Abstract
Infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV) is a rhabdovirus that causes an acute disease in salmon and trout. In this study, a correlation between changes in tissue tropism and specific changes in the virus genome appeared to be made by examining four IHNV neutralization-resistant variants (RB-1, RB-2, RB-3, and RB-4) that had been selected with the glycoprotein (G)-specific monoclonal antibody RB/B5. These variants were compared with the parental strain (RB-76) for their virulence and pathogenicity in rainbow trout after waterborne challenge. Variants RB-2, RB-3, and RB-4 were only slightly attenuated and showed distributions of viral antigen in the livers and hematopoietic tissues of infected fish similar to those of the parental strain. Variant RB-1, however, was highly attenuated and the tissue distribution of viral antigen in RB-1-infected fish was markedly different, with more viral antigen in brain tissue. The sequences of the G genes of all four variants and RB-76 were determined. No significant changes were found for the slightly attenuated variants, but RB-1 G had two changes at amino acids 78 and 218 that dramatically altered its predicted secondary structure. These changes are thought to be responsible for the altered tissue tropism of the virus. Thus, IHNV G, like that of rabies virus and vesicular stomatitis virus, plays an integral part in the pathogenesis of viral infection.
Full text
PDF
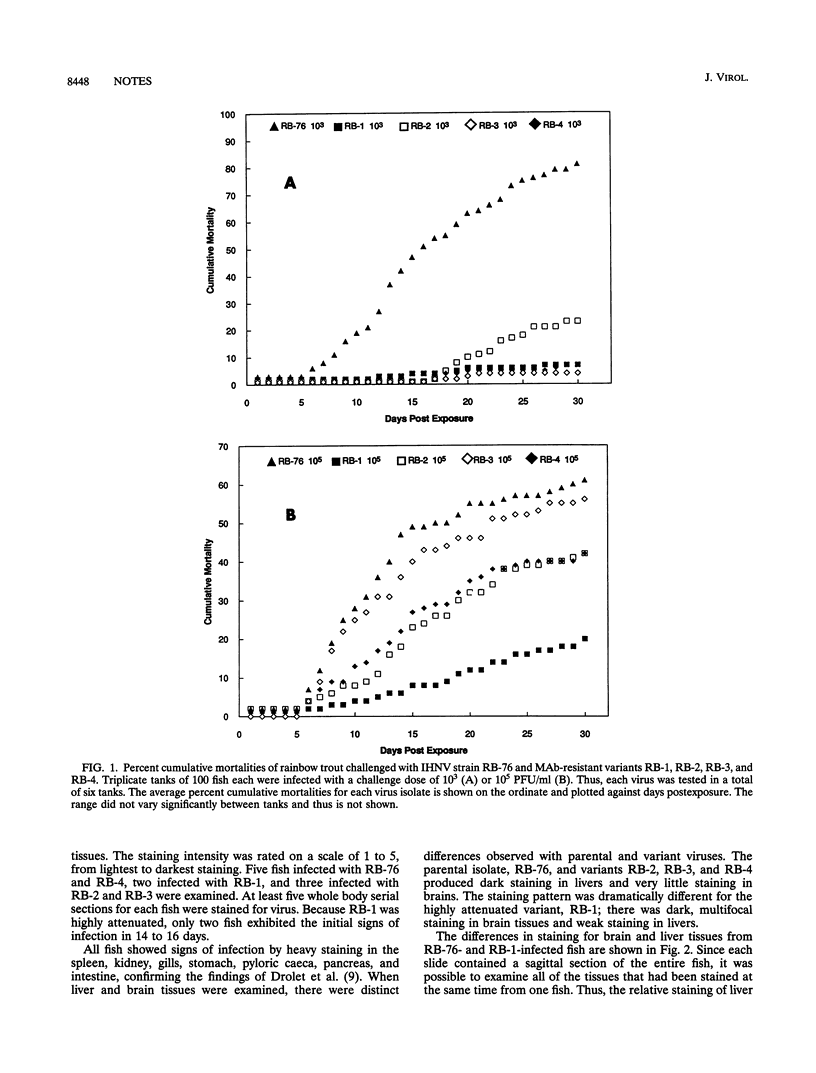




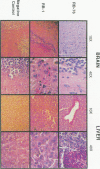
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benmansour A., Leblois H., Coulon P., Tuffereau C., Gaudin Y., Flamand A., Lafay F. Antigenicity of rabies virus glycoprotein. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4198–4203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4198-4203.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootland L. M., Leong J. A. Staphylococcal coagglutination, a rapid method of identifying infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):6–13. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.6-13.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd M. T., Simpson G. R., Cann A. J., Johnson M. A., Weiss R. A. A single amino acid substitution in the V1 loop of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp120 alters cellular tropism. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3649–3652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3649-3652.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cann A. J., Churcher M. J., Boyd M., O'Brien W., Zhao J. Q., Zack J., Chen I. S. The region of the envelope gene of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 responsible for determination of cell tropism. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):305–309. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.305-309.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Wiktor T. J., Trojanowski J. Q., Macfarlan R. I., Wunner W. H., Torres-Anjel M. J., Koprowski H. Differences in cell-to-cell spread of pathogenic and apathogenic rabies virus in vivo and in vitro. J Virol. 1985 Oct;56(1):12–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.1.12-18.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Wunner W. H., Wiktor T. J., Lopes A. D., Lafon M., Smith C. L., Koprowski H. Characterization of an antigenic determinant of the glycoprotein that correlates with pathogenicity of rabies virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):70–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S. S., Boyle T. J., Lyerly H. K., Cullen B. R. Identification of the envelope V3 loop as the primary determinant of cell tropism in HIV-1. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):71–74. doi: 10.1126/science.1905842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. C. Biological basis of rabies virus neurovirulence in mice: comparative pathogenesis study using the immunoperoxidase technique. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):537–540. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.537-540.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil W., Wagner R. R. Epitope mapping by deletion mutants and chimeras of two vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein genes expressed by a vaccinia virus vector. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):392–407. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90430-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koener J. F., Passavant C. W., Kurath G., Leong J. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone carrying the glycoprotein gene of infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus, a fish rhabdovirus. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1342–1349. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1342-1349.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera P., Dolivo M., Coulon P., Flamand A. Pathways of the early propagation of virulent and avirulent rabies strains from the eye to the brain. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):158–162. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.158-162.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafay F., Coulon P., Astic L., Saucier D., Riche D., Holley A., Flamand A. Spread of the CVS strain of rabies virus and of the avirulent mutant AvO1 along the olfactory pathways of the mouse after intranasal inoculation. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):320–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90145-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lannan C. N., Winton J. R., Fryer J. L. Fish cell lines: establishment and characterization of nine cell lines from salmonids. In Vitro. 1984 Sep;20(9):671–676. doi: 10.1007/BF02618871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matloubian M., Kolhekar S. R., Somasundaram T., Ahmed R. Molecular determinants of macrophage tropism and viral persistence: importance of single amino acid changes in the polymerase and glycoprotein of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7340–7349. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7340-7349.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehaud C., Coulon P., LaFay F., Thiers C., Flamand A. Antigenic site II of the rabies virus glycoprotein: structure and role in viral virulence. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):1–7. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.1-7.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Coulon P., Rollin P. E., Flamand A. Rabies virulence: effect on pathogenicity and sequence characterization of rabies virus mutations affecting antigenic site III of the glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):926–934. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.926-934.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Levy J. A., Cheng-Mayer C. Macrophage and T cell-line tropisms of HIV-1 are determined by specific regions of the envelope gp120 gene. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):167–169. doi: 10.1038/349167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szepanski S., Gross H. J., Brossmer R., Klenk H. D., Herrler G. A single point mutation of the influenza C virus glycoprotein (HEF) changes the viral receptor-binding activity. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90737-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westervelt P., Trowbridge D. B., Epstein L. G., Blumberg B. M., Li Y., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M., Price R. W., Ratner L. Macrophage tropism determinants of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vivo. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):2577–2582. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.2577-2582.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wunner W. H., Dietzschold B., Smith C. L., Lafon M., Golub E. Antigenic variants of CVS rabies virus with altered glycosylation sites. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90440-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu L., Mourich D. V., Engelking H. M., Ristow S., Arnzen J., Leong J. C. Epitope mapping and characterization of the infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus glycoprotein, using fusion proteins synthesized in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1611–1615. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1611-1615.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C., Jackson A. C. Basis of neurovirulence of avirulent rabies virus variant Av01 with stereotaxic brain inoculation in mice. J Gen Virol. 1992 Apr;73(Pt 4):895–900. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-4-895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]