Abstract
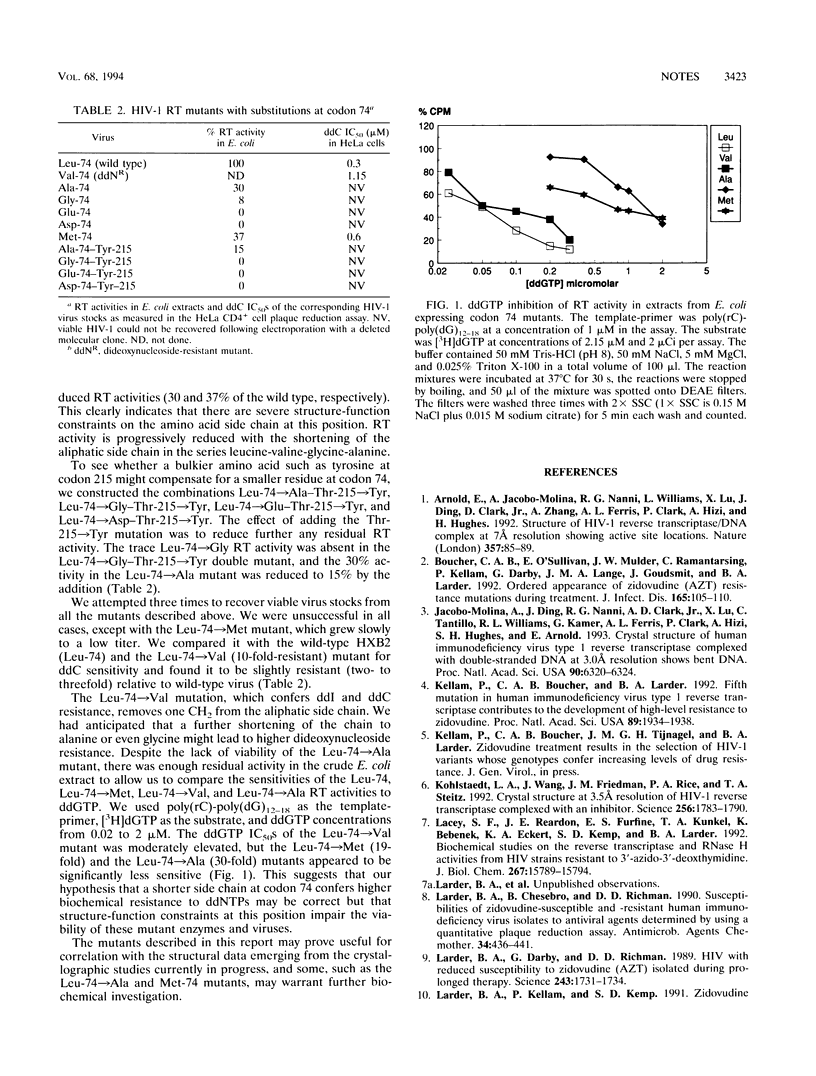
Mutation in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase (RT) at codon 215 has been shown to play a significant role in resistance to zidovudine (AZT). Substitution of threonine with tyrosine or phenylalanine alone confers decreased susceptibility to the inhibitor. In this study we constructed a panel of 10 viruses with different amino acids at this codon, including 7 novel mutants, and assessed their susceptibilities to AZT. The majority of the new mutants were AZT sensitive, whereas the Thr-215-->Trp mutant was partially resistant (threefold less susceptible). A combination of the Thr-215-->Trp with the other AZT resistance mutations Lys-70-->Arg and Met-41-->Leu gave additive resistance. The Thr-215-->Phe virus was less AZT resistant than the Thr-215-->Tyr mutant, both on its own and when each was combined with the Met-41-->Leu mutant. These observations confirm the general hypothesis that increased bulk of the amino acid side chains at this position confers decreased AZT sensitivity. A leucine-to-valine substitution at codon 74 has previously been found to confer dideoxynucleoside resistance. We constructed mutants with five novel amino acid substitutions (Ala, Gly, Glu, Met, and Asp) at codon 74. Of these, only one (that with the Met substitution) retained enough RT activity to yield viable virus. It thus appears that there are severe structure-function constraints on the amino acid side chains at this position in the enzyme. The activities of the Leu-74-->Ala and Leu-74-->Met RT enzymes expressed in Escherichia coli appeared to have reduced susceptibility to ddGTP compared with the wild-type enzyme. The mutants described in this work may prove useful for correlation with structural studies of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RT.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arnold E., Jacobo-Molina A., Nanni R. G., Williams R. L., Lu X., Ding J., Clark A. D., Jr, Zhang A., Ferris A. L., Clark P. Structure of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase/DNA complex at 7 A resolution showing active site locations. Nature. 1992 May 7;357(6373):85–89. doi: 10.1038/357085a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher C. A., O'Sullivan E., Mulder J. W., Ramautarsing C., Kellam P., Darby G., Lange J. M., Goudsmit J., Larder B. A. Ordered appearance of zidovudine resistance mutations during treatment of 18 human immunodeficiency virus-positive subjects. J Infect Dis. 1992 Jan;165(1):105–110. doi: 10.1093/infdis/165.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobo-Molina A., Ding J., Nanni R. G., Clark A. D., Jr, Lu X., Tantillo C., Williams R. L., Kamer G., Ferris A. L., Clark P. Crystal structure of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase complexed with double-stranded DNA at 3.0 A resolution shows bent DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6320–6324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellam P., Boucher C. A., Larder B. A. Fifth mutation in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase contributes to the development of high-level resistance to zidovudine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1934–1938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohlstaedt L. A., Wang J., Friedman J. M., Rice P. A., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. Science. 1992 Jun 26;256(5065):1783–1790. doi: 10.1126/science.1377403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacey S. F., Reardon J. E., Furfine E. S., Kunkel T. A., Bebenek K., Eckert K. A., Kemp S. D., Larder B. A. Biochemical studies on the reverse transcriptase and RNase H activities from human immunodeficiency virus strains resistant to 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15789–15794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Chesebro B., Richman D. D. Susceptibilities of zidovudine-susceptible and -resistant human immunodeficiency virus isolates to antiviral agents determined by using a quantitative plaque reduction assay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):436–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D. Multiple mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase confer high-level resistance to zidovudine (AZT). Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1155–1158. doi: 10.1126/science.2479983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin J. L., Wilson J. E., Haynes R. L., Furman P. A. Mechanism of resistance of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 to 2',3'-dideoxyinosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6135–6139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Martin J. L., Tudor-Williams G., Bach M. C., Vavro C. L., King D. M., Kellam P., Kemp S. D., Larder B. A. Resistance to ddI and sensitivity to AZT induced by a mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.1716788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


