Abstract
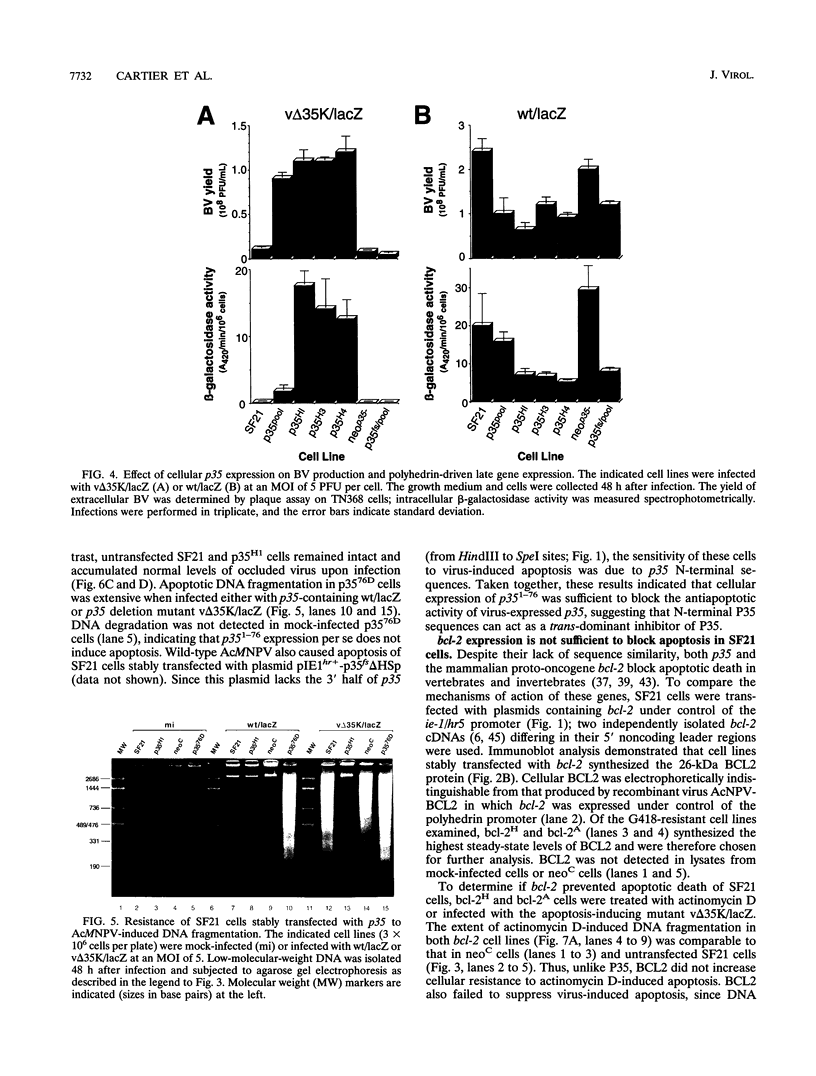
Expression of p35 from the DNA genome of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcMNPV) suppresses virus-induced apoptosis and promotes virus replication in Spodoptera frugiperda (SF21) cells. To examine the molecular mechanism by which p35 prevents apoptosis in insects, SF21 cells were stably transfected with p35. Neomycin-resistant cell lines that synthesized protein P35 were identified. Stable transfection with p35 protected SF21 cells from apoptosis induced by actinomycin D concentrations that caused apoptotic death of untransfected cells. Cellular expression of p35 also blocked apoptosis induced by infection with p35 null mutants and restored mutant replication to levels comparable to those of wild-type virus. In contrast, stable expression of the mammalian death suppressor bcl-2 failed to block actinomycin D- or AcMNPV-induced apoptosis. Thus, p35 was sufficient to prevent apoptosis, whereas bcl-2 was not, suggesting that the activities of the two nonhomologous death regulators are functionally distinct. Stable expression of the truncation mutant p35(1-76), containing the N terminus of p35, failed to block apoptosis. However, p35(1-76) interfered with p35 antiapoptotic activity, since stably transfected cells underwent apoptosis upon infection with wild-type AcMNPV. Despite normal levels of viral p35 transcription, P35 levels were selectively reduced during infection. Thus, p35(1-76) acted as a dominant inhibitor by directly or indirectly affecting the synthesis or stability of viral P35. These results suggested that the N terminus of P35 constitutes a functional domain which is required to interact with other proteins, possibly host invertebrate death regulators or P35 itself.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alnemri E. S., Robertson N. M., Fernandes T. F., Croce C. M., Litwack G. Overexpressed full-length human BCL2 extends the survival of baculovirus-infected Sf9 insect cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7295–7299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Clem R. J., Miller L. K. An apoptosis-inhibiting gene from a nuclear polyhedrosis virus encoding a polypeptide with Cys/His sequence motifs. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2521–2528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2521-2528.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J., Roizman B. The gamma 1(34.5) gene of herpes simplex virus 1 precludes neuroblastoma cells from triggering total shutoff of protein synthesis characteristic of programed cell death in neuronal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3266–3270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Smith S. D., Sklar J. Cloning and structural analysis of cDNAs for bcl-2 and a hybrid bcl-2/immunoglobulin transcript resulting from the t(14;18) translocation. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clem R. J., Fechheimer M., Miller L. K. Prevention of apoptosis by a baculovirus gene during infection of insect cells. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1388–1390. doi: 10.1126/science.1962198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clem R. J., Miller L. K. Apoptosis reduces both the in vitro replication and the in vivo infectivity of a baculovirus. J Virol. 1993 Jul;67(7):3730–3738. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.7.3730-3738.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crook N. E., Clem R. J., Miller L. K. An apoptosis-inhibiting baculovirus gene with a zinc finger-like motif. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2168–2174. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2168-2174.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson J. A., Friesen P. D. Identification of upstream promoter elements mediating early transcription from the 35,000-molecular-weight protein gene of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4006–4016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4006-4016.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Divergent transcription of early 35- and 94-kilodalton protein genes encoded by the HindIII K genome fragment of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2264–2272. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2264-2272.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardini V., Fernandez P. A., Lee R. K., Drexler H. C., Rotello R. J., Fishman M. C., Yuan J. Prevention of vertebrate neuronal death by the crmA gene. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):826–828. doi: 10.1126/science.8303301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Interspersed Homologous DNA of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Enhances Delayed-Early Gene Expression. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):215–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.215-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haldar S., Beatty C., Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. The bcl-2 gene encodes a novel G protein. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):195–198. doi: 10.1038/342195a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S., Huen D., Rowe M., Dawson C., Johnson G., Rickinson A. Epstein-Barr virus-coded BHRF1 protein, a viral homologue of Bcl-2, protects human B cells from programmed cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8479–8483. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner M. O., Ellis R. E., Horvitz H. R. Caenorhabditis elegans gene ced-9 protects cells from programmed cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):494–499. doi: 10.1038/356494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner M. O., Horvitz H. R. C. elegans cell survival gene ced-9 encodes a functional homolog of the mammalian proto-oncogene bcl-2. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):665–676. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90506-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershberger P. A., Dickson J. A., Friesen P. D. Site-specific mutagenesis of the 35-kilodalton protein gene encoded by Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus: cell line-specific effects on virus replication. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5525–5533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5525-5533.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershberger P. A., LaCount D. J., Friesen P. D. The apoptotic suppressor P35 is required early during baculovirus replication and is targeted to the cytosol of infected cells. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3467–3477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3467-3477.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hink W. F. Established insect cell line from the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni. Nature. 1970 May 2;226(5244):466–467. doi: 10.1038/226466b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinshaw V. S., Olsen C. W., Dybdahl-Sissoko N., Evans D. Apoptosis: a mechanism of cell killing by influenza A and B viruses. J Virol. 1994 Jun;68(6):3667–3673. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.6.3667-3673.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A. W., Faulkner P. Monoclonal antibodies to baculovirus structural proteins: determination of specificities by Western blot analysis. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):432–444. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida Y., Agata Y., Shibahara K., Honjo T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3887–3895. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05481.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L. Effects of baculovirus infection on IE1-mediated foreign gene expression in stably transformed insect cells. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2583–2591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2583-2591.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis D. L., Fleming J. A., Kovacs G. R., Summers M. D., Guarino L. A. Use of early baculovirus promoters for continuous expression and efficient processing of foreign gene products in stably transformed lepidopteran cells. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Oct;8(10):950–955. doi: 10.1038/nbt1090-950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeurissen S. H., Wagenaar F., Pol J. M., van der Eb A. J., Noteborn M. H. Chicken anemia virus causes apoptosis of thymocytes after in vivo infection and of cell lines after in vitro infection. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7383–7388. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7383-7388.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamita S. G., Majima K., Maeda S. Identification and characterization of the p35 gene of Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus that prevents virus-induced apoptosis. J Virol. 1993 Jan;67(1):455–463. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.1.455-463.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane D. J., Sarafian T. A., Anton R., Hahn H., Gralla E. B., Valentine J. S., Ord T., Bredesen D. E. Bcl-2 inhibition of neural death: decreased generation of reactive oxygen species. Science. 1993 Nov 19;262(5137):1274–1277. doi: 10.1126/science.8235659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent-Crawford A. G., Krust B., Muller S., Rivière Y., Rey-Cuillé M. A., Béchet J. M., Montagnier L., Hovanessian A. G. The cytopathic effect of HIV is associated with apoptosis. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):829–839. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90554-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. H., Miller L. K. Isolation of genotypic variants of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):754–767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.754-767.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerch R. A., Friesen P. D. The 35-kilodalton protein gene (p35) of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus and the neomycin resistance gene provide dominant selection of recombinant baculoviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Apr 25;21(8):1753–1760. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.8.1753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B., Huang Q., Isaacs J. T., Reed J. C., Griffin D. E., Hardwick J. M. Conversion of lytic to persistent alphavirus infection by the bcl-2 cellular oncogene. Nature. 1993 Feb 25;361(6414):739–742. doi: 10.1038/361739a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen M. S., Friesen P. D. Molecular analysis of the transcriptional regulatory region of an early baculovirus gene. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):493–503. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.493-503.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabizadeh S., LaCount D. J., Friesen P. D., Bredesen D. E. Expression of the baculovirus p35 gene inhibits mammalian neural cell death. J Neurochem. 1993 Dec;61(6):2318–2321. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb07477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L., Debbas M., Sabbatini P., Hockenbery D., Korsmeyer S., White E. The adenovirus E1A proteins induce apoptosis, which is inhibited by the E1B 19-kDa and Bcl-2 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7742–7746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodems S. M., Friesen P. D. The hr5 transcriptional enhancer stimulates early expression from the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome but is not required for virus replication. J Virol. 1993 Oct;67(10):5776–5785. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.10.5776-5785.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheffner M., Werness B. A., Huibregtse J. M., Levine A. J., Howley P. M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1129–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto A., Friesen P. D., Rothman J. H. Baculovirus p35 prevents developmentally programmed cell death and rescues a ced-9 mutant in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. EMBO J. 1994 May 1;13(9):2023–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06475.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa T., Matsukawa S., Higuchi Y., Nakamura S., Nakanishi Y., Fukuda R. Induction of programmed cell death (apoptosis) by influenza virus infection in tissue culture cells. J Gen Virol. 1993 Nov;74(Pt 11):2347–2355. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-74-11-2347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto Y., Croce C. M. Analysis of the structure, transcripts, and protein products of bcl-2, the gene involved in human follicular lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5214–5218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. L., Goodwin R. H., Tompkins G. J., McCawley P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro. 1977 Apr;13(4):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02615077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Haecker G., Strasser A. An evolutionary perspective on apoptosis. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):777–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Weissman I. L., Kim S. K. Prevention of programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans by human bcl-2. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1955–1957. doi: 10.1126/science.1470921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White E. Regulation of apoptosis by the transforming genes of the DNA tumor virus adenovirus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1993 Oct;204(1):30–39. doi: 10.3181/00379727-204-43631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin X. M., Oltvai Z. N., Korsmeyer S. J. BH1 and BH2 domains of Bcl-2 are required for inhibition of apoptosis and heterodimerization with Bax. Nature. 1994 May 26;369(6478):321–323. doi: 10.1038/369321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong L. T., Sarafian T., Kane D. J., Charles A. C., Mah S. P., Edwards R. H., Bredesen D. E. bcl-2 inhibits death of central neural cells induced by multiple agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]