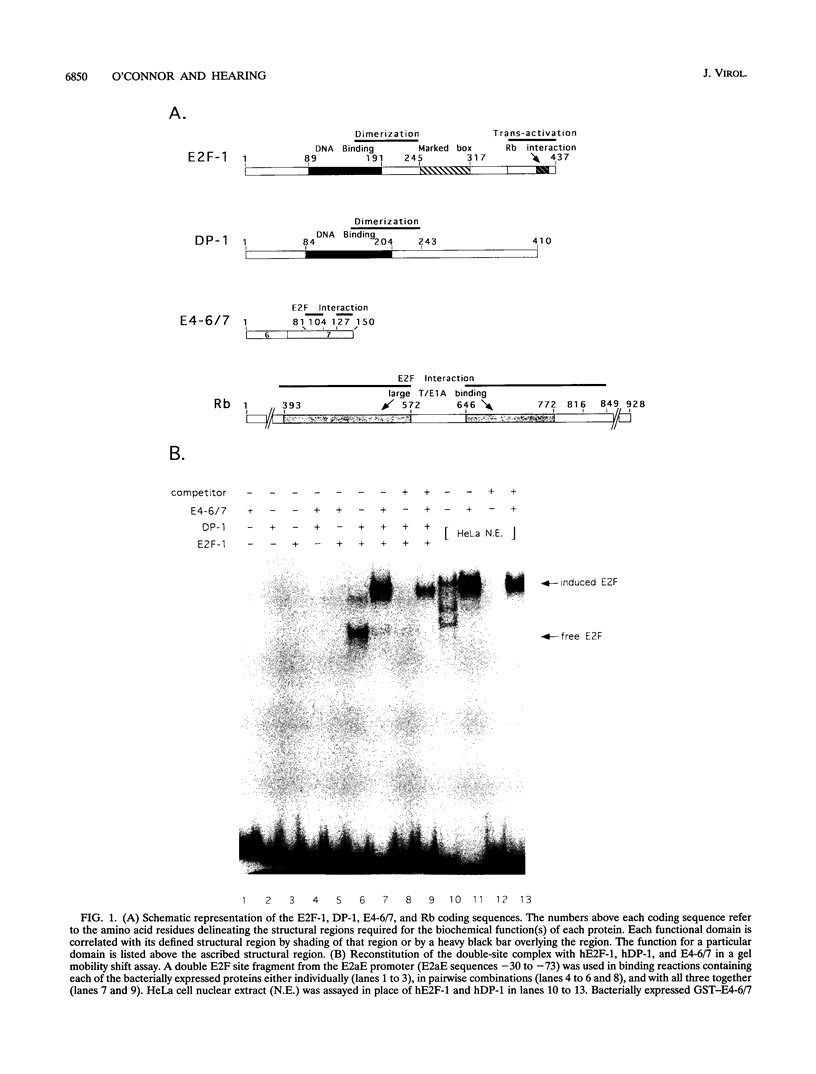
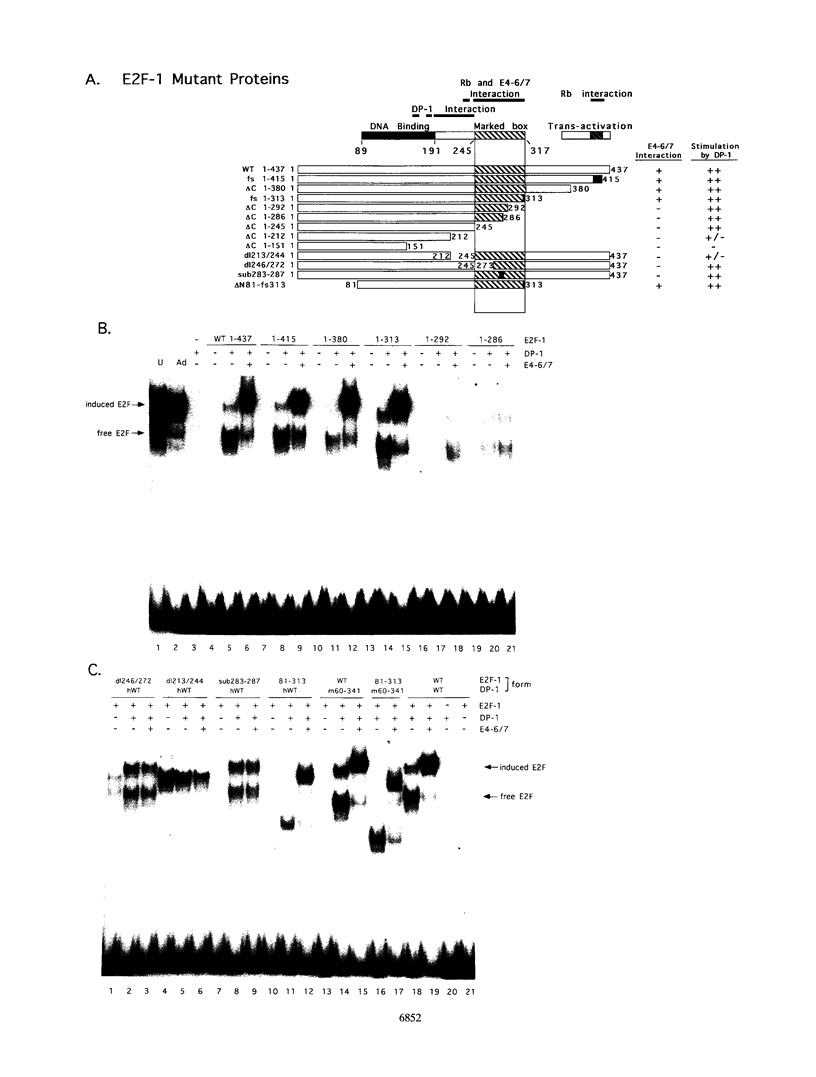
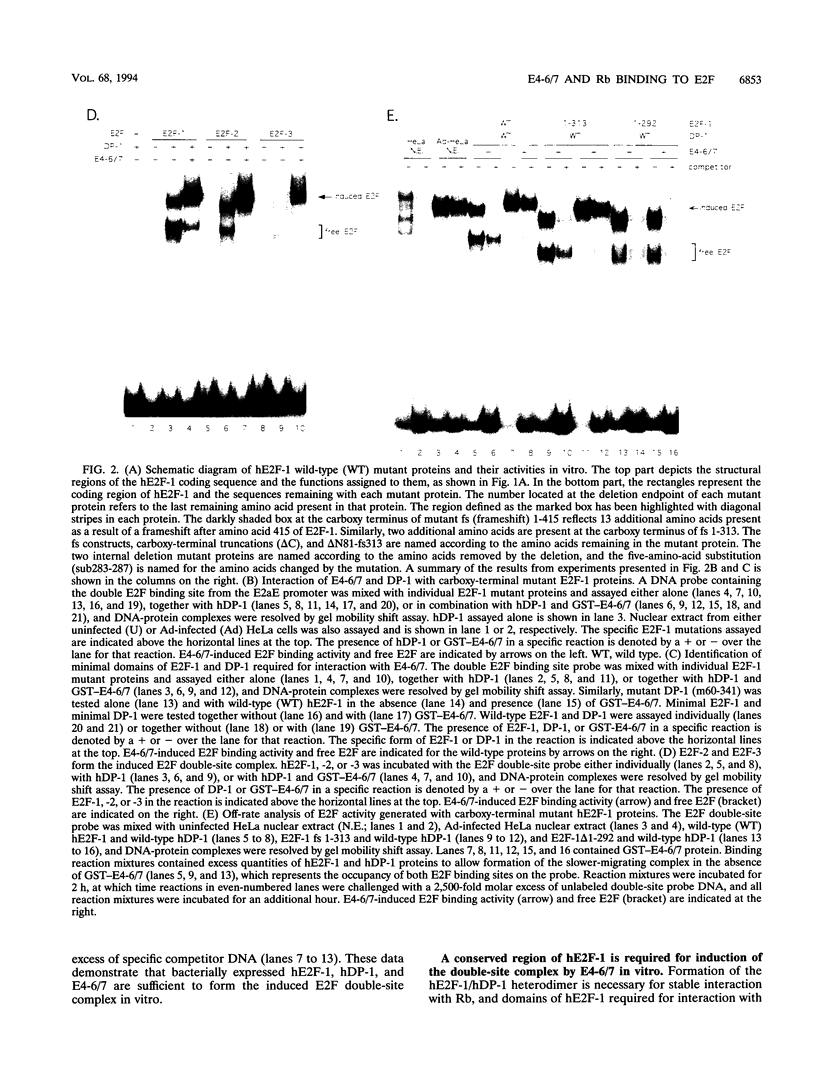
Abstract
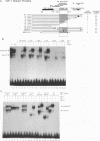
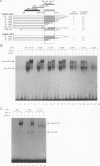
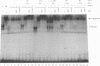
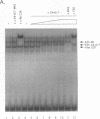
The binding of E2F to the adenovirus (Ad) E2a promoter is stimulated by the Ad E4-6/7 protein. E2F DNA binding activity is composed of a heterodimer of related but distinct proteins of the E2F-1 and DP-1 families. The E4-6/7 protein induces the cooperative and stable binding of E2F to an inverted repeat binding site in the E2a promoter apparently by providing a dimerization interface to two adjacent E2F heterodimers. The product of the retinoblastoma gene product (Rb) represses the transcriptional activity of E2F by direct protein-protein interaction. In this report, we have examined the regions of E2F-1 and DP-1 that are required for the induction of cooperative E2F binding to the E2a promoter by the E4-6/7 protein. Our results demonstrate that an internal segment of E2F-1, that is conserved among members of the E2F family, is required for functional interaction with the E4-6/7 product. Consistent with this observation, other members of the E2F family (E2F-2 and E2F-3) productively interact with E4-6/7. DP-1 also is necessary for stable interaction with E4-6/7 and an internal segment of DP-1 is required that is positioned in a location similar to that of the conserved E2F-1 domain. Interestingly, the binding of E4-6/7 and the binding of Rb to E2F are mutually exclusive, and our results show that the same internal segments of E2F-1 and DP-1 that are required for E4-6/7 binding are also required for stable interaction with Rb. These results suggest that the Ad E4-6/7 protein mimics Rb in part for the protein interaction requirements for E2F binding, although with different functional consequences. While Rb binding represses E2F activity, the E4-6/7 protein stimulates transactivation of the Ad E2a promoter.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A proteins can dissociate heteromeric complexes involving the E2F transcription factor: a novel mechanism for E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90112-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Weinmann R., Raychaudhuri P. The retinoblastoma protein copurifies with E2F-I, an E1A-regulated inhibitor of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1063–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90558-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., Adamczewski J. P., Hunt T., La Thangue N. B. Cyclin A and the retinoblastoma gene product complex with a common transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jul 18;352(6332):249–251. doi: 10.1038/352249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., Buck V. M., Zamanian M., Johnston L. H., La Thangue N. B. Functional synergy between DP-1 and E2F-1 in the cell cycle-regulating transcription factor DRTF1/E2F. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4317–4324. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06116.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandara L. R., La Thangue N. B. Adenovirus E1a prevents the retinoblastoma gene product from complexing with a cellular transcription factor. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):494–497. doi: 10.1038/351494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. C., Azizkhan J. C. Transcription factor E2F is required for efficient expression of the hamster dihydrofolate reductase gene in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):4994–5002. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.4994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bocco J. L., Reimund B., Chatton B., Kedinger C. Rb may act as a transcriptional co-activator in undifferentiated F9 cells. Oncogene. 1993 Nov;8(11):2977–2986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L., Faha B., Dembski M., Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Dyson N. Independent binding of the retinoblastoma protein and p107 to the transcription factor E2F. Nature. 1992 Jan 9;355(6356):176–179. doi: 10.1038/355176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S. P., Hiebert S., Mudryj M., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The E2F transcription factor is a cellular target for the RB protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90557-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chellappan S., Kraus V. B., Kroger B., Munger K., Howley P. M., Phelps W. C., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus E1A, simian virus 40 tumor antigen, and human papillomavirus E7 protein share the capacity to disrupt the interaction between transcription factor E2F and the retinoblastoma gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4549–4553. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., DeCaprio J. A. Cell cycle analysis of E2F in primary human T cells reveals novel E2F complexes and biochemically distinct forms of free E2F. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):3975–3983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.3975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr The T/E1A-binding domain of the retinoblastoma product can interact selectively with a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1073–1082. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90559-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobrinik D., Whyte P., Peeper D. S., Jacks T., Weinberg R. A. Cell cycle-specific association of E2F with the p130 E1A-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2392–2404. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress W. D., Johnson D. G., Nevins J. R. A genetic analysis of the E2F1 gene distinguishes regulation by Rb, p107, and adenovirus E4. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6314–6325. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S. Cell cycle regulation of the human cdc2 gene. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1797–1804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devoto S. H., Mudryj M., Pines J., Hunter T., Nevins J. R. A cyclin A-protein kinase complex possesses sequence-specific DNA binding activity: p33cdk2 is a component of the E2F-cyclin A complex. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson N., Harlow E. Adenovirus E1A targets key regulators of cell proliferation. Cancer Surv. 1992;12:161–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Faha B., Harlow E., Livingston D. M. Interaction of p107 with cyclin A independent of complex formation with viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.1532457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Xing Y. G., Lawrence J. B., Livingston D. M. Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and expression of the cDNA for p107, a retinoblastoma gene product-related protein. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1155–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90038-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faha B., Ewen M. E., Tsai L. H., Livingston D. M., Harlow E. Interaction between human cyclin A and adenovirus E1A-associated p107 protein. Science. 1992 Jan 3;255(5040):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1532458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flemington E. K., Speck S. H., Kaelin W. G., Jr E2F-1-mediated transactivation is inhibited by complex formation with the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6914–6918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girling R., Partridge J. F., Bandara L. R., Burden N., Totty N. F., Hsuan J. J., La Thangue N. B. A new component of the transcription factor DRTF1/E2F. Nature. 1993 Mar 4;362(6415):83–87. doi: 10.1038/362083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem. 1991 Feb 1;192(2):262–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90534-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Demetrick D., Beach D. Isolation of the Rb-related p130 through its interaction with CDK2 and cyclins. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2378–2391. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Harlow E., Fattaey A. Inhibition of E2F-1 transactivation by direct binding of the retinoblastoma protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6501–6508. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Lees J. A., Vidal M., Dyson N., Harlow E., Fattaey A. A cDNA encoding a pRB-binding protein with properties of the transcription factor E2F. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):337–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90107-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Wu C. L., Fattaey A. R., Lees J. A., Dynlacht B. D., Ngwu C., Harlow E. Heterodimerization of the transcription factors E2F-1 and DP-1 leads to cooperative trans-activation. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1850–1861. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Chellappan S. P., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The interaction of RB with E2F coincides with an inhibition of the transcriptional activity of E2F. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):177–185. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Lipp M., Nevins J. R. E1A-dependent trans-activation of the human MYC promoter is mediated by the E2F factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3594–3598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Q. J., Dyson N., Harlow E. The regions of the retinoblastoma protein needed for binding to adenovirus E1A or SV40 large T antigen are common sites for mutations. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1147–1155. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. M., Hearing P. The adenovirus early region 4 open reading frame 6/7 protein regulates the DNA binding activity of the cellular transcription factor, E2F, through a direct complex. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1699–1710. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Wang N. P., Tseng B. Y., Lee W. H., Lee E. H. Two distinct and frequently mutated regions of retinoblastoma protein are required for binding to SV40 T antigen. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1815–1822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunninghake G. W., Monks B. G., Geist L. J., Monick M. M., Monroy M. A., Stinski M. F., Webb A. C., Dayer J. M., Auron P. E., Fenton M. J. The functional importance of a cap site-proximal region of the human prointerleukin 1 beta gene is defined by viral protein trans-activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;12(8):3439–3448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.8.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivey-Hoyle M., Conroy R., Huber H. E., Goodhart P. J., Oliff A., Heimbrook D. C. Cloning and characterization of E2F-2, a novel protein with the biochemical properties of transcription factor E2F. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7802–7812. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Ewen M. E., Livingston D. M. Definition of the minimal simian virus 40 large T antigen- and adenovirus E1A-binding domain in the retinoblastoma gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3761–3769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelin W. G., Jr, Krek W., Sellers W. R., DeCaprio J. A., Ajchenbaum F., Fuchs C. S., Chittenden T., Li Y., Farnham P. J., Blanar M. A. Expression cloning of a cDNA encoding a retinoblastoma-binding protein with E2F-like properties. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):351–364. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90108-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. E1A transcription induction: enhanced binding of a factor to upstream promoter sequences. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):719–722. doi: 10.1126/science.2935935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Identification of a cellular transcription factor involved in E1A trans-activation. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90386-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Livingston D. M., Shirodkar S. Binding to DNA and the retinoblastoma gene product promoted by complex formation of different E2F family members. Science. 1993 Dec 3;262(5139):1557–1560. doi: 10.1126/science.8248803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E. W., Watson R. J. An E2F-binding site mediates cell-cycle regulated repression of mouse B-myb transcription. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2705–2713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees E., Faha B., Dulic V., Reed S. I., Harlow E. Cyclin E/cdk2 and cyclin A/cdk2 kinases associate with p107 and E2F in a temporally distinct manner. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1874–1885. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees J. A., Saito M., Vidal M., Valentine M., Look T., Harlow E., Dyson N., Helin K. The retinoblastoma protein binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7813–7825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Graham C., Lacy S., Duncan A. M., Whyte P. The adenovirus E1A-associated 130-kD protein is encoded by a member of the retinoblastoma gene family and physically interacts with cyclins A and E. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2366–2377. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manohar C. F., Kratochvil J., Thimmapaya B. The adenovirus EII early promoter has multiple EIA-sensitive elements, two of which function cooperatively in basal and virus-induced transcription. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2457–2466. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2457-2466.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marton M. J., Baim S. B., Ornelles D. A., Shenk T. The adenovirus E4 17-kilodalton protein complexes with the cellular transcription factor E2F, altering its DNA-binding properties and stimulating E1A-independent accumulation of E2 mRNA. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2345–2359. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2345-2359.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Devoto S. H., Hiebert S. W., Hunter T., Pines J., Nevins J. R. Cell cycle regulation of the E2F transcription factor involves an interaction with cyclin A. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1243–1253. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90019-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mudryj M., Hiebert S. W., Nevins J. R. A role for the adenovirus inducible E2F transcription factor in a proliferation dependent signal transduction pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07387.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill S. D., Hemstrom C., Virtanen A., Nevins J. R. An adenovirus E4 gene product trans-activates E2 transcription and stimulates stable E2F binding through a direct association with E2F. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):2008–2012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neill S. D., Nevins J. R. Genetic analysis of the adenovirus E4 6/7 trans activator: interaction with E2F and induction of a stable DNA-protein complex are critical for activity. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5364–5373. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5364-5373.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Transcriptional regulation. A closer look at E2F. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):375–376. doi: 10.1038/358375a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor R. J., Hearing P. The C-terminal 70 amino acids of the adenovirus E4-ORF6/7 protein are essential and sufficient for E2F complex formation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6579–6586. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obert S., O'Connor R. J., Schmid S., Hearing P. The adenovirus E4-6/7 protein transactivates the E2 promoter by inducing dimerization of a heteromeric E2F complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1333–1346. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette M. M., Chen J., Wright W. E., Shay J. W. Complexes containing the retinoblastoma gene product recognize different DNA motifs related to the E2F binding site. Oncogene. 1992 Jun;7(6):1075–1081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Draetta G., Jansen-Dürr P. Association of cdk2 kinase with the transcription factor E2F during S phase. Science. 1992 Feb 28;255(5048):1144–1147. doi: 10.1126/science.1312258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian Y., Luckey C., Horton L., Esser M., Templeton D. J. Biological function of the retinoblastoma protein requires distinct domains for hyperphosphorylation and transcription factor binding. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5363–5372. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin X. Q., Chittenden T., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr Identification of a growth suppression domain within the retinoblastoma gene product. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):953–964. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri P., Bagchi S., Devoto S. H., Kraus V. B., Moran E., Nevins J. R. Domains of the adenovirus E1A protein required for oncogenic activity are also required for dissociation of E2F transcription factor complexes. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1200–1211. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichel R., Kovesdi I., Nevins J. R. Activation of a preexisting cellular factor as a basis for adenovirus E1A-mediated transcription control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):387–390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. K., Devoto S. H., Smith E. J., Chellappan S. P., Jakoi L., Nevins J. R. Interactions of the p107 and Rb proteins with E2F during the cell proliferation response. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1013–1020. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05742.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirodkar S., Ewen M., DeCaprio J. A., Morgan J., Livingston D. M., Chittenden T. The transcription factor E2F interacts with the retinoblastoma product and a p107-cyclin A complex in a cell cycle-regulated manner. Cell. 1992 Jan 10;68(1):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B. Two promoter-specific host factors interact with adjacent sequences in an EIA-inducible adenovirus promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6112–6116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thalmeier K., Synovzik H., Mertz R., Winnacker E. L., Lipp M. Nuclear factor E2F mediates basic transcription and trans-activation by E1a of the human MYC promoter. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):527–536. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N. J., Green S., Tasset D., Ponglikitmongkol M., Chambon P. The transcriptional activation function located in the hormone-binding domain of the human oestrogen receptor is not encoded in a single exon. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1441–1446. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03526.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The retinoblastoma gene and gene product. Cancer Surv. 1992;12:43–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Prater C. A., Dean D. C. Retinoblastoma protein switches the E2F site from positive to negative element. Nature. 1992 Jul 16;358(6383):259–261. doi: 10.1038/358259a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamanian M., La Thangue N. B. Transcriptional repression by the Rb-related protein p107. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Apr;4(4):389–396. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., van den Heuvel S., Helin K., Fattaey A., Ewen M., Livingston D., Dyson N., Harlow E. Inhibition of cell proliferation by p107, a relative of the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1111–1125. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]