Abstract
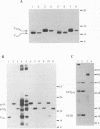
According to the existing model of flavivirus polyprotein processing, one of the cleavages in the amino-terminal part of the flavivirus polyprotein by host cell signalases results in formation of prM (precursor to one of the structural proteins, M) and the membrane-bound intracellular form of the viral capsid protein (Cint) retaining the prM signal sequence at its carboxy terminus. This hydrophobic anchor is subsequently removed by the viral protease, resulting in formation of the mature viral capsid protein found in virions (Cvir). We have prepared in vitro expression cassettes coding for both forms of the capsid protein, for the prM protein, for the C-prM precursor, and for the viral protease components of West Nile flavivirus and characterized their translation products. Using Cint and Cvir translation products as molecular markers, we have observed processing of the intracellular form of the West Nile capsid protein by the viral protease in vitro both upon cotranslation of the C-prM precursor and the viral protease-encoding cassette and by incubation of C-prM translation products with a detergent-solubilized extract of cells infected with a recombinant vaccinia virus expressing the active viral protease. The cleavage of Cint by the viral protease at the predicted dibasic site was verified by introduction of point mutations into the cleavage site and an adjacent region. These studies provide the first direct demonstration of processing of the intracellular form of the flavivirus capsid protein by the viral protease.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amberg S. M., Nestorowicz A., McCourt D. W., Rice C. M. NS2B-3 proteinase-mediated processing in the yellow fever virus structural region: in vitro and in vivo studies. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3794–3802. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3794-3802.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J. Detection of a trypsin-like serine protease domain in flaviviruses and pestiviruses. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):637–639. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90639-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedrzycka A., Cauchi M. R., Bartholomeusz A., Gorman J. J., Wright P. J. Characterization of protease cleavage sites involved in the formation of the envelope glycoprotein and three non-structural proteins of dengue virus type 2, New Guinea C strain. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1317–1326. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle E., Leidner U., Nowak T., Wengler G., Wengler G. Primary structure of the West Nile flavivirus genome region coding for all nonstructural proteins. Virology. 1986 Feb;149(1):10–26. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90082-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castle E., Nowak T., Leidner U., Wengler G., Wengler G. Sequence analysis of the viral core protein and the membrane-associated proteins V1 and NV2 of the flavivirus West Nile virus and of the genome sequence for these proteins. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):227–236. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90156-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Grakoui A., Rice C. M. Processing of the yellow fever virus nonstructural polyprotein: a catalytically active NS3 proteinase domain and NS2B are required for cleavages at dibasic sites. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6042–6050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6042-6050.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Hahn C. S., Galler R., Rice C. M. Flavivirus genome organization, expression, and replication. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:649–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., McCourt D. W., Rice C. M. Production of yellow fever virus proteins in infected cells: identification of discrete polyprotein species and analysis of cleavage kinetics using region-specific polyclonal antisera. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):159–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90470-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., McCourt D. W., Rice C. M. Yellow fever virus proteins NS2A, NS2B, and NS4B: identification and partial N-terminal amino acid sequence analysis. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):100–109. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Weir R. C., Grakoui A., McCourt D. W., Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J., Rice C. M. Evidence that the N-terminal domain of nonstructural protein NS3 from yellow fever virus is a serine protease responsible for site-specific cleavages in the viral polyprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8898–8902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falgout B., Chanock R., Lai C. J. Proper processing of dengue virus nonstructural glycoprotein NS1 requires the N-terminal hydrophobic signal sequence and the downstream nonstructural protein NS2a. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1852–1860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1852-1860.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falgout B., Pethel M., Zhang Y. M., Lai C. J. Both nonstructural proteins NS2B and NS3 are required for the proteolytic processing of dengue virus nonstructural proteins. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2467–2475. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2467-2475.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Donchenko A. P., Blinov V. M., Koonin E. V. Cysteine proteases of positive strand RNA viruses and chymotrypsin-like serine proteases. A distinct protein superfamily with a common structural fold. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jan 30;243(2):103–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80109-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz F. X., Stiasny K., Püschner-Auer G., Holzmann H., Allison S. L., Mandl C. W., Kunz C. Structural changes and functional control of the tick-borne encephalitis virus glycoprotein E by the heterodimeric association with protein prM. Virology. 1994 Jan;198(1):109–117. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Lai C. J. Cleavage of dengue virus NS1-NS2A requires an octapeptide sequence at the C terminus of NS1. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4573–4577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4573-4577.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hunt H. D., Ho S. N., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever A., Gottlinger H., Haseltine W., Sodroski J. Identification of a sequence required for efficient packaging of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA into virions. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):4085–4087. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.4085-4087.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C., Amberg S. M., Chambers T. J., Rice C. M. Cleavage at a novel site in the NS4A region by the yellow fever virus NS2B-3 proteinase is a prerequisite for processing at the downstream 4A/4B signalase site. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2327–2335. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2327-2335.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobigs M. Flavivirus premembrane protein cleavage and spike heterodimer secretion require the function of the viral proteinase NS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6218–6222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandl C. W., Heinz F. X., Kunz C. Sequence of the structural proteins of tick-borne encephalitis virus (western subtype) and comparative analysis with other flaviviruses. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason P. W. Maturation of Japanese encephalitis virus glycoproteins produced by infected mammalian and mosquito cells. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):354–364. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90161-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila P., Korpela J., Tenkanen T., Pitkänen K. Fidelity of DNA synthesis by the Thermococcus litoralis DNA polymerase--an extremely heat stable enzyme with proofreading activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Sep 25;19(18):4967–4973. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.18.4967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestorowicz A., Chambers T. J., Rice C. M. Mutagenesis of the yellow fever virus NS2A/2B cleavage site: effects on proteolytic processing, viral replication, and evidence for alternative processing of the NS2A protein. Virology. 1994 Feb 15;199(1):114–123. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak T., Färber P. M., Wengler G., Wengler G. Analyses of the terminal sequences of West Nile virus structural proteins and of the in vitro translation of these proteins allow the proposal of a complete scheme of the proteolytic cleavages involved in their synthesis. Virology. 1989 Apr;169(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Strauss J. H. Processing of nonstructural proteins NS4A and NS4B of dengue 2 virus in vitro and in vivo. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):689–697. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90540-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preugschat F., Yao C. W., Strauss J. H. In vitro processing of dengue virus type 2 nonstructural proteins NS2A, NS2B, and NS3. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4364–4374. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4364-4374.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph V. B., Winkler G., Stollar V. Acidotropic amines inhibit proteolytic processing of flavivirus prM protein. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):450–458. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90099-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice C. M., Lenches E. M., Eddy S. R., Shin S. J., Sheets R. L., Strauss J. H. Nucleotide sequence of yellow fever virus: implications for flavivirus gene expression and evolution. Science. 1985 Aug 23;229(4715):726–733. doi: 10.1126/science.4023707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Linares A., Cahour A., Després P., Girard M., Bouloy M. Processing of yellow fever virus polyprotein: role of cellular proteases in maturation of the structural proteins. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4199–4209. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4199-4209.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speight G., Coia G., Parker M. D., Westaway E. G. Gene mapping and positive identification of the non-structural proteins NS2A, NS2B, NS3, NS4B and NS5 of the flavivirus Kunjin and their cleavage sites. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):23–34. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speight G., Westaway E. G. Carboxy-terminal analysis of nine proteins specified by the flavivirus Kunjin: evidence that only the intracellular core protein is truncated. J Gen Virol. 1989 Aug;70(Pt 8):2209–2214. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-8-2209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Temin H. M. Encapsidation sequences for spleen necrosis virus, an avian retrovirus, are between the 5' long terminal repeat and the start of the gag gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5986–5990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss B., Nitschko H., Ghattas I., Wright R., Schlesinger S. Evidence for specificity in the encapsidation of Sindbis virus RNAs. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5310–5318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5310-5318.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wengler G., Czaya G., Färber P. M., Hegemann J. H. In vitro synthesis of West Nile virus proteins indicates that the amino-terminal segment of the NS3 protein contains the active centre of the protease which cleaves the viral polyprotein after multiple basic amino acids. J Gen Virol. 1991 Apr;72(Pt 4):851–858. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-4-851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright P. J., Cauchi M. R., Ng M. L. Definition of the carboxy termini of the three glycoproteins specified by dengue virus type 2. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):61–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamshchikov V. F., Compans R. W. Regulation of the late events in flavivirus protein processing and maturation. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):38–51. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong W., Dasgupta R., Rueckert R. Evidence that the packaging signal for nodaviral RNA2 is a bulged stem-loop. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11146–11150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]