Abstract
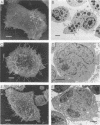
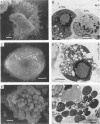
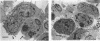
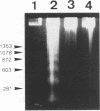
Morphological changes of mouse hepatitis virus-infected J774.1 cells cocultured with cloned mouse hepatitis virus-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes were examined by electron microscopy. Condensation and margination of chromatin, cellular shrinkage with severe vacuolar degeneration, and blebbing were observed. In addition, fragmentation of cellular DNA was observed, and a decrease in virus titer was accompanied by those changes. These findings show that the cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes induce in the target cell an internal degradation program termed apoptosis, which results in virus clearance.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apasov S., Redegeld F., Sitkovsky M. Cell-mediated cytotoxicity: contact and secreted factors. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Jun;5(3):404–410. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90060-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Dalziel R. G., Koolen M. J. Coronavirus-induced CNS disease: a model for virus-induced demyelination. J Neuroimmunol. 1988 Dec;20(2-3):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(88)90141-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrows S. R., Fernan A., Argaet V., Suhrbier A. Bystander apoptosis induced by CD8+ cytotoxic T cell (CTL) clones: implications for CTL lytic mechanisms. Int Immunol. 1993 Sep;5(9):1049–1058. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.9.1049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne J. A., Oldstone M. B. Biology of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: clearance of virus in vivo. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.682-686.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C., Fadok V. A., Sellins K. S. Apoptosis and programmed cell death in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1992;10:267–293. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.10.040192.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dealtry G. B., Naylor M. S., Fiers W., Balkwill F. R. DNA fragmentation and cytotoxicity caused by tumor necrosis factor is enhanced by interferon-gamma. Eur J Immunol. 1987 May;17(5):689–693. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Wang F. I., Trousdale M. D., Hinton D. R., Stohlman S. A. Interaction of immune and central nervous systems: contribution of anti-viral Thy-1+ cells to demyelination induced by coronavirus JHM. Reg Immunol. 1993 Jan-Feb;5(1):37–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackett C. J., Sullivan K., Lin Y. L. Ultrastructure of an influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T-cell clone and its interaction with P815 and macrophage targets. Cell Immunol. 1982 Apr;68(2):276–286. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heusel J. W., Wesselschmidt R. L., Shresta S., Russell J. H., Ley T. J. Cytotoxic lymphocytes require granzyme B for the rapid induction of DNA fragmentation and apoptosis in allogeneic target cells. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):977–987. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90376-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klavinskis L. S., Geckeler R., Oldstone M. B. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte control of acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection: interferon gamma, but not tumour necrosis factor alpha, displays antiviral activity in vivo. J Gen Virol. 1989 Dec;70(Pt 12):3317–3325. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-12-3317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukacher A. E., Braciale V. L., Braciale T. J. In vivo effector function of influenza virus-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones is highly specific. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):814–826. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martz E., Howell D. M. CTL: virus control cells first and cytolytic cells second? DNA fragmentation, apoptosis and the prelytic halt hypothesis. Immunol Today. 1989 Mar;10(3):79–86. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90231-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullbacher A., Ada G. L. How do cytotoxic T lymphocytes work in vivo? Microb Pathog. 1987 Nov;3(5):315–318. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(87)90001-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono N., Ko K. K., Hosaka Y. Ultrastructural changes during lysis of L929 target cells by class II-restricted influenza virus-specific murine cytotoxic T-lymphocyte clones. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2442–2447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2442-2447.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson S., Byrne J. A., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Morphologic analysis of the interactions between lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-specific cloned cytotoxic T cells and virus infected targets. Lab Invest. 1987 Jul;57(1):29–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. H., Dobos C. B. Mechanisms of immune lysis. II. CTL-induced nuclear disintegration of the target begins within minutes of cell contact. J Immunol. 1980 Sep;125(3):1256–1261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. L., Barthold S. W., de Souza M. S., Bottomly K. The role of gamma interferon in infection of susceptible mice with murine coronavirus, MHV-JHM. Arch Virol. 1991;121(1-4):89–100. doi: 10.1007/BF01316746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Kingston R., Jenkinson E. J., Owen J. J. Antibodies to CD3/T-cell receptor complex induce death by apoptosis in immature T cells in thymic cultures. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):181–184. doi: 10.1038/337181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Takahashi T., Golstein P., Nagata S. Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor family. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1169–1178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90326-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A., Bodmer H. Antigen recognition by class I-restricted T lymphocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:601–624. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. M., Nishioka W. K., Antia R., Dundon P. L. Mechanism of killing by virus-induced cytotoxic T lymphocytes elicited in vivo. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3726–3733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3726-3733.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Goto N., Kyuwa S., Hayami M., Toyoda Y. Protection of mice from a lethal coronavirus infection in the central nervous system by adoptive transfer of virus-specific T cell clones. J Neuroimmunol. 1991 Apr;32(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(91)90065-F. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi K., Kyuwa S., Nakanaga K., Hayami M. Establishment of cytotoxic T-cell clones specific for cells infected with mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2505–2507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2505-2507.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]