Abstract
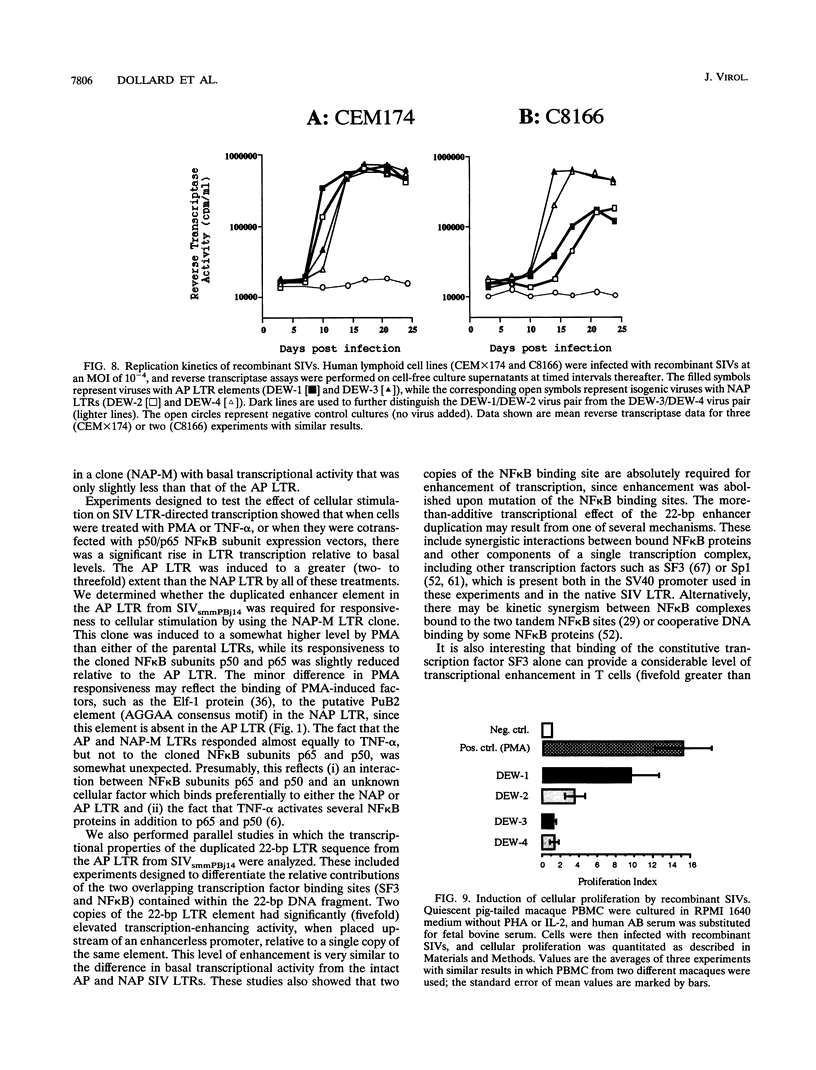
Infection with a variant of simian immunodeficiency virus, SIVsmmPBj14, leads to severe acute disease in macaques. This study was designed to investigate the functional significance of previously described mutations in the viral long terminal repeat (LTR) and to elucidate their contribution to the unique phenotype of SIVsmmPBj14. LTR-directed transcription was measured by using luciferase reporter constructs that were transiently transfected into cultured cells. In a wide range of cell types, the basal transcriptional activity of the LTR from SIVsmmPBj14 was found to be 2- to 4.5-fold higher than that of an LTR from a non-acutely pathogenic strain. These LTRs differ by five point mutations and a 22-bp duplication in SIVsmmPBj14, which includes a nuclear factor kappa B (NF kappa B) site. Transcriptional differences between these LTRs were further enhanced by two- to threefold upon treatment of cells with phorbol ester or tumor necrosis factor alpha or by cotransfection with plasmids expressing NF kappa B subunits. Mutagenesis studies, and the use of a reporter construct containing an enhancerless promoter, indicate that these transcriptional effects are due principally to the 22-bp sequence duplication and the NF kappa B site contained within it. Finally, infectious virus stocks that were isogenic except for the LTR were generated. The LTR from SIVsmmPBj14 was found to confer an increase in the kinetics of virus replication in cultured cells. Inclusion of this LTR in recombinant SIVs also resulted in a two- to threefold rise in the extent of cellular proliferation that was induced in quiescent simian peripheral blood mononuclear cells. These studies are consistent with the hypothesis that LTR mutations assist SIVsmmPBj14 in responding efficiently to cellular stimulation and allow it to replicate to high titers during the acute phase of viral infection.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson M. G., Clements J. E. Comparison of the transcriptional activity of the long terminal repeats of simian immunodeficiency viruses SIVmac251 and SIVmac239 in T-cell lines and macrophage cell lines. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):51–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.51-60.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson M. G., Clements J. E. Two strains of SIVmac show differential transactivation mediated by sequences in the promoter. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90231-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aukrust P., Liabakk N. B., Müller F., Lien E., Espevik T., Frøland S. S. Serum levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) and soluble TNF receptors in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection--correlations to clinical, immunologic, and virologic parameters. J Infect Dis. 1994 Feb;169(2):420–424. doi: 10.1093/infdis/169.2.420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Baldwin A. S., Jr Activation of multiple NF-kappa B/Rel DNA-binding complexes by tumor necrosis factor. Oncogene. 1994 May;9(5):1487–1492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellas R. E., Hopkins N., Li Y. The NF-kappa B binding site is necessary for efficient replication of simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques in primary macrophages but not in T cells in vitro. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2908–2913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2908-2913.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birx D. L., Lewis M. G., Vahey M., Tencer K., Zack P. M., Brown C. R., Jahrling P. B., Tosato G., Burke D., Redfield R. Association of interleukin-6 in the pathogenesis of acutely fatal SIVsmm/PBj-14 in pigtailed macaques. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Nov;9(11):1123–1129. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.1123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birx D. L., Redfield R. R., Tencer K., Fowler A., Burke D. S., Tosato G. Induction of interleukin-6 during human immunodeficiency virus infection. Blood. 1990 Dec 1;76(11):2303–2310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswas D. K., Ahlers C. M., Dezube B. J., Pardee A. B. Cooperative inhibition of NF-kappa B and Tat-induced superactivation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11044–11048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. J., Saag M. S., Decker W. D., Campbell-Hill S., Roberson J. L., Veldkamp P. J., Kappes J. C., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M. High titers of cytopathic virus in plasma of patients with symptomatic primary HIV-1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 4;324(14):954–960. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104043241404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. A., Gold J., Maclean P., Donovan B., Finlayson R., Barnes T. G., Michelmore H. M., Brooke P., Penny R. Acute AIDS retrovirus infection. Definition of a clinical illness associated with seroconversion. Lancet. 1985 Mar 9;1(8428):537–540. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)91205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courgnaud V., Lauré F., Fultz P. N., Montagnier L., Bréchot C., Sonigo P. Genetic differences accounting for evolution and pathogenicity of simian immunodeficiency virus from a sooty mangabey monkey after cross-species transmission to a pig-tailed macaque. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):414–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.414-419.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar E. S., Moudgil T., Meyer R. D., Ho D. D. Transient high levels of viremia in patients with primary human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 1991 Apr 4;324(14):961–964. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199104043241405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Embretson J. E., Anderson D. C., Mullins J. I., Fultz P. N. Sequence analysis and acute pathogenicity of molecularly cloned SIVSMM-PBj14. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):636–640. doi: 10.1038/345636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Embretson J. E., Fultz P. N., Mullins J. I. Molecular clones from a non-acutely pathogenic derivative of SIVsmmPBj14: characterization and comparison to acutely pathogenic clones. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Jun;8(6):1179–1187. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue P. R., Quackenbush S. L., Gallo M. V., deNoronha C. M., Overbaugh J., Hoover E. A., Mullins J. I. Viral genetic determinants of T-cell killing and immunodeficiency disease induction by the feline leukemia virus FeLV-FAIDS. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4461–4469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4461-4469.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh E. J., Maury W. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Rabson A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embretson J., Zupancic M., Ribas J. L., Burke A., Racz P., Tenner-Racz K., Haase A. T. Massive covert infection of helper T lymphocytes and macrophages by HIV during the incubation period of AIDS. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):359–362. doi: 10.1038/362359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton R., Plumb M., Shield L., Neil J. C. Structural diversity and nuclear protein binding sites in the long terminal repeats of feline leukemia virus. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1675–1682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1675-1682.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N., McClure H. M., Anderson D. C., Switzer W. M. Identification and biologic characterization of an acutely lethal variant of simian immunodeficiency virus from sooty mangabeys (SIV/SMM). AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1989 Aug;5(4):397–409. doi: 10.1089/aid.1989.5.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fultz P. N. Replication of an acutely lethal simian immunodeficiency virus activates and induces proliferation of lymphocytes. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4902–4909. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4902-4909.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S., Traktman P., Baltimore D. Isolation and properties of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants: use of a rapid assay for release of virion reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.239-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannibal M. C., Markovitz D. M., Clark N., Nabel G. J. Differential activation of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and 2 transcription by specific T-cell activation signals. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):5035–5040. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.5035-5040.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschlag D., Johnson F. B. Synergism in transcriptional activation: a kinetic view. Genes Dev. 1993 Feb;7(2):173–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.2.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi R., Krummel B., Saiki R. K. A general method of in vitro preparation and specific mutagenesis of DNA fragments: study of protein and DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7351–7367. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Thomas C. Y., Chattopadhyay S. K., Koehne C., O'Donnell P. V. Influence of enhancer sequences on thymotropism and leukemogenicity of mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1284–1292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1284-1292.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel Z. R., Dean G. A., Maul D. H., O'Neil S. P., Dreitz M. J., Mullins J. I., Fultz P. N., Hoover E. A. Early pathogenesis of disease caused by SIVsmmPBj14 molecular clone 1.9 in macaques. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1993 Mar;9(3):277–286. doi: 10.1089/aid.1993.9.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi S., Hamamoto Y., Kobayashi N., Yamamoto N. Serum level of TNF alpha in HIV-infected individuals. AIDS. 1990 Feb;4(2):169–170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang S. M., Weeger M., Stahl-Hennig C., Coulibaly C., Hunsmann G., Müller J., Müller-Hermelink H., Fuchs D., Wachter H., Daniel M. M. Importance of vpr for infection of rhesus monkeys with simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1993 Feb;67(2):902–912. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.2.902-912.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Bindereif A., Green M. R. A small-scale procedure for preparation of nuclear extracts that support efficient transcription and pre-mRNA splicing. Gene Anal Tech. 1988 Mar-Apr;5(2):22–31. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(88)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Wang C. Y., Petryniak B., Markovitz D. M., Nabel G. J., Thompson C. B. A novel Ets-related transcription factor, Elf-1, binds to human immunodeficiency virus type 2 regulatory elements that are required for inducible trans activation in T cells. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5890–5897. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5890-5897.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J., Parrott C., Buckler-White A. J., Turner W., Ross E. K., Martin M. A., Rabson A. B. The NF-kappa B binding sites in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat are not required for virus infectivity. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4919–4924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4919-4924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letvin N. L., King N. W. Immunologic and pathologic manifestations of the infection of rhesus monkeys with simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(11):1023–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. G., Zack P. M., Elkins W. R., Jahrling P. B. Infection of rhesus and cynomolgus macaques with a rapidly fatal SIV (SIVSMM/PBj) isolate from sooty mangabeys. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Sep;8(9):1631–1639. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.1631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Golemis E., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Disease specificity of nondefective Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses is controlled by a small number of nucleotides. J Virol. 1987 Mar;61(3):693–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.3.693-700.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Greene W. C. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces proteins that bind specifically to kappa B-like enhancer elements and regulate interleukin 2 receptor alpha-chain gene expression in primary human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2331–2335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makonkawkeyoon S., Limson-Pobre R. N., Moreira A. L., Schauf V., Kaplan G. Thalidomide inhibits the replication of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markovitz D. M., Smith M. J., Hilfinger J., Hannibal M. C., Petryniak B., Nabel G. J. Activation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 enhancer is dependent on purine box and kappa B regulatory elements. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5479–5484. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5479-5484.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure H. M., Anderson D. C., Fultz P. N., Ansari A. A., Lockwood E., Brodie A. Spectrum of disease in macaque monkeys chronically infected with SIV/SMM. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 May;21(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0165-2427(89)90126-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto K., Tomita N., Hayashi K., Akagi T. Transformation of animal cells with human T-cell leukemia virus type II. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1990 Aug;81(8):720–722. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1990.tb02634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K. Luciferase reporter gene vectors for analysis of promoters and enhancers. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):454–458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novembre F. J., Johnson P. R., Lewis M. G., Anderson D. C., Klumpp S., McClure H. M., Hirsch V. M. Multiple viral determinants contribute to pathogenicity of the acutely lethal simian immunodeficiency virus SIVsmmPBj variant. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2466–2474. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2466-2474.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Demarest J. F., Butini L., Montroni M., Fox C. H., Orenstein J. M., Kotler D. P., Fauci A. S. HIV infection is active and progressive in lymphoid tissue during the clinically latent stage of disease. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):355–358. doi: 10.1038/362355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins N. D., Edwards N. L., Duckett C. S., Agranoff A. B., Schmid R. M., Nabel G. J. A cooperative interaction between NF-kappa B and Sp1 is required for HIV-1 enhancer activation. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3551–3558. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06029.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poli G., Bressler P., Kinter A., Duh E., Timmer W. C., Rabson A., Justement J. S., Stanley S., Fauci A. S. Interleukin 6 induces human immunodeficiency virus expression in infected monocytic cells alone and in synergy with tumor necrosis factor alpha by transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms. J Exp Med. 1990 Jul 1;172(1):151–158. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann K. A., Tenner-Racz K., Racz P., Montefiori D. C., Yasutomi Y., Lin W., Ransil B. J., Letvin N. L. Immunopathogenic events in acute infection of rhesus monkeys with simian immunodeficiency virus of macaques. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2362–2370. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2362-2370.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renjifo B., Speck N. A., Winandy S., Hopkins N., Li Y. cis-acting elements in the U3 region of a simian immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3130–3134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3130-3134.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roederer M., Staal F. J., Raju P. A., Ela S. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Cytokine-stimulated human immunodeficiency virus replication is inhibited by N-acetyl-L-cysteine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4884–4888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwiebert R., Fultz P. N. Immune activation and viral burden in acute disease induced by simian immunodeficiency virus SIVsmmPBj14: correlation between in vitro and in vivo events. J Virol. 1994 Sep;68(9):5538–5547. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.9.5538-5547.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsujimoto H., Komuro A., Iijima K., Miyamoto J., Ishikawa K., Hayami M. Isolation of simian retroviruses closely related to human T-cell leukemia virus by establishment of lymphoid cell lines from various non-human primates. Int J Cancer. 1985 Mar 15;35(3):377–384. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viglianti G. A., Mullins J. I. Functional comparison of transactivation by simian immunodeficiency virus from rhesus macaques and human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4523–4532. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4523-4532.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Flores P., Gutman A., Wasylyk B. PEA3 is a nuclear target for transcription activation by non-nuclear oncogenes. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3371–3378. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08500.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winandy S., Renjifo B., Li Y., Hopkins N. Nuclear factors that bind two regions important to transcriptional activity of the simian immunodeficiency virus long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5216–5223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5216-5223.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Hoff M. J., Moorman A. F., Lamers W. H. Electroporation in 'intracellular' buffer increases cell survival. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 11;20(11):2902–2902. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.11.2902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]