Abstract
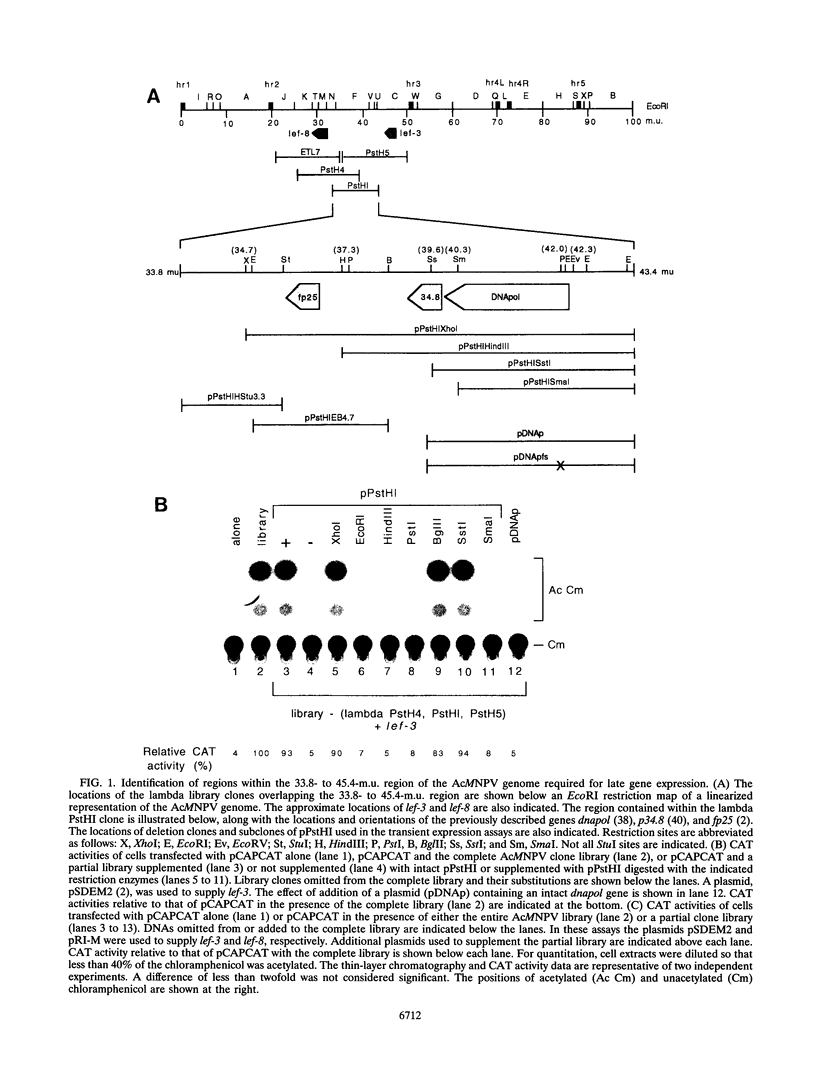
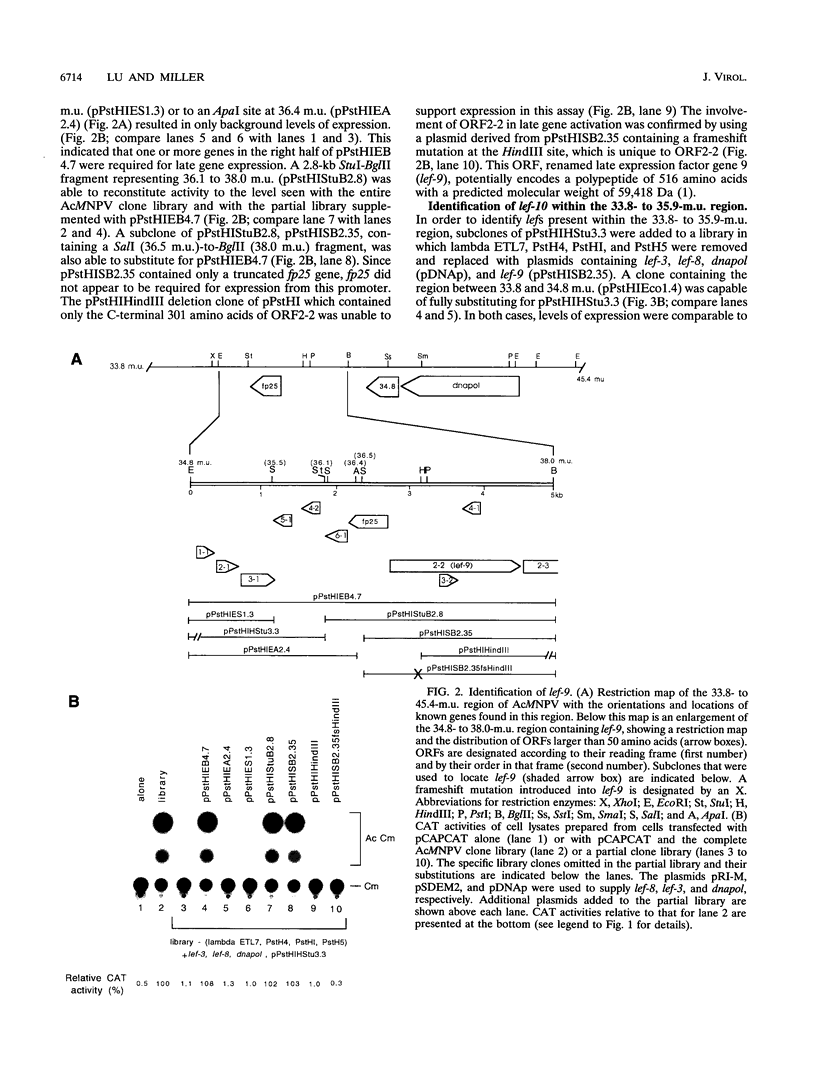
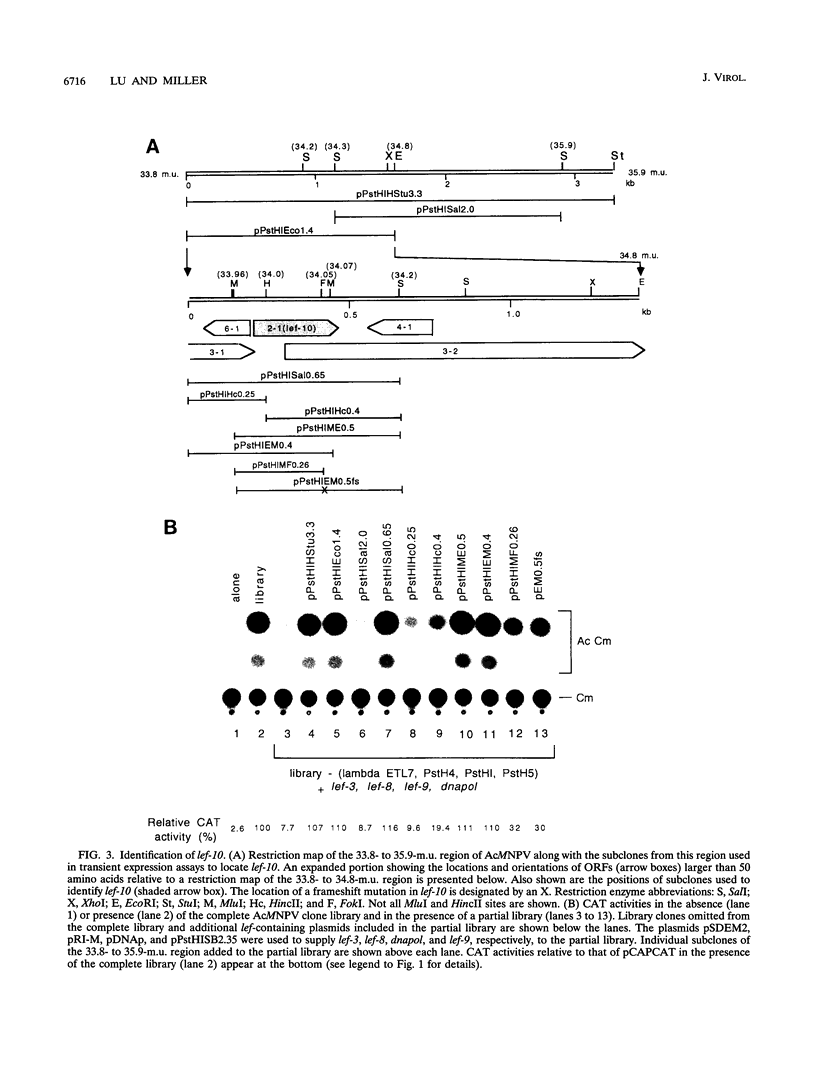
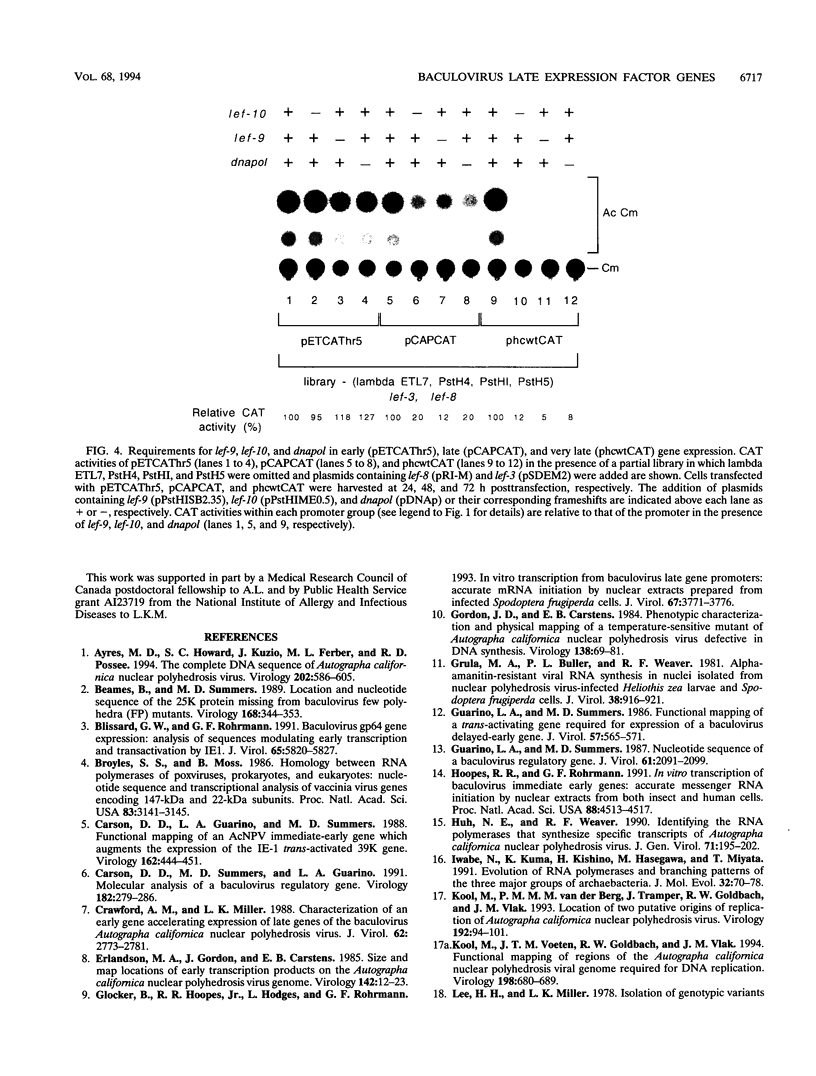
A transient transactivation assay system was used in combination with an overlapping Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus clone library to identify genes involved in late and very late baculovirus gene expression. We have identified three genes within the 33.8- to 43.4-map-unit region of the A. californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome which contribute to expression from promoters of the vp39 major capsid protein and polyhedrin genes. One of these three genes corresponds to the previously identified DNA polymerase gene, while the other two genes encode previously unidentified polypeptides of 59,418 and 8,706 Da. None of these genes were required for expression from the early etl promoter.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayres M. D., Howard S. C., Kuzio J., Lopez-Ferber M., Possee R. D. The complete DNA sequence of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1994 Aug 1;202(2):586–605. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beames B., Summers M. D. Location and nucleotide sequence of the 25K protein missing from baculovirus few polyhedra (FP) mutants. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):344–353. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90275-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blissard G. W., Rohrmann G. F. Baculovirus gp64 gene expression: analysis of sequences modulating early transcription and transactivation by IE1. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5820–5827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5820-5827.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Moss B. Homology between RNA polymerases of poxviruses, prokaryotes, and eukaryotes: nucleotide sequence and transcriptional analysis of vaccinia virus genes encoding 147-kDa and 22-kDa subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3141–3145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. D., Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of an AcNPV immediately early gene which augments expression of the IE-1 trans-activated 39K gene. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):444–451. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90485-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson D. D., Summers M. D., Guarino L. A. Molecular analysis of a baculovirus regulatory gene. Virology. 1991 May;182(1):279–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90671-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford A. M., Miller L. K. Characterization of an early gene accelerating expression of late genes of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2773–2781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2773-2781.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandson M. A., Gordon J., Carstens E. B. Size and map locations of early transcription products on the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome. Virology. 1985 Apr 15;142(1):12–23. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90418-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glocker B., Hoopes R. R., Jr, Hodges L., Rohrmann G. F. In vitro transcription from baculovirus late gene promoters: accurate mRNA initiation by nuclear extracts prepared from infected Spodoptera frugiperda cells. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):3771–3776. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.3771-3776.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. D., Carstens E. B. Phenotypic characterization and physical mapping of a temperature-sensitive mutant of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus defective in DNA synthesis. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grula M. A., Buller P. L., Weaver R. F. alpha-Amanitin-Resistant Viral RNA Synthesis in Nuclei Isolated from Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus-Infected Heliothis zea Larvae and Spodoptera frugiperda Cells. J Virol. 1981 Jun;38(3):916–921. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.3.916-921.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of a trans-activating gene required for expression of a baculovirus delayed-early gene. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.563-571.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Nucleotide sequence and temporal expression of a baculovirus regulatory gene. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2091–2099. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2091-2099.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoopes R. R., Jr, Rohrmann G. F. In vitro transcription of baculovirus immediate early genes: accurate mRNA initiation by nuclear extracts from both insect and human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4513–4517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huh N. E., Weaver R. F. Identifying the RNA polymerases that synthesize specific transcripts of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Gen Virol. 1990 Jan;71(Pt 1):195–201. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-1-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwabe N., Kuma K., Kishino H., Hasegawa M., Miyata T. Evolution of RNA polymerases and branching patterns of the three major groups of Archaebacteria. J Mol Evol. 1991 Jan;32(1):70–78. doi: 10.1007/BF02099931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kool M., Voeten J. T., Goldbach R. W., Vlak J. M. Functional mapping of regions of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis viral genome required for DNA replication. Virology. 1994 Feb;198(2):680–689. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kool M., van den Berg P. M., Tramper J., Goldbach R. W., Vlak J. M. Location of two putative origins of DNA replication of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):94–101. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. H., Miller L. K. Isolation of genotypic variants of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):754–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.754-767.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leisy D. J., Rohrmann G. F. Characterization of the replication of plasmids containing hr sequences in baculovirus-infected Spodoptera frugiperda cells. Virology. 1993 Oct;196(2):722–730. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Passarelli A. L., Miller L. K. Identification, sequence, and transcriptional mapping of lef-3, a baculovirus gene involved in late and very late gene expression. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5260–5268. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5260-5268.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu A., Carstens E. B. Nucleotide sequence of a gene essential for viral DNA replication in the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):336–347. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90500-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris T. D., Todd J. W., Fisher B., Miller L. K. Identification of lef-7: a baculovirus gene affecting late gene expression. Virology. 1994 May 1;200(2):360–369. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen M. S., Friesen P. D. Molecular analysis of the transcriptional regulatory region of an early baculovirus gene. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):493–503. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.493-503.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly D. R., Crawford A. M., Miller L. K. Viral proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):606–606. doi: 10.1038/337606a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi B. G., Rankin C., Miller L. K. Downstream sequences augment transcription from the essential initiation site of a baculovirus polyhedrin gene. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 20;210(4):721–736. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passarelli A. L., Miller L. K. Identification and characterization of lef-1, a baculovirus gene involved in late and very late gene expression. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3481–3488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3481-3488.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passarelli A. L., Miller L. K. Identification and transcriptional regulation of the baculovirus lef-6 gene. J Virol. 1994 Jul;68(7):4458–4467. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4458-4467.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passarelli A. L., Miller L. K. Identification of genes encoding late expression factors located between 56.0 and 65.4 map units of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome. Virology. 1993 Dec;197(2):704–714. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passarelli A. L., Miller L. K. Three baculovirus genes involved in late and very late gene expression: ie-1, ie-n, and lef-2. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2149–2158. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2149-2158.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passarelli A. L., Todd J. W., Miller L. K. A baculovirus gene involved in late gene expression predicts a large polypeptide with a conserved motif of RNA polymerases. J Virol. 1994 Jul;68(7):4673–4678. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.7.4673-4678.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson M. N., Bjornson R. M., Ahrens C., Rohrmann G. F. Identification and characterization of a putative origin of DNA replication in the genome of a baculovirus pathogenic for Orgyia pseudotsugata. Virology. 1993 Dec;197(2):715–725. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson M., Bjornson R., Pearson G., Rohrmann G. The Autographa californica baculovirus genome: evidence for multiple replication origins. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1382–1384. doi: 10.1126/science.1529337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin C., Ooi B. G., Miller L. K. Eight base pairs encompassing the transcriptional start point are the major determinant for baculovirus polyhedrin gene expression. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):39–49. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro B. M., Hutchinson K., Miller L. K. A mutant baculovirus with a temperature-sensitive IE-1 transregulatory protein. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):1075–1084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.1075-1084.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiem S. M., Miller L. K. Differential gene expression mediated by late, very late and hybrid baculovirus promoters. Gene. 1990 Jul 2;91(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90166-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomalski M. D., Wu J. G., Miller L. K. The location, sequence, transcription, and regulation of a baculovirus DNA polymerase gene. Virology. 1988 Dec;167(2):591–600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. L., Goodwin R. H., Tompkins G. J., McCawley P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro. 1977 Apr;13(4):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02615077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. G., Miller L. K. Sequence, transcription and translation of a late gene of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus encoding a 34.8K polypeptide. J Gen Virol. 1989 Sep;70(Pt 9):2449–2459. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-9-2449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]