Abstract
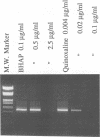
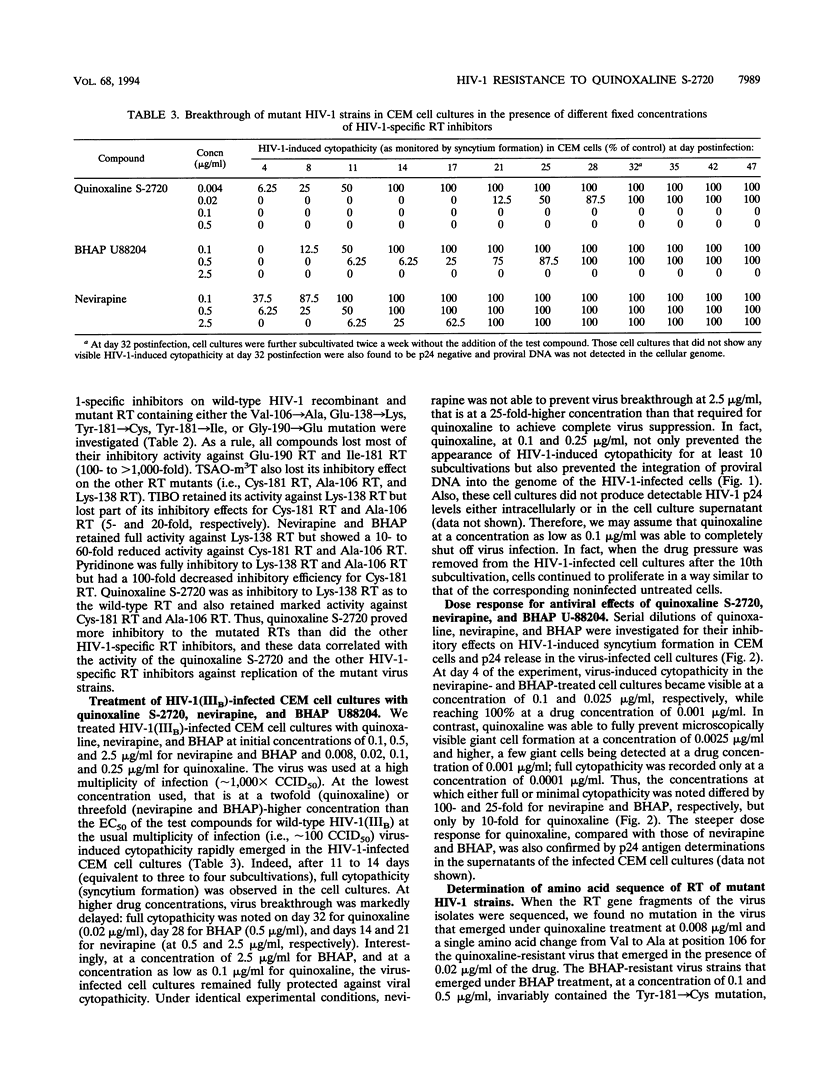
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-specific reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitor quinoxaline S-2720 showed a more-potent inhibitory effect on HIV-1-induced cytopathicity in CEM cells than either nevirapine, pyridinone L-697,661, bis-heteroarylpiperazine (BHAP) U-88204, TSAO ([2',5'-bis-O-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-beta-D-ribofuranosyl]-3'-spiro-5 "- (4-amino-1",2"-oxathiole-2",2"-dioxide)-N3-ethylthymine, or 4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-5-methylimidazo[4,5,1-jk][1,4-benzodiazepin-2(I H)-one (TIBO) R82913. The quinoxaline derivative was also markedly more inhibitory to the mutant HIV-1 strains containing in their RT Ile-100, Asn-103, Ala-106, Lys-138, Cys-181, or His-188 substitutions than were the other HIV-1-specific RT inhibitors. Moreover, quinoxaline S-2720 totally prevented HIV-1 infection and emergence of drug-resistant mutant virus strains in CEM cell cultures at concentrations (i.e., 0.35 microM) that are 10- to 25-fold lower than those required for BHAP U-88204 and nevirapine to knock out the virus. Also, the concentration-response curve for S-2720 was markedly steeper than for BHAP and nevirapine, as reflected by the ratio of the 95% to the 50% antivirally effective concentration. Lower concentrations of quinoxaline dominantly lead to the appearance of the Ala-106 RT mutation, causing low-level resistance to the compound. At higher quinoxaline concentrations, the Glu-190 RT and/or the Cys-181 RT mutation is added to the Ala-106 mutation, whereas at the highest quinoxaline concentrations, the Ala-106 mutation tends to disappear from the virus pool, leaving the Glu-190 RT and Cys-181 RT mutations as the only mutations conferring high-level resistance to the compound.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balzarini J., Karlsson A., Pérez-Pérez M. J., Camarasa M. J., De Clercq E. Knocking-out concentrations of HIV-1-specific inhibitors completely suppress HIV-1 infection and prevent the emergence of drug-resistant virus. Virology. 1993 Oct;196(2):576–585. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Karlsson A., Pérez-Pérez M. J., Camarasa M. J., Tarpley W. G., De Clercq E. Treatment of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)-infected cells with combinations of HIV-1-specific inhibitors results in a different resistance pattern than does treatment with single-drug therapy. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5353–5359. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5353-5359.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Karlsson A., Pérez-Pérez M. J., Vrang L., Walbers J., Zhang H., Oberg B., Vandamme A. M., Camarasa M. J., De Clercq E. HIV-1-specific reverse transcriptase inhibitors show differential activity against HIV-1 mutant strains containing different amino acid substitutions in the reverse transcriptase. Virology. 1993 Jan;192(1):246–253. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Karlsson A., Sardana V. V., Emini E. A., Camarasa M. J., De Clercq E. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1)-specific reverse transcriptase (RT) inhibitors may suppress the replication of specific drug-resistant (E138K)RT HIV-1 mutants or select for highly resistant (Y181C-->C181I)RT HIV-1 mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 5;91(14):6599–6603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.14.6599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Karlsson A., Vandamme A. M., Pérez-Pérez M. J., Zhang H., Vrang L., Oberg B., Bäckbro K., Unge T., San-Félix A. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) strains selected for resistance against the HIV-1-specific [2',5'-bis-O-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-3'-spiro- 5''-(4''-amino-1'',2''-oxathiole-2'',2''-dioxide)]-beta-D-pentofurano syl (TSAO) nucleoside analogues retain sensitivity to HIV-1-specific nonnucleoside inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6952–6956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Pérez-Pérez M. J., San-Félix A., Camarasa M. J., Bathurst I. C., Barr P. J., De Clercq E. Kinetics of inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) reverse transcriptase by the novel HIV-1-specific nucleoside analogue [2',5'-bis-O-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-beta-D-ribofuranosyl]-3'-spiro-5 "- (4"-amino-1",2"-oxathiole-2",2"-dioxide)thymine (TSAO-T). J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 15;267(17):11831–11838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzarini J., Velazquez S., San-Felix A., Karlsson A., Perez-Perez M. J., Camarasa M. J., De Clercq E. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific [2',5'-bis-O-(tert- butyldimethylsilyl)-beta-D-ribofuranosyl]-3'-spiro-5"-(4"-amino-1",2"- oxathiole-2",2"-dioxide)-purine analogues show a resistance spectrum that is different from that of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific non-nucleoside analogues. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;43(1):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camarasa M. J., Pérez-Pérez M. J., San-Félix A., Balzarini J., De Clercq E. 3'-Spiro nucleosides, a new class of specific human immunodeficiency virus type 1 inhibitors: synthesis and antiviral activity of [2'-5'-bis-O-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-beta-D-xylo- and -ribofuranose]-3'-spiro-5"-[4"-amino-1",2"-oxathiole 2",2"-dioxide] (TSAO) pyrimidine nucleosides. J Med Chem. 1992 Jul 24;35(15):2721–2727. doi: 10.1021/jm00093a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Clercq E. HIV resistance to reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol. 1994 Jan 20;47(2):155–169. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(94)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dueweke T. J., Poppe S. M., Romero D. L., Swaney S. M., So A. G., Downey K. M., Althaus I. W., Reusser F., Busso M., Resnick L. U-90152, a potent inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 May;37(5):1127–1131. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.5.1127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dueweke T. J., Pushkarskaya T., Poppe S. M., Swaney S. M., Zhao J. Q., Chen I. S., Stevenson M., Tarpley W. G. A mutation in reverse transcriptase of bis(heteroaryl)piperazine-resistant human immunodeficiency virus type 1 that confers increased sensitivity to other nonnucleoside inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4713–4717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellam P., Boucher C. A., Tijnagel J. M., Larder B. A. Zidovudine treatment results in the selection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants whose genotypes confer increasing levels of drug resistance. J Gen Virol. 1994 Feb;75(Pt 2):341–351. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-75-2-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleim J. P., Bender R., Billhardt U. M., Meichsner C., Riess G., Rösner M., Winkler I., Paessens A. Activity of a novel quinoxaline derivative against human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase and viral replication. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Aug;37(8):1659–1664. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.8.1659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleim J. P., Bender R., Kirsch R., Meichsner C., Paessens A., Riess G. Mutational analysis of residue 190 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase. Virology. 1994 May 1;200(2):696–701. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors J. W., Dutschman G. E., Im G. J., Tramontano E., Winkler S. R., Cheng Y. C. In vitro selection and molecular characterization of human immunodeficiency virus-1 resistant to non-nucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Mar;41(3):446–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellors J. W., Im G. J., Tramontano E., Winkler S. R., Medina D. J., Dutschman G. E., Bazmi H. Z., Piras G., Gonzalez C. J., Cheng Y. C. A single conservative amino acid substitution in the reverse transcriptase of human immunodeficiency virus-1 confers resistance to (+)-(5S)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-5-methyl-6-(3-methyl-2-butenyl)imidazo[4,5, 1- jk][1,4]benzodiazepin-2(1H)-thione (TIBO R82150). Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jan;43(1):11–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Schleif W. A., Boots E. J., O'Brien J. A., Quintero J. C., Hoffman J. M., Emini E. A., Goldman M. E. Viral resistance to human immunodeficiency virus type 1-specific pyridinone reverse transcriptase inhibitors. J Virol. 1991 Sep;65(9):4887–4892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.9.4887-4892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Pérez M. J., San-Félix A., Balzarini J., De Clercq E., Camarasa M. J. TSAO analogues. Stereospecific synthesis and anti-HIV-1 activity of 1-[2',5'-bis-O-(tert-butyldimethylsilyl)-beta-D-ribofuranosyl]-3'-spiro -5''- (4''-amino-1'',2''-oxathiole 2'',2''-dioxide) pyrimidine and pyrimidine-modified nucleosides. J Med Chem. 1992 Aug 7;35(16):2988–2995. doi: 10.1021/jm00094a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D. Resistance of clinical isolates of human immunodeficiency virus to antiretroviral agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 Jun;37(6):1207–1213. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.6.1207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D., Shih C. K., Lowy I., Rose J., Prodanovich P., Goff S., Griffin J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 mutants resistant to nonnucleoside inhibitors of reverse transcriptase arise in tissue culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11241–11245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandamme A. M., Debyser Z., Pauwels R., De Vreese K., Goubau P., Youle M., Gazzard B., Stoffels P. A., Cauwenbergh G. F., Anne J. Characterization of HIV-1 strains isolated from patients treated with TIBO R82913. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1994 Jan;10(1):39–46. doi: 10.1089/aid.1994.10.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevachari M. B., Battista C., Lane H. C., Psallidopoulos M. C., Zhao B., Cook J., Palmer J. R., Romero D. L., Tarpley W. G., Salzman N. P. Prevention of the spread of HIV-1 infection with nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Virology. 1992 Sep;190(1):269–277. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)91213-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]