Abstract
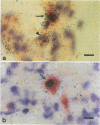
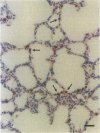
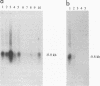
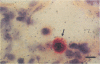
Neonatal mink kits infected with Aleutian mink disease parvovirus (ADV) develop an acute interstitial pneumonia with clinical symptoms and pathological lesions that resemble those seen in preterm human infants with respiratory distress syndrome and in human adults with adult respiratory distress syndrome. We have previously suggested that ADV replicates in the alveolar type II epithelial cells of the lung. By using double in situ hybridization, with the simultaneous use of a probe to detect ADV replication and a probe to demonstrate alveolar type II cells, we now confirm this hypothesis. Furthermore, Northern (RNA) blot hybridization showed that the infection caused a significant decrease of surfactant-associated protein C mRNA produced by the alveolar type II cells. We therefore suggest that the severe clinical symptoms and pathological changes characterized by hyaline membrane formation observed in ADV-infected mink kits are caused by a dysfunction of alveolar surfactant similar to that observed in respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants. However, in the infected mink kits the dysfunction is due to the replication of ADV in the lungs, whereas the dysfunction of surfactant in preterm infants is due to lung immaturity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aasted B. Aleutian disease of mink. Virology and immunology. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand Suppl. 1985;287:1–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S. Acute interstitial pneumonia in mink kits: experimental reproduction of the disease. Vet Pathol. 1986 Sep;23(5):579–588. doi: 10.1177/030098588602300506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Perryman S. Detailed transcription map of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3684–3694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3684-3694.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E. Studies on the sequential development of acute interstitial pneumonia caused by Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):81–86. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.81-86.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Wolfinbarger J. Evidence of restricted viral replication in adult mink infected with Aleutian disease of mink parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1495–1507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1495-1507.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Bloom M. E., Wolfinbarger J., Race R. E. In situ molecular hybridization for detection of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus DNA by using strand-specific probes: identification of target cells for viral replication in cell cultures and in mink kits with virus-induced interstitial pneumonia. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2407–2419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2407-2419.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S., Larsen S., Cohn A., Uttenthal A., Race R. E., Aasted B., Hansen M., Bloom M. E. Passive transfer of antiviral antibodies restricts replication of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus in vivo. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):9–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.9-17.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexandersen S. Pathogenesis of disease caused by Aleutian mink disease parvovirus. APMIS Suppl. 1990;14:1–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashbaugh D. G., Bigelow D. B., Petty T. L., Levine B. E. Acute respiratory distress in adults. Lancet. 1967 Aug 12;2(7511):319–323. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)90168-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachofen M., Weibel E. R. Alterations of the gas exchange apparatus in adult respiratory insufficiency associated with septicemia. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Oct;116(4):589–615. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.116.4.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard P. L. Hormonal regulation of pulmonary surfactant. Endocr Rev. 1989 May;10(2):165–181. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-2-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Race R. E., Wolfinbarger J. B. Analysis of Aleutian disease of mink parvovirus infection using strand-specific hybridization probes. Intervirology. 1987;27(2):102–111. doi: 10.1159/000149727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen J., Storgaard T., Viuff B., Aasted B., Alexandersen S. Comparison of promoter activity in Aleutian mink disease parvovirus, minute virus of mice, and canine parvovirus: possible role of weak promoters in the pathogenesis of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus infection. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):1877–1886. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.1877-1886.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connelly I. H., Hammond G. L., Harding P. G., Possmayer F. Levels of surfactant-associated protein messenger ribonucleic acids in rabbit lung during perinatal development and after hormonal treatment. Endocrinology. 1991 Nov;129(5):2583–2591. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-5-2583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore-Bruno M. A., Wikenheiser K. A., Carter J. E., Clark J. C., Whitsett J. A. Sequence, ontogeny, and cellular localization of murine surfactant protein B mRNA. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jan;262(1 Pt 1):L40–L47. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.1.L40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. M., Avery M. E. Hyaline membrane disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 May;111(5):657–688. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.5.657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floros J., Phelps D. S., deMello D. E., Longmate J., Harding H., Benson B., White T. The utility of postmortem lung for RNA studies; variability and correlation of the expression of surfactant proteins in human lung. Exp Lung Res. 1991 Jan-Feb;17(1):91–104. doi: 10.3109/01902149109063284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory T. J., Longmore W. J., Moxley M. A., Whitsett J. A., Reed C. R., Fowler A. A., 3rd, Hudson L. D., Maunder R. J., Crim C., Hyers T. M. Surfactant chemical composition and biophysical activity in acute respiratory distress syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1991 Dec;88(6):1976–1981. doi: 10.1172/JCI115523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haies D. M., Gil J., Weibel E. R. Morphometric study of rat lung cells. I. Numerical and dimensional characteristics of parenchymal cell population. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1981 May;123(5):533–541. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1981.123.5.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawgood S. Pulmonary surfactant apoproteins: a review of protein and genomic structure. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):L13–L22. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.2.L13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe A. H. Pathogenesis of respiratory failure in the preterm infant. Ann Med. 1991 Dec;23(6):687–691. doi: 10.3109/07853899109148104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobe A., Ikegami M. Surfactant for the treatment of respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Nov;136(5):1256–1275. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.5.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman S. L. Cell proliferation in the mammalian lung. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1980;22:131–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Coalson J. J., Seidenfeld J. J., Anzueto A. R., Smith D. B., Peters J. I. O2- and pneumonia-induced lung injury. II. Properties of pulmonary surfactant. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Jul;67(1):357–365. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.1.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Jones M. B., Minoo P. Regulation of lung cell proliferation by polypeptide growth factors. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):L23–L38. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1989.257.2.L23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen S., Alexandersen S., Lund E., Have P., Hansen M. Acute interstitial pneumonitis caused by Aleutian disease virus in mink kits. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand A. 1984 Sep;92(5):391–393. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1984.tb04419.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liley H. G., White R. T., Warr R. G., Benson B. J., Hawgood S., Ballard P. L. Regulation of messenger RNAs for the hydrophobic surfactant proteins in human lung. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1191–1197. doi: 10.1172/JCI114000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. S., Floros J. Localization of pulmonary surfactant proteins using immunohistochemistry and tissue in situ hybridization. Exp Lung Res. 1991 Nov-Dec;17(6):985–995. doi: 10.3109/01902149109064330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps D. S., Floros J. Localization of surfactant protein synthesis in human lung by in situ hybridization. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1988 Apr;137(4):939–942. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.4.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pison U., Obertacke U., Seeger W., Hawgood S. Surfactant protein A (SP-A) is decreased in acute parenchymal lung injury associated with polytrauma. Eur J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;22(11):712–718. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1992.tb01434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D. Aleutian disease: a persistent parvovirus infection of mink with a maximal but ineffective host humoral immune response. Prog Med Virol. 1986;33:42–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Possmayer F. The role of surfactant-associated proteins. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Oct;142(4):749–752. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.4.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd, Richard S. M. Characterization of the trans-activation-responsive element of the parvovirus H-1 P38 promoter. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2807–2815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2807-2815.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider E. D., Ikegami M., Jobe A. H. Intrapulmonary catabolism of surfactant-saturated phosphatidylcholine in rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990 Nov;69(5):1856–1862. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1990.69.5.1856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rust K., Grosso L., Zhang V., Chang D., Persson A., Longmore W., Cai G. Z., Crouch E. Human surfactant protein D: SP-D contains a C-type lectin carbohydrate recognition domain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Oct;290(1):116–126. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90597-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu H., Fisher J. H., Papst P., Benson B., Lau K., Mason R. J., Voelker D. R. Primary structure of rat pulmonary surfactant protein D. cDNA and deduced amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1853–1857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Bates R. C., Berns K. I., Carter B. J., Kelly D. C., Kurstak E., Tattersall P. Characteristics and taxonomy of Parvoviridae. Intervirology. 1985;23(2):61–73. doi: 10.1159/000149587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. H., Nash G., Brigham K. L., Tierney D. F., Simmons D. H. Adult respiratory distress syndrome. West J Med. 1979 Mar;130(3):218–235. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran Van Nhieu J., Misset B., Lebargy F., Carlet J., Bernaudin J. F. Expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene in alveolar macrophages from patients with the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1993 Jun;147(6 Pt 1):1585–1589. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/147.6_Pt_1.1585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veletza S. V., Nichols K. V., Gross I., Lu H., Dynia D. W., Floros J. Surfactant protein C: hormonal control of SP-C mRNA levels in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):L684–L687. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.6.L684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitsett J. A., Clark J. C., Wispé J. R., Pryhuber G. S. Effects of TNF-alpha and phorbol ester on human surfactant protein and MnSOD gene transcription in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1992 Jun;262(6 Pt 1):L688–L693. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1992.262.6.L688. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Clements J. A. Metabolism and turnover of lung surfactant. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1987 Aug;136(2):426–444. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/136.2.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young S. L., Ho Y. S., Silbajoris R. A. Surfactant apoprotein in adult rat lung compartments is increased by dexamethasone. Am J Physiol. 1991 Feb;260(2 Pt 1):L161–L167. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1991.260.2.L161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]