus productively infects primary differentiated macrophages. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6581–6588. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6581-6588.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob C. O., van der Meide P. H., McDevitt H. O. In vivo treatment of (NZB X NZW)F1 lupus-like nephritis with monoclonal antibody to gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1987 Sep 1;166(3):798–803. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.3.798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klavinskis L. S., Geckeler R., Oldstone M. B. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte control of acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection: interferon gamma, but not tumour necrosis factor alpha, displays antiviral activity in vivo. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3317–3325. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., O'Brien W. A., Zhao J. Q., Golde D. W., Gasson J. C., Chen I. S. Cytokines alter production of HIV-1 from primary mononuclear phagocytes. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1673–1675. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kündig T. M., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. T cell-dependent IFN-gamma exerts an antiviral effect in the central nervous system but not in peripheral solid organs. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2316–2321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F., Assmann U., Löliger C., Moskophidis D., Löhler J. Mechanism of recovery from acute virus infection. I. Role of T lymphocytes in the clearance of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus from spleens of mice. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):608–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibson H. J., Gefter M., Zlotnik A., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Role of gamma-interferon in antibody-producing responses. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):799–801. doi: 10.1038/309799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist T. P., Eppler M., Zinkernagel R. M. Enhanced virus replication and inhibition of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus disease in anti-gamma interferon-treated mice. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2813–2819. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2813-2819.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Janeway C. A., Jr Interferon gamma plays a critical role in induced cell death of effector T cell: a possible third mechanism of self-tolerance. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1735–1739. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucin P., Pavić I., Polić B., Jonjić S., Koszinowski U. H. Gamma interferon-dependent clearance of cytomegalovirus infection in salivary glands. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1977–1984. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1977-1984.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. G., Lin Y. L., Askonas B. A. Immune interferon release when a cloned cytotoxic T-cell line meets its correct influenza-infected target cell. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):150–152. doi: 10.1038/295150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neta R., Oppenheim J. J., Schreiber R. D., Chizzonite R., Ledney G. D., MacVittie T. J. Role of cytokines (interleukin 1, tumor necrosis factor, and transforming growth factor beta) in natural and lipopolysaccharide-enhanced radioresistance. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1177–1182. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson T., Bakhiet M., Edlund C., Höjeberg B., Van der Meide P. H., Kristensson K. Bidirectional activating signals between Trypanosoma brucei and CD8+ T cells: a trypanosome-released factor triggers interferon-gamma production that stimulates parasite growth. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2447–2454. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinaldo C. R., Jr, Carney W. P., Richter B. S., Black P. H., Hirsch M. S. Mechanisms of immunosuppression in cytomegaloviral mononucleosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Apr;141(4):488–495. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Norley S., Martin S. Antiviral cytotoxic T lymphocyte induction and vaccination. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Jan-Feb;10(1):16–33. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schijns V. E., Borman T. H., Schellekens H., Horzinek M. C. Antiviral activity of recombinant rat interferon gamma in immunologically impaired and immunosuppressed rats. J Gen Virol. 1988 Aug;69(Pt 8):1979–1985. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-8-1979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schijns V. E., Van der Neut R., Haagmans B. L., Bar D. R., Schellekens H., Horzinek M. C. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interferon-gamma and interferon-beta exert antiviral activity in nervous tissue cells. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):809–815. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stals F. S., Bosman F., van Boven C. P., Bruggeman C. A. An animal model for therapeutic intervention studies of CMV infection in the immunocompromised host. Arch Virol. 1990;114(1-2):91–107. doi: 10.1007/BF01311014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton G. J., Jordan C., Hart A., Heard H., Langford M. P., Baron S. Nondetectable levels of interferon gamma is a critical host defense during the first day of herpes simplex virus infection. Microb Pathog. 1987 Sep;3(3):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90094-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiniger B., Falk P., Van der Meide P. H. Interferon-gamma in vivo. Induction and loss of class II MHC antigens and immature myelomonocytic cells in rat organs. Eur J Immunol. 1988 May;18(5):661–669. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulker N., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: inhibition of vesicular stomatitis virus replication in human amnion U cells by cloned human gamma-interferon. I. Effect on early and late stages of the viral multiplication cycle. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4319–4323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wille A., Gessner A., Lother H., Lehmann-Grube F. Mechanism of recovery from acute virus infection. VIII. Treatment of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-infected mice with anti-interferon-gamma monoclonal antibody blocks generation of virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes and virus elimination. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Jul;19(7):1283–1288. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong G. H., Goeddel D. V. Tumour necrosis factors alpha and beta inhibit virus replication and synergize with interferons. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):819–822. doi: 10.1038/323819a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. H., Liu C. C., Joag S., Rafii S., Young J. D. How lymphocytes kill. Annu Rev Med. 1990;41:45–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.41.020190.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Eertwegh A. J., Fasbender M. J., Schellekens M. M., van Oudenaren A., Boersma W. J., Claassen E. In vivo kinetics and characterization of IFN-gamma-producing cells during a thymus-independent immune response. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 15;147(2):439–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Borman A. H., Beljaars H. G., Dubbeld M. A., Botman C. A., Schellekens H. Isolation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies directed to rat interferon-gamma. Lymphokine Res. 1989 Winter;8(4):439–449. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Dubbeld M., Vijverberg K., Kos T., Schellekens H. The purification and characterization of rat gamma interferon by use of two monoclonal antibodies. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jun;67(Pt 6):1059–1071. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-6-1059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]