Abstract
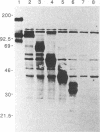
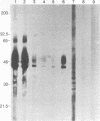
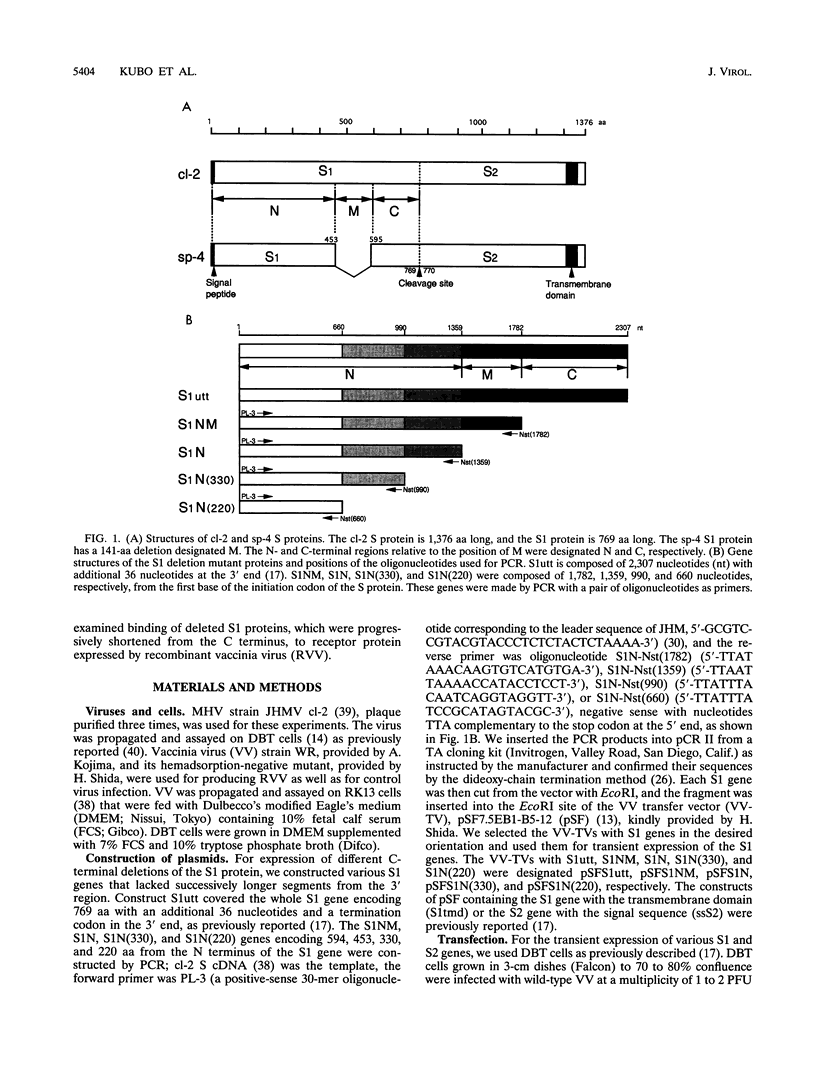
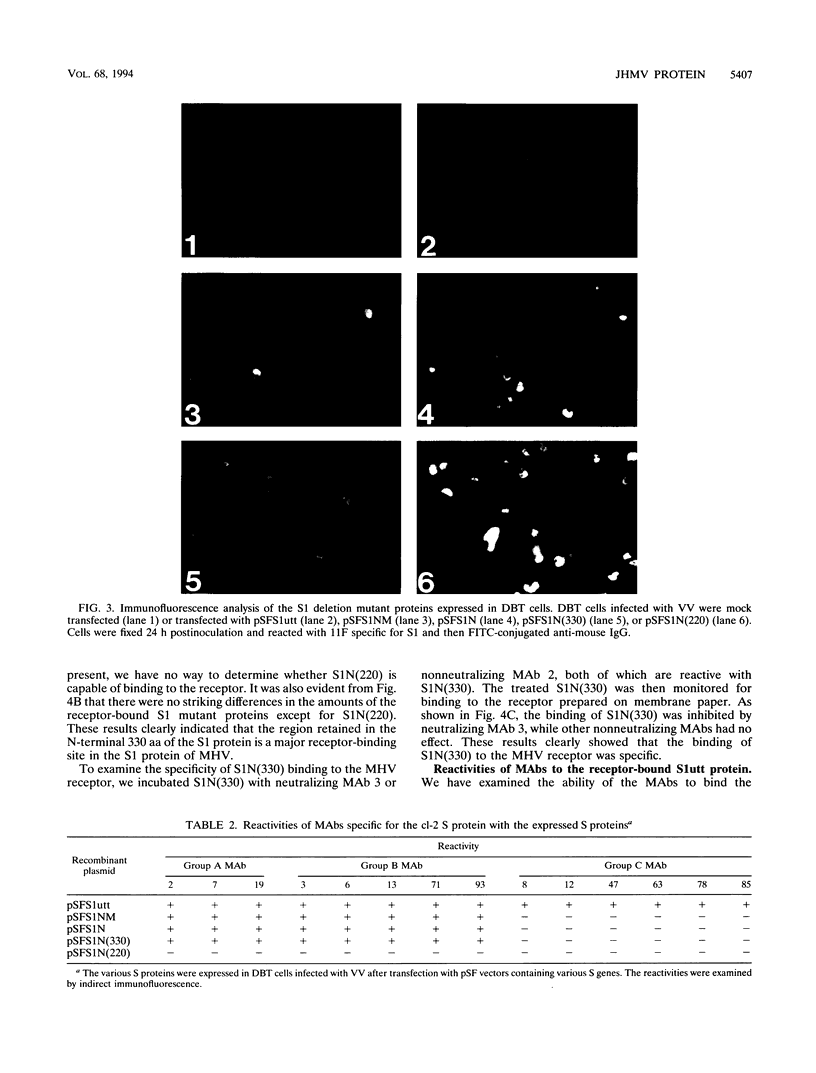
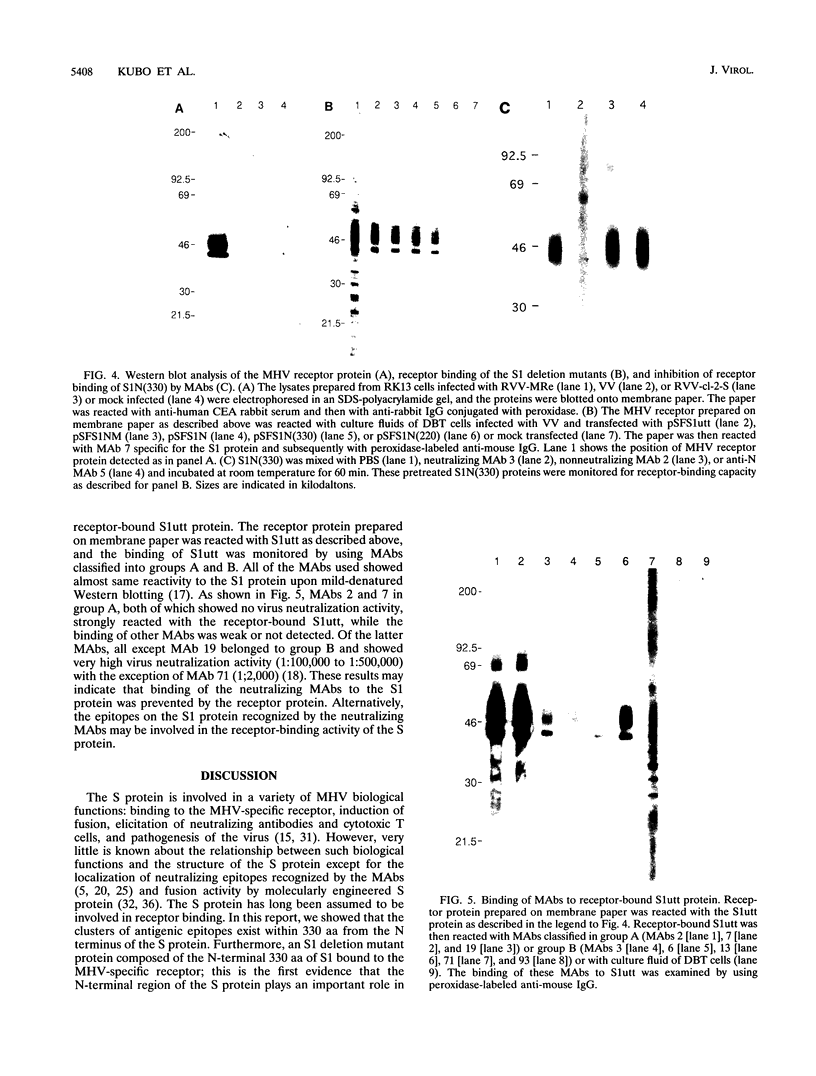
To localize the epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) specific for the S1 subunit of the murine coronavirus JHMV spike protein, we have expressed S1 proteins with different deletions from the C terminus of S1. S1utt is composed of the entire 769-amino-acid (aa) S1 protein; S1NM, S1N, S1n(330), and S1n(220) are deletion mutants with 594, 453, 330, and 220 aa from the N terminus of the S1 protein. The expressed S1 deletion mutant proteins were examined for reactivities to a panel of MAbs. All MAbs classified in groups A and B, those reactive to most mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) strains and those specific for isolate JHMV, respectively, recognized S1N(330) and the larger S1 deletion mutants but failed to react with S1N(220). MAbs in group C, specific for the larger S protein of JHMV, reacted only with the S1utt protein without any deletion. These results indicated that the domain composed of the N-terminal 330 aa comprised the cluster of conformational epitopes recognized by MAbs in groups A and B. It was also shown that the epitopes of MAbs in group C were not restricted to the region missing in the smaller S protein. These results together with the fact that all MAbs in group B retained high neutralizing activity suggested the possibility that the N-terminal 330 aa are responsible for binding to the MHV-specific receptors. In investigate this possibility, we expressed the receptor protein and examined the binding of each S1 deletion mutant to the receptor. It was demonstrated that the S1N(330) protein as well as other S1 deletion mutants larger than S1N(330) bound to the receptor. These results indicated that a domain composed of 330 aa at the N terminus of the S1 protein is responsible for binding to the MHV-specific receptor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cavanagh D., Davis P. J. Coronavirus IBV: removal of spike glycopolypeptide S1 by urea abolishes infectivity and haemagglutination but not attachment to cells. J Gen Virol. 1986 Jul;67(Pt 7):1443–1448. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-7-1443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. R., Knobler R. L., Powell H., Buchmeier M. J. Monoclonal antibodies to murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM) define the viral glycoprotein responsible for attachment and cell--cell fusion. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):358–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90095-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel R. G., Lampert P. W., Talbot P. J., Buchmeier M. J. Site-specific alteration of murine hepatitis virus type 4 peplomer glycoprotein E2 results in reduced neurovirulence. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.463-471.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel C., Anderson R., Buchmeier M. J., Fleming J. O., Spaan W. J., Wege H., Talbot P. J. Identification of an immunodominant linear neutralization domain on the S2 portion of the murine coronavirus spike glycoprotein and evidence that it forms part of complex tridimensional structure. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1185–1194. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1185-1194.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dveksler G. S., Dieffenbach C. W., Cardellichio C. B., McCuaig K., Pensiero M. N., Jiang G. S., Beauchemin N., Holmes K. V. Several members of the mouse carcinoembryonic antigen-related glycoprotein family are functional receptors for the coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus-A59. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.1-8.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dveksler G. S., Pensiero M. N., Cardellichio C. B., Williams R. K., Jiang G. S., Holmes K. V., Dieffenbach C. W. Cloning of the mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) receptor: expression in human and hamster cell lines confers susceptibility to MHV. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6881–6891. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6881-6891.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dveksler G. S., Pensiero M. N., Dieffenbach C. W., Cardellichio C. B., Basile A. A., Elia P. E., Holmes K. V. Mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 and blocking antireceptor monoclonal antibody bind to the N-terminal domain of cellular receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1716–1720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazakerley J. K., Parker S. E., Bloom F., Buchmeier M. J. The V5A13.1 envelope glycoprotein deletion mutant of mouse hepatitis virus type-4 is neuroattenuated by its reduced rate of spread in the central nervous system. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):178–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90306-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Trousdale M. D., el-Zaatari F. A., Stohlman S. A., Weiner L. P. Pathogenicity of antigenic variants of murine coronavirus JHM selected with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):869–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.869-875.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funahashi S., Itamura S., Iinuma H., Nerome K., Sugimoto M., Shida H. Increased expression in vivo and in vitro of foreign genes directed by A-type inclusion body hybrid promoters in recombinant vaccinia viruses. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5584–5588. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5584-5588.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano N., Fujiwara K., Hino S., Matumoto M. Replication and plaque formation of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-2) in mouse cell line DBT culture. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;44(3):298–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01240618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Doller E. W., Behnke J. N. Analysis of the functions of coronavirus glycoproteins by differential inhibition of synthesis with tunicamycin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;142:133–142. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0456-3_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Ise I., Nomoto A. Functional domains of the poliovirus receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4104–4108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo H., Taguchi F. Expression of the S1 and S2 subunits of murine coronavirus JHMV spike protein by a vaccinia virus transient expression system. J Gen Virol. 1993 Nov;74(Pt 11):2373–2383. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-11-2373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo H., Takase-Yoden S., Taguchi F. Neutralization and fusion inhibition activities of monoclonal antibodies specific for the S1 subunit of the spike protein of neurovirulent murine coronavirus JHMV c1-2 variant. J Gen Virol. 1993 Jul;74(Pt 7):1421–1425. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-7-1421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Geerts D., Posthumus W., Meloen R., Spaan W. Amino acid sequence of a conserved neutralizing epitope of murine coronaviruses. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1408–1412. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1408-1412.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara Y., Watanabe R., Taguchi F. Neurovirulence of six different murine coronavirus JHMV variants for rats. Virus Res. 1991 Jun;20(1):45–58. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(91)90060-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCuaig K., Rosenberg M., Nédellec P., Turbide C., Beauchemin N. Expression of the Bgp gene and characterization of mouse colon biliary glycoprotein isoforms. Gene. 1993 May 30;127(2):173–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90716-G. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn C. L., Wimmer E., Racaniello V. R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence, and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):855–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90690-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Arnold E., Erickson J. W., Frankenberger E. A., Griffith J. P., Hecht H. J., Johnson J. E., Kamer G., Luo M., Mosser A. G. Structure of a human common cold virus and functional relationship to other picornaviruses. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):145–153. doi: 10.1038/317145a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge E., Stauber R., Pfleiderer M., Siddell S. G. Analysis of murine coronavirus surface glycoprotein functions by using monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):254–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.254-262.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt I., Skinner M., Siddell S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the surface projection glycoprotein of coronavirus MHV-JHM. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):47–56. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selinka H. C., Zibert A., Wimmer E. Poliovirus can enter and infect mammalian cells by way of an intercellular adhesion molecule 1 pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3598–3602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S., Wege H., Ter Meulen V. The biology of coronaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1983 Apr;64(Pt 4):761–776. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Siddell S. G. Coronavirus JHM: nucleotide sequence of the mRNA that encodes nucleocapsid protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5045–5054. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W., Cavanagh D., Horzinek M. C. Coronaviruses: structure and genome expression. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):2939–2952. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauber R., Pfleiderera M., Siddell S. Proteolytic cleavage of the murine coronavirus surface glycoprotein is not required for fusion activity. J Gen Virol. 1993 Feb;74(Pt 2):183–191. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-2-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Dustin M. L., Erickson H. P., Springer T. A. The arrangement of the immunoglobulin-like domains of ICAM-1 and the binding sites for LFA-1 and rhinovirus. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):243–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90805-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staunton D. E., Merluzzi V. J., Rothlein R., Barton R., Marlin S. D., Springer T. A. A cell adhesion molecule, ICAM-1, is the major surface receptor for rhinoviruses. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):849–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90689-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of peplomeric glycoprotein E2 of MHV yields two 90K subunits and activates cell fusion. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;173:25–35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9373-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi F., Fleming J. O. Comparison of six different murine coronavirus JHM variants by monoclonal antibodies against the E2 glycoprotein. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):233–235. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90061-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi F. Fusion formation by the uncleaved spike protein of murine coronavirus JHMV variant cl-2. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1195–1202. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1195-1202.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi F., Ikeda T., Shida H. Molecular cloning and expression of a spike protein of neurovirulent murine coronavirus JHMV variant cl-2. J Gen Virol. 1992 May;73(Pt 5):1065–1072. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-5-1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi F., Siddell S. G., Wege H., ter Meulen V. Characterization of a variant virus selected in rat brains after infection by coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus JHM. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):429–435. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.429-435.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi F., Yamada A., Fujiwara K. Resistance to highly virulent mouse hepatitis virus acquired by mice after low-virulence infection: enhanced antiviral activity of macrophages. Infect Immun. 1980 Jul;29(1):42–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.1.42-49.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennema H., Heijnen L., Zijderveld A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Intracellular transport of recombinant coronavirus spike proteins: implications for virus assembly. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):339–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.339-346.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Siddell S., ter Meulen V. The biology and pathogenesis of coronaviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;99:165–200. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68528-6_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weismiller D. G., Sturman L. S., Buchmeier M. J., Fleming J. O., Holmes K. V. Monoclonal antibodies to the peplomer glycoprotein of coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus identify two subunits and detect a conformational change in the subunit released under mild alkaline conditions. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3051–3055. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3051-3055.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Viral and cellular membrane fusion proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:675–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. K., Jiang G. S., Holmes K. V. Receptor for mouse hepatitis virus is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen family of glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5533–5536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y. K., Yabe M., Yamada A., Taguchi F. Detection of mouse hepatitis virus by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to the rapid diagnosis of infection. Lab Anim Sci. 1993 Aug;43(4):285–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokomori K., Lai M. M. Mouse hepatitis virus utilizes two carcinoembryonic antigens as alternative receptors. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6194–6199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6194-6199.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. J., Luytjes W., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A., Spaan W. J., Lenstra J. A. Evidence for a coiled-coil structure in the spike proteins of coronaviruses. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):963–966. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90422-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]