Abstract
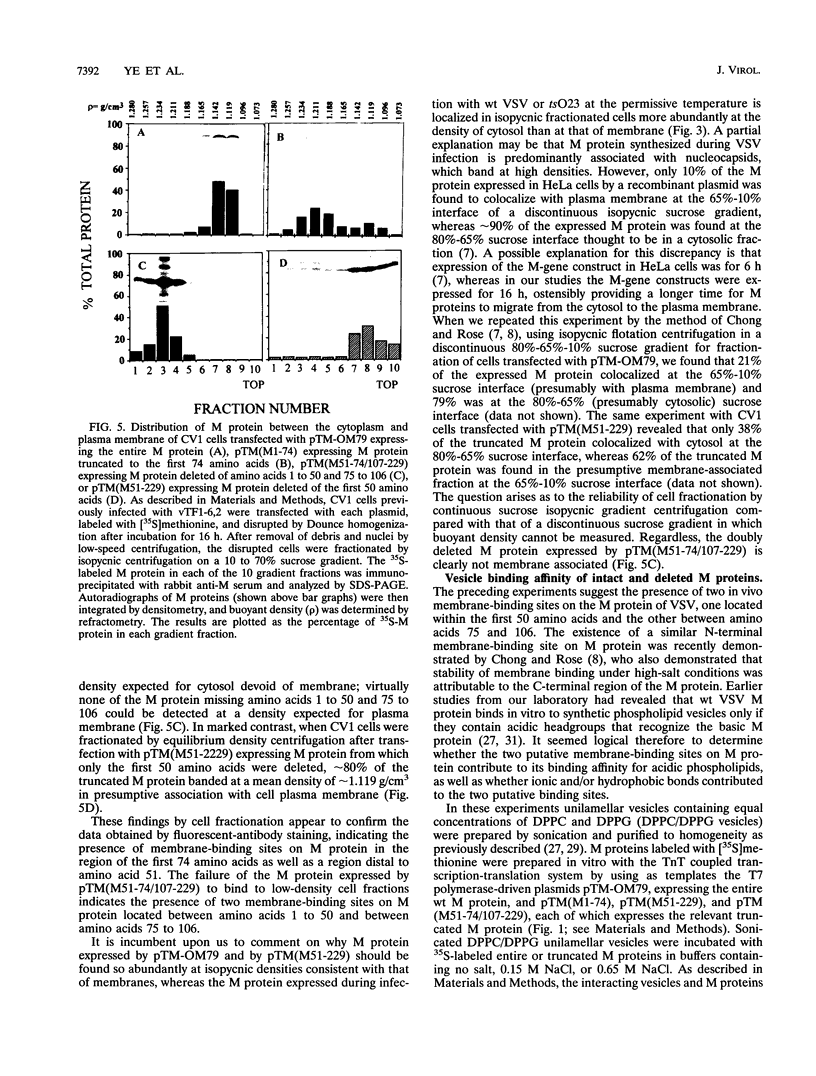
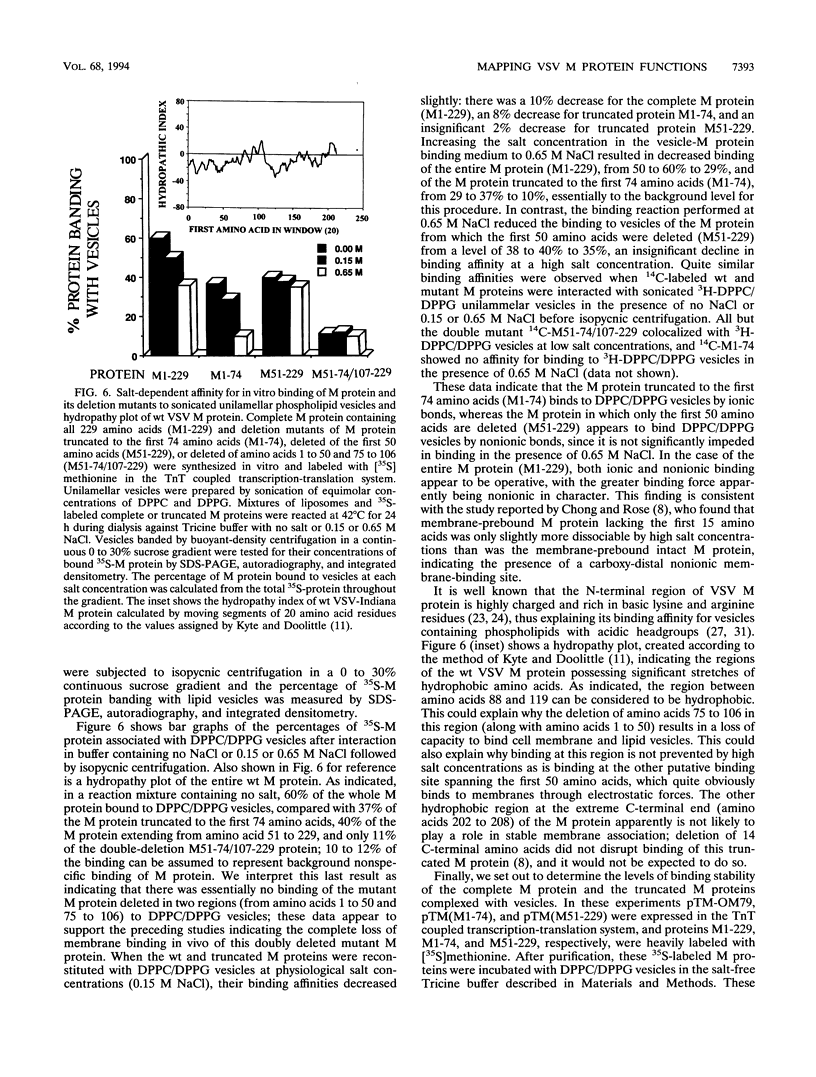
The membrane-binding affinity of the matrix (M) protein of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) was examined by comparing the cellular distribution of wild-type (wt) virus M protein with that of temperature-sensitive (ts) and deletion mutants probed by indirect fluorescent-antibody staining and fractionation of infected or plasmid-transfected CV1 cells. The M-gene mutant tsO23 caused cytopathic rounding of cells infected at permissive temperature but not of cells at the nonpermissive temperature; wt VSV also causes rounding, which prohibits study of M protein distribution by fluorescent-antibody staining. Little or no M protein can be detected in the plasma membrane of cells infected with tsO23 at the nonpermissive temperature, whereas approximately 20% of the M protein colocalized with the membrane fraction of cells infected with tsO23 at the permissive temperature. Cells transfected with a plasmid expressing intact 229-amino-acid wt M protein (M1-229) exhibited cytopathic cell rounding and actin filament dissolution, whereas cells retained normal polygonal morphology and actin filaments when transfected with plasmids expressing M proteins truncated to the first 74 N-terminal amino acids (M1-74) or deleted of the first 50 amino acids (M51-229) or amino acids 1 to 50 and 75 to 106 (M51-74/107-229). Truncated proteins M1-74 and M51-229 were readily detectable in the plasma membrane and cytosol of transfected cells as determined by both fluorescent-antibody staining and cell fractionation, as was the plasmid-expressed intact wt M protein. However, the expressed doubly deleted protein M51-74/107-229 could not be detected in plasma membrane by fluorescent-antibody staining or by cell fractionation, suggesting the presence of two membrane-binding sites spanning the region of amino acids 1 to 50 and amino acids 75 to 106 of the VSV M protein. These in vivo data were confirmed by an in vitro binding assay in which intact M protein and its deletion mutants were reconstituted in high- or low-ionic-strength buffers with synthetic membranes in the form of sonicated unilammelar vesicles. The results of these experiments appear to confirm the presence of two membrane-binding sites on the VSV M protein, one binding peripherally by electrostatic forces at the highly charged NH2 terminus and the other stably binding membrane integration of hydrophobic amino acids and located by a hydropathy plot between amino acids 88 and 119.
Full text
PDF


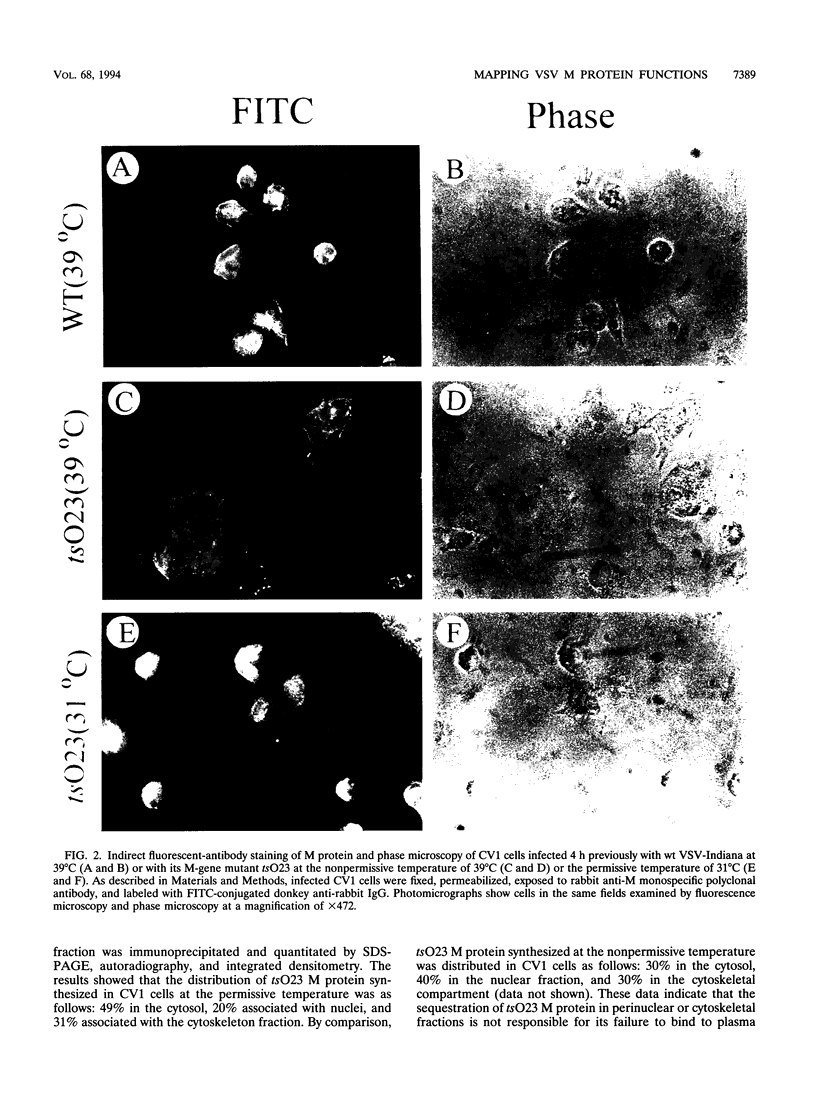
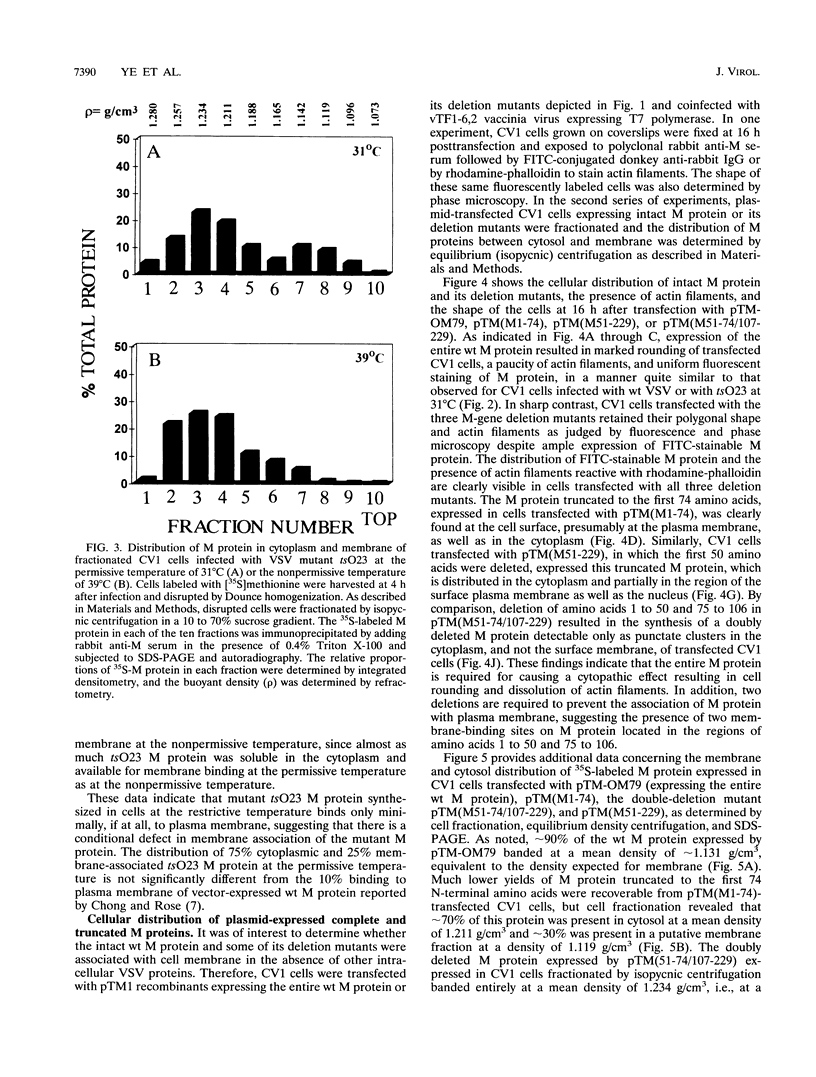
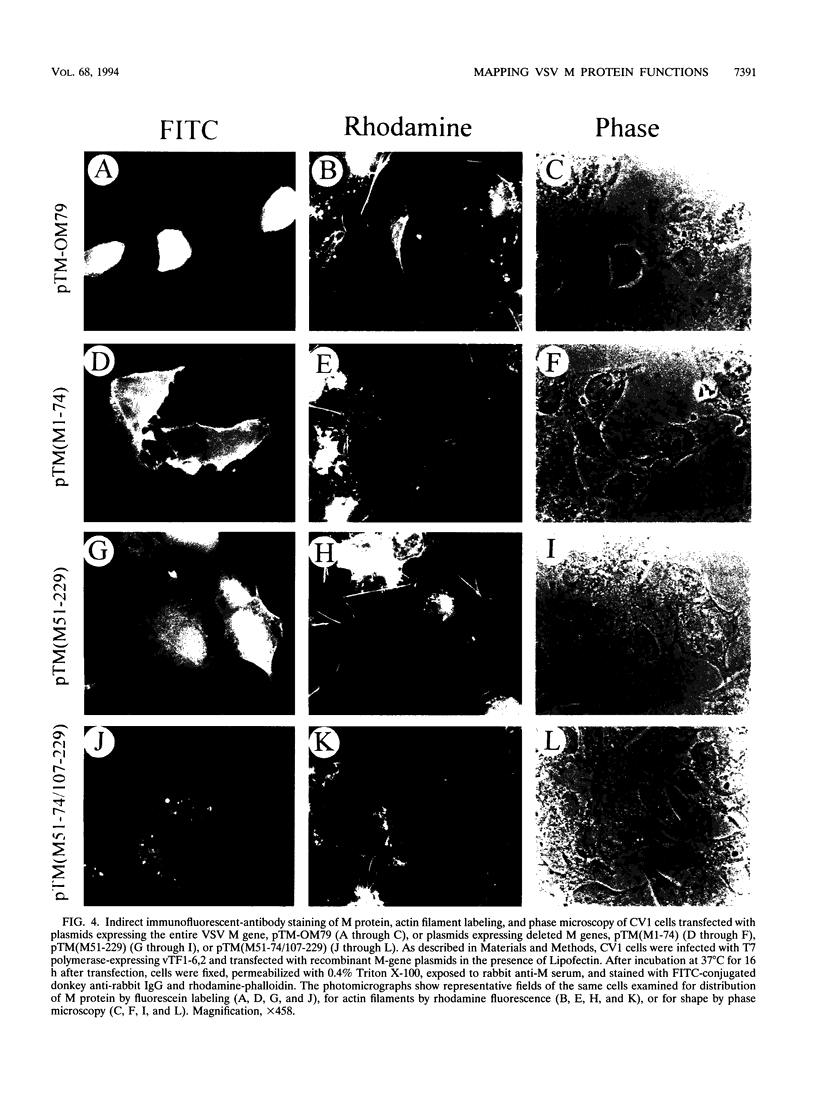



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barenholz Y., Moore N. F., Wagner R. R. Enveloped viruses as model membrane systems: microviscosity of vesicular stomatitis virus and host cell membranes. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 10;15(16):3563–3570. doi: 10.1021/bi00661a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barge A., Gaudin Y., Coulon P., Ruigrok R. W. Vesicular stomatitis virus M protein may be inside the ribonucleocapsid coil. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7246–7253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7246-7253.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann J. E., Fusco P. J. The M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus associates specifically with the basolateral membranes of polarized epithelial cells independently of the G protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1707–1715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black B. L., Lyles D. S. Vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein inhibits host cell-directed transcription of target genes in vivo. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4058–4064. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4058-4064.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blondel D., Harmison G. G., Schubert M. Role of matrix protein in cytopathogenesis of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1716–1725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1716-1725.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll A. R., Wagner R. R. Role of the membrane (M) protein in endogenous inhibition of in vitro transcription by vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):134–142. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.134-142.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong L. D., Rose J. K. Interactions of normal and mutant vesicular stomatitis virus matrix proteins with the plasma membrane and nucleocapsids. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):441–447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.441-447.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong L. D., Rose J. K. Membrane association of functional vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein in vivo. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):407–414. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.407-414.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubovi E. J., Wagner R. R. Spatial relationships of the proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus: induction of reversible oligomers by cleavable protein cross-linkers and oxidation. J Virol. 1977 May;22(2):500–509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.2.500-509.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaptur P. E., Rhodes R. B., Lyles D. S. Sequences of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein involved in binding to nucleocapsids. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1057–1065. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1057-1065.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Vanderoef R. Localization of the membrane-associated region of vesicular stomatitis virus M protein at the N terminus, using the hydrophobic, photoreactive probe 125I-TID. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3486–3491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3486-3491.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Luo L. Z., Wagner R. R. Transcription inhibition site on the M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus located by marker rescue of mutant tsO23(III) with M-gene expression vectors. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2841–2843. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2841-2843.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Luo L., Schubert M., Wagner R. R., Kang C. Y. Viral liposomes released from insect cells infected with recombinant baculovirus expressing the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):4415–4420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.4415-4420.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles D. S., McKenzie M., Parce J. W. Subunit interactions of vesicular stomatitis virus envelope glycoprotein stabilized by binding to viral matrix protein. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):349–358. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.349-358.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyles D. S., Puddington L., McCreedy B. J., Jr Vesicular stomatitis virus M protein in the nuclei of infected cells. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4387–4392. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4387-4392.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancarella D. A., Lenard J. Interactions of wild-type and mutant M protein of vesicular stomatitis virus with viral nucleocapsid and envelope in intact virions. Evidence from [125I]iodonaphthyl azide labeling and specific cross-linking. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6872–6877. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Elroy-Stein O., Mizukami T., Alexander W. A., Fuerst T. R. Product review. New mammalian expression vectors. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):91–92. doi: 10.1038/348091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb W. W., Brown J. C. Role of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein in maintaining the viral nucleocapsid in the condensed form found in native virions. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):295–299. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.295-299.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogden J. R., Pal R., Wagner R. R. Mapping regions of the matrix protein of vesicular stomatitis virus which bind to ribonucleocapsids, liposomes, and monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):860–868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.860-868.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Dubois-Dalcq M. E., Schubert M., Lazzarini R. A. A mutated membrane protein of vesicular stomatitis virus has an abnormal distribution within the infected cell and causes defective budding. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1332–1341. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1332-1341.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley J. B., Pal R., Wagner R. R. Antigenicity, function, and conformation of synthetic oligopeptides corresponding to amino-terminal sequences of wild-type and mutant matrix proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2569–2577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2569-2577.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D., Newcomb W. W., Brown J. C., Wall J. S., Hainfeld J. F., Trus B. L., Steven A. C. Mass and molecular composition of vesicular stomatitis virus: a scanning transmission electron microscopy analysis. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):598–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.598-607.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener J. R., Pal R., Barenholz Y., Wagner R. R. Effect of the vesicular stomatitis virus matrix protein on the lateral organization of lipid bilayers containing phosphatidylglycerol: use of fluorescent phospholipid analogues. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 17;24(26):7651–7658. doi: 10.1021/bi00347a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Lenard J. Interaction of wild-type and mutant M protein vesicular stomatitis virus with nucleocapsids in vitro. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 3;20(5):1349–1354. doi: 10.1021/bi00508a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye Z. P., Pal R., Fox J. W., Wagner R. R. Functional and antigenic domains of the matrix (M1) protein of influenza A virus. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):239–246. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.239-246.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakowski J. J., Petri W. A., Jr, Wagner R. R. Role of matrix protein in assembling the membrane of vesicular stomatitis virus: reconstitution of matrix protein with negatively charged phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1981 Jun 23;20(13):3902–3907. doi: 10.1021/bi00516a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakowski J. J., Wagner R. R. Localization of membrane-associated proteins in vesicular stomatitis virus by use of hydrophobic membrane probes and cross-linking reagents. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):93–102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.93-102.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]