Abstract
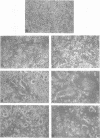
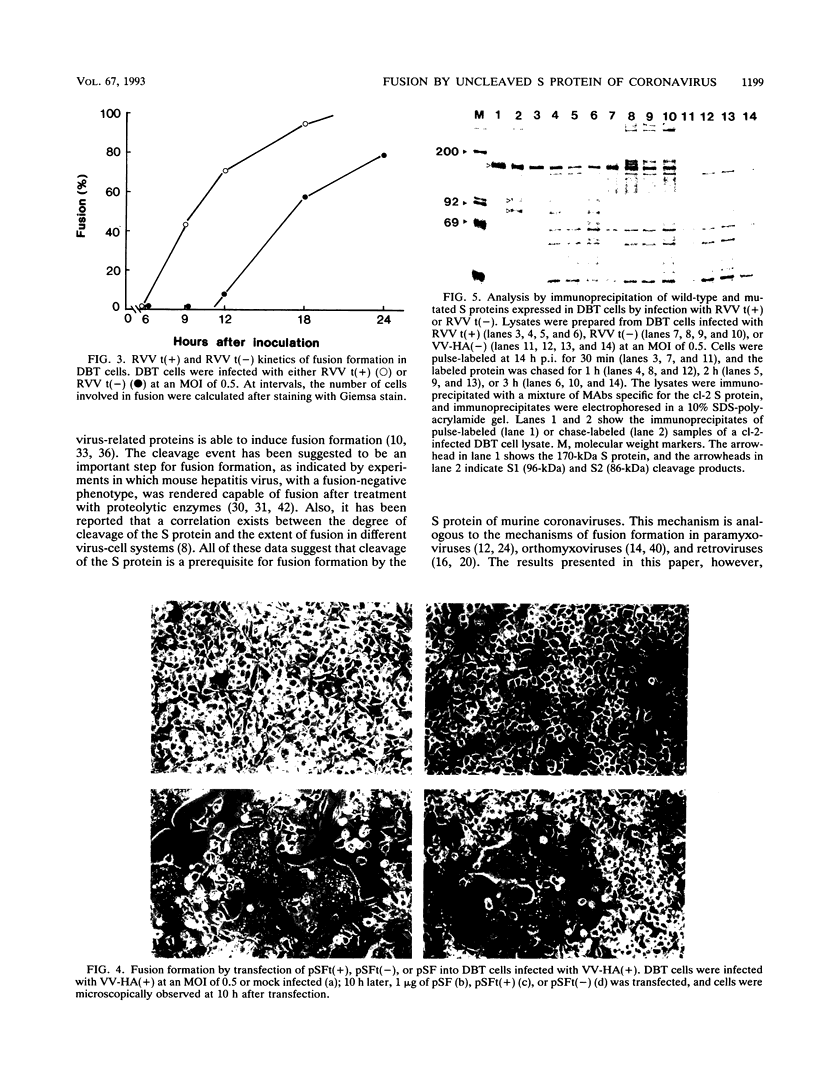
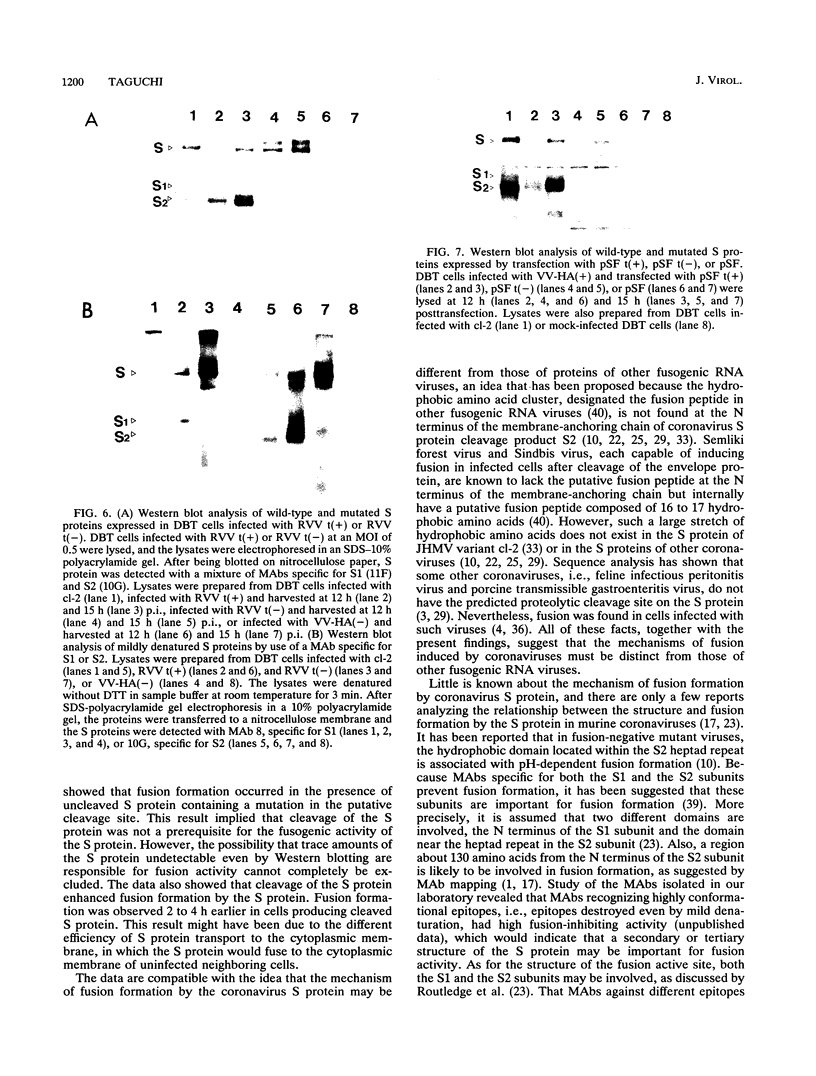
The fusogenic properties of the uncleaved spike (S) protein of murine coronavirus JHMV variant cl-2 were studied by expressing the S protein with a deleted putative cleavage site. The amino acid sequence of the putative cleavage site, Arg-Arg-Ala-Arg-Arg, was replaced by Arg-Thr-Ala-Leu-Glu by in vitro mutagenesis of the cl-2 S protein cDNA. Recombinant vaccinia viruses containing the cl-2 S cDNA [RVV t(+)] or the mutated cDNA [RVV t(-)] were constructed and monitored for fusion formation and cleavage of the expressed S proteins. When cultured DBT cells were infected with RVV t(+) at a multiplicity of infection of 0.5, fusion formation was first observed at 10 to 12 h postinoculation and spread throughout the whole culture by 20 to 24 h postinoculation. In cells infected with RVV t(-) under the same conditions, fusion formation appeared by 12 to 14 h. This result represented a 2- to 4-h delay in the onset of fusion, compared with its appearance in cells expressing the wild-type S protein. By 25 to 30 h, most of the cells infected by RVV t(-) had fused. By immunoprecipitation and Western blotting (immunoblotting), the 170-kDa S protein was detected in DBT cells expressing the wild-type S protein and the mutated S protein. However, interestingly, the cleavage products of the S protein, S1 and S2, were not detected in RVV t(-)-infected cells, producing the mutated S protein, even though fusion was clearly visible. Both products were, of course, detected in RVV t(+)-infected DBT cells, producing the wild-type S protein. The same results concerning the fusion formation and cleavage properties of the S proteins were reproduced by the transiently expressed S proteins. These results suggest that the cleavage event in the S protein of murine coronavirus JHMV is not a prerequisite for fusion formation but that it does facilitate fusion formation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
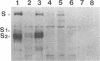
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Collins A. R., Knobler R. L., Powell H., Buchmeier M. J. Monoclonal antibodies to murine hepatitis virus-4 (strain JHM) define the viral glycoprotein responsible for attachment and cell--cell fusion. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):358–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90095-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel R. G., Lampert P. W., Talbot P. J., Buchmeier M. J. Site-specific alteration of murine hepatitis virus type 4 peplomer glycoprotein E2 results in reduced neurovirulence. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.463-471.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Groot R. J., Van Leen R. W., Dalderup M. J., Vennema H., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Stably expressed FIPV peplomer protein induces cell fusion and elicits neutralizing antibodies in mice. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90619-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dveksler G. S., Pensiero M. N., Cardellichio C. B., Williams R. K., Jiang G. S., Holmes K. V., Dieffenbach C. W. Cloning of the mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) receptor: expression in human and hamster cell lines confers susceptibility to MHV. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6881–6891. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6881-6891.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazakerley J. K., Parker S. E., Bloom F., Buchmeier M. J. The V5A13.1 envelope glycoprotein deletion mutant of mouse hepatitis virus type-4 is neuroattenuated by its reduced rate of spread in the central nervous system. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):178–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90306-A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming J. O., Trousdale M. D., el-Zaatari F. A., Stohlman S. A., Weiner L. P. Pathogenicity of antigenic variants of murine coronavirus JHM selected with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):869–875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.869-875.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frana M. F., Behnke J. N., Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of the E2 glycoprotein of murine coronavirus: host-dependent differences in proteolytic cleavage and cell fusion. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):912–920. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.912-920.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funahashi S., Itamura S., Iinuma H., Nerome K., Sugimoto M., Shida H. Increased expression in vivo and in vitro of foreign genes directed by A-type inclusion body hybrid promoters in recombinant vaccinia viruses. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5584–5588. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5584-5588.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. M., Escarmis C., Buchmeier M. J. Alteration of the pH dependence of coronavirus-induced cell fusion: effect of mutations in the spike glycoprotein. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1916–1928. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1916-1928.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. V., Doller E. W., Behnke J. N. Analysis of the functions of coronavirus glycoproteins by differential inhibition of synthesis with tunicamycin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1981;142:133–142. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-0456-3_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homma M., Ouchi M. Trypsin action on the growth of Sendai virus in tissue culture cells. 3. Structural difference of Sendai viruses grown in eggs and tissue culture cells. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1457–1465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1457-1465.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. J., Shieh C. K., Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., La Monica N., Tuler J., Bagdzhadzhyan A., Lai M. M. The complete sequence (22 kilobases) of murine coronavirus gene 1 encoding the putative proteases and RNA polymerase. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):567–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90071-I. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifson J. D., Feinberg M. B., Reyes G. R., Rabin L., Banapour B., Chakrabarti S., Moss B., Wong-Staal F., Steimer K. S., Engleman E. G. Induction of CD4-dependent cell fusion by the HTLV-III/LAV envelope glycoprotein. Nature. 1986 Oct 23;323(6090):725–728. doi: 10.1038/323725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luytjes W., Geerts D., Posthumus W., Meloen R., Spaan W. Amino acid sequence of a conserved neutralizing epitope of murine coronaviruses. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1408–1412. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1408-1412.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara Y., Watanabe R., Taguchi F. Neurovirulence of six different murine coronavirus JHMV variants for rats. Virus Res. 1991 Jun;20(1):45–58. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(91)90060-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCune J. M., Rabin L. B., Feinberg M. B., Lieberman M., Kosek J. C., Reyes G. R., Weissman I. L. Endoproteolytic cleavage of gp160 is required for the activation of human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):55–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris V. L., Tieszer C., Mackinnon J., Percy D. Characterization of coronavirus JHM variants isolated from Wistar Furth rats with a viral-induced demyelinating disease. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker S. E., Gallagher T. M., Buchmeier M. J. Sequence analysis reveals extensive polymorphism and evidence of deletions within the E2 glycoprotein gene of several strains of murine hepatitis virus. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):664–673. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge E., Stauber R., Pfleiderer M., Siddell S. G. Analysis of murine coronavirus surface glycoprotein functions by using monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):254–262. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.254-262.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Identification of biological activities of paramyxovirus glycoproteins. Activation of cell fusion, hemolysis, and infectivity of proteolytic cleavage of an inactive precursor protein of Sendai virus. Virology. 1974 Feb;57(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90187-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt I., Skinner M., Siddell S. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the surface projection glycoprotein of coronavirus MHV-JHM. J Gen Virol. 1987 Jan;68(Pt 1):47–56. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-1-47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seki M., Oie M., Ichihashi Y., Shida H. Hemadsorption and fusion inhibition activities of hemagglutinin analyzed by vaccinia virus mutants. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):372–384. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90422-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S., Wege H., Barthel A., ter Meulen V. Coronavirus JHM: intracellular protein synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1981 Mar;53(Pt 1):145–155. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-1-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S., Wege H., Ter Meulen V. The biology of coronaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1983 Apr;64(Pt 4):761–776. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-4-761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W., Cavanagh D., Horzinek M. C. Coronaviruses: structure and genome expression. J Gen Virol. 1988 Dec;69(Pt 12):2939–2952. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-12-2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of peplomeric glycoprotein E2 of MHV yields two 90K subunits and activates cell fusion. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1984;173:25–35. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9373-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S., Ricard C. S., Holmes K. V. Proteolytic cleavage of the E2 glycoprotein of murine coronavirus: activation of cell-fusing activity of virions by trypsin and separation of two different 90K cleavage fragments. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):904–911. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.904-911.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi F., Fleming J. O. Comparison of six different murine coronavirus JHM variants by monoclonal antibodies against the E2 glycoprotein. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):233–235. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90061-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi F., Ikeda T., Shida H. Molecular cloning and expression of a spike protein of neurovirulent murine coronavirus JHMV variant cl-2. J Gen Virol. 1992 May;73(Pt 5):1065–1072. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-5-1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi F., Siddell S. G., Wege H., ter Meulen V. Characterization of a variant virus selected in rat brains after infection by coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus JHM. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):429–435. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.429-435.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennema H., Heijnen L., Zijderveld A., Horzinek M. C., Spaan W. J. Intracellular transport of recombinant coronavirus spike proteins: implications for virus assembly. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):339–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.339-346.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Dörries R., Wege H. Hybridoma antibodies to the murine coronavirus JHM: characterization of epitopes on the peplomer protein (E2). J Gen Virol. 1984 Nov;65(Pt 11):1931–1942. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-11-1931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Winter J., Meyermann R. The peplomer protein E2 of coronavirus JHM as a determinant of neurovirulence: definition of critical epitopes by variant analysis. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jan;69(Pt 1):87–98. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-1-87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weismiller D. G., Sturman L. S., Buchmeier M. J., Fleming J. O., Holmes K. V. Monoclonal antibodies to the peplomer glycoprotein of coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus identify two subunits and detect a conformational change in the subunit released under mild alkaline conditions. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):3051–3055. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.3051-3055.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. M. Viral and cellular membrane fusion proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:675–697. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. K., Jiang G. S., Holmes K. V. Receptor for mouse hepatitis virus is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen family of glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5533–5536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikura H., Tejima S. Role of protease in mouse hepatitis virus-induced cell fusion. Studies with a cold-sensitive mutant isolated from a persistent infection. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot R. J., Maduro J., Lenstra J. A., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A., Spaan W. J. cDNA cloning and sequence analysis of the gene encoding the peplomer protein of feline infectious peritonitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1987 Oct;68(Pt 10):2639–2646. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-10-2639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]