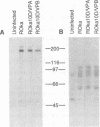
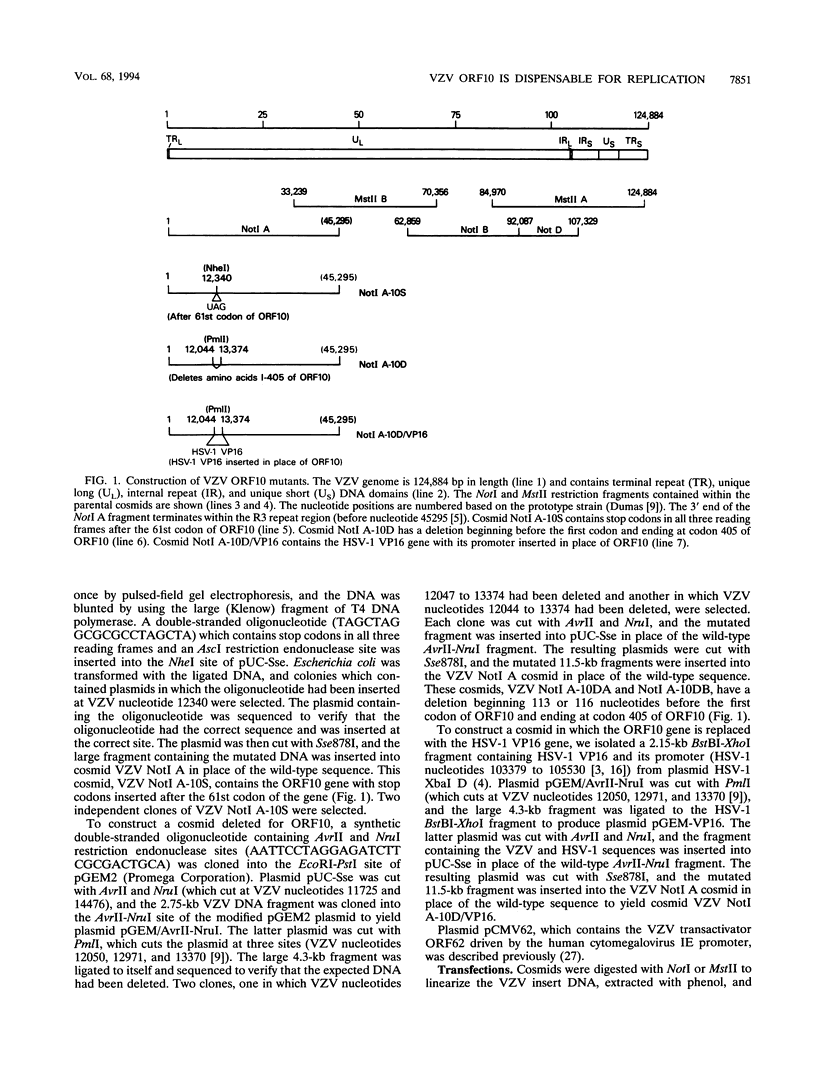
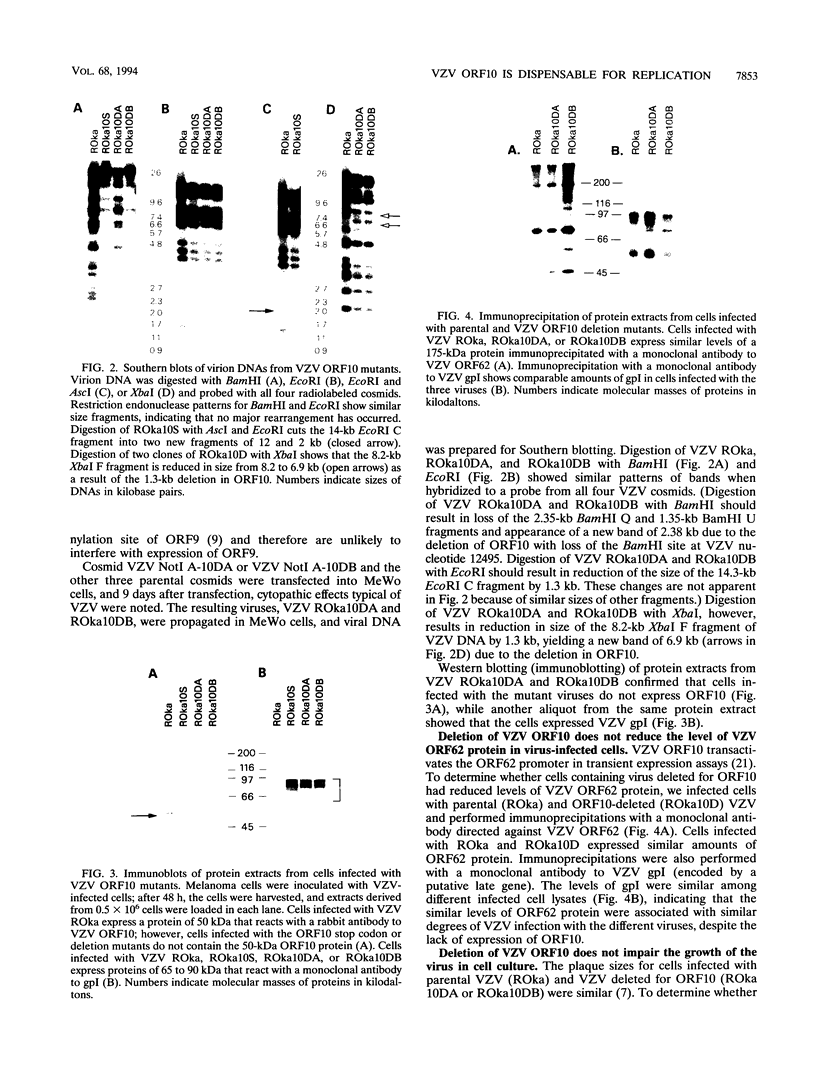
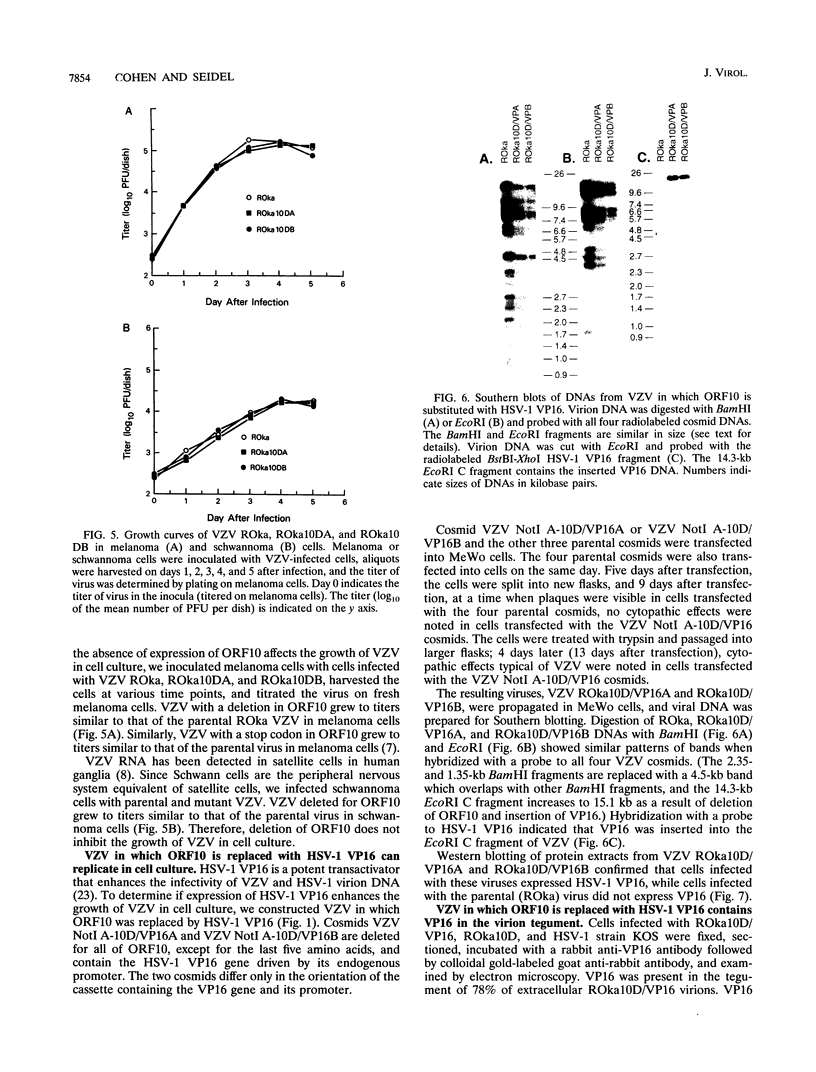
Abstract
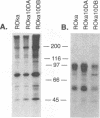
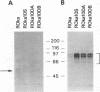
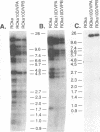
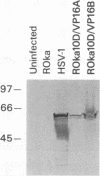
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) open reading frame 10 (ORF10) protein in the homolog of the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) protein VP16. VZV ORF10 transactivates the VZV IE62 gene and is a tegument protein present in the virion. HSV-1 VP16, a potent transactivator of HSV-1 immediate-early genes and tegument protein, is essential for HSV-1 replication in vitro. To determine whether VZV ORF10 is required for viral replication in vitro, we constructed two VZV mutants which were unable to express ORF10. One mutant had a stop codon after the 61st codon of the ORF10 gene, and the other mutant was deleted for all but the last five codons of the gene. Both VZV mutants grew in cell culture to titers similar to that of the parental virus. To determine whether HSV-1 VP16 alters the growth of VZV, we constructed a VZV mutant in which VP16 was inserted in place of ORF10. Using immune electron microscopy, we found that HSV-1 VP16 was present in the tegument of the recombinant VZV virions. The VZV VP16 substitution mutant produced smaller plaques and grew to a lower titer than parental virus. Thus, VZV ORF10 is not required for growth of the virus in vitro, and substitution of HSV-1 VP16 for VZV ORF10 impairs the growth of VZV.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ace C. I., Dalrymple M. A., Ramsay F. H., Preston V. G., Preston C. M. Mutational analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 1 trans-inducing factor Vmw65. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2595–2605. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ace C. I., McKee T. A., Ryan J. M., Cameron J. M., Preston C. M. Construction and characterization of a herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant unable to transinduce immediate-early gene expression. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2260–2269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2260-2269.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D. A method for identifying the viral genes required for herpesvirus DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9094–9098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Seidel K. E. Generation of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and viral mutants from cosmid DNAs: VZV thymidylate synthetase is not essential for replication in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):7376–7380. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.7376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croen K. D., Ostrove J. M., Dragovic L. J., Straus S. E. Patterns of gene expression and sites of latency in human nerve ganglia are different for varicella-zoster and herpes simplex viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9773–9777. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heineman T. C., Cohen J. I. Deletion of the varicella-zoster virus large subunit of ribonucleotide reductase impairs growth of virus in vitro. J Virol. 1994 May;68(5):3317–3323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.5.3317-3323.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Nagpal S., Ostrove J. M. Mapping of two varicella-zoster virus-encoded genes that activate the expression of viral early and late genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):700–709. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackers P., Defechereux P., Baudoux L., Lambert C., Massaer M., Merville-Louis M. P., Rentier B., Piette J. Characterization of regulatory functions of the varicella-zoster virus gene 63-encoded protein. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3899–3903. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3899-3903.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinchington P. R., Hougland J. K., Arvin A. M., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. The varicella-zoster virus immediate-early protein IE62 is a major component of virus particles. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):359–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.359-366.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe R. S., Keller P. M., Keech B. J., Davison A. J., Whang Y., Morgan A. J., Kieff E., Ellis R. W. Varicella-zoster virus as a live vector for the expression of foreign genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dalrymple M. A., Davison A. J., Dolan A., Frame M. C., McNab D., Perry L. J., Scott J. E., Taylor P. The complete DNA sequence of the long unique region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1531–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKee T. A., Disney G. H., Everett R. D., Preston C. M. Control of expression of the varicella-zoster virus major immediate early gene. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):897–906. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J. L., Holman R. P., Croen K. D., Smialek J. E., Straus S. E. Varicella-zoster virus transcription in human trigeminal ganglia. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):193–200. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriuchi H., Moriuchi M., Smith H. A., Cohen J. I. Varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 4 protein is functionally distinct from and does not complement its herpes simplex virus type 1 homolog, ICP27. J Virol. 1994 Mar;68(3):1987–1992. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.3.1987-1992.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriuchi H., Moriuchi M., Smith H. A., Straus S. E., Cohen J. I. Varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 61 protein is functionally homologous to herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP0. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7303–7308. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7303-7308.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriuchi H., Moriuchi M., Straus S. E., Cohen J. I. Varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 10 protein, the herpes simplex virus VP16 homolog, transactivates herpesvirus immediate-early gene promoters. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2739–2746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2739-2746.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriuchi M., Moriuchi H., Straus S. E., Cohen J. I. Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) virion-associated transactivator open reading frame 62 protein enhances the infectivity of VZV DNA. Virology. 1994 Apr;200(1):297–300. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L. Comparative fine structure of the trigeminal ganglia, including human autopsy studies. J Neurosurg. 1967 Jan;26(1 Suppl):112–126. doi: 10.3171/jns.1967.26.1part2.0112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagpal S., Ostrove J. M. Characterization of a potent varicella-zoster virus-encoded trans-repressor. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5289–5296. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5289-5296.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Kaushal S., Kinchington P. R., Mosca J. D., Hayward G. S., Straus S. E. Varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 4 encodes a transcriptional activator that is functionally distinct from that of herpes simplex virus homology ICP27. J Virol. 1994 Apr;68(4):2468–2477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.4.2468-2477.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Mosca J. D., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. Regulation of varicella-zoster virus gene expression in human T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5298–5304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5298-5304.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. E., Fletcher J. A., Lytle C. H., Nie L., Morton C. C., Diehl S. R. Molecular characterization of a 17q11.2 translocation in a malignant schwannoma cell line. Hum Genet. 1992 Dec;90(4):450–456. doi: 10.1007/BF00220476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraki K., Hyman R. W. The immediate early proteins of varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90423-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Okuno Y., Otsuka T., Osame J., Takamizawa A. Development of a live attenuated varicella vaccine. Biken J. 1975 Mar;18(1):25–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., Kingsbury R. C., McKnight S. L. Functional dissection of VP16, the trans-activator of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):718–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinheimer S. P., Boyd B. A., Durham S. K., Resnick J. L., O'Boyle D. R., 2nd Deletion of the VP16 open reading frame of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):258–269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.258-269.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]