Abstract
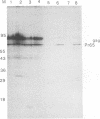
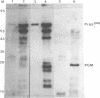
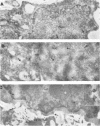
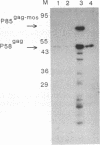
Nuclei of cells infected with Moloney murine leukemia virus (MoMuLV) were examined for the presence of gag proteins. This analysis was performed in conjunction with other studies suggesting a possible role for gag proteins in regulating nuclear events relating to processing and/or transport of viral genomic RNA. We detected Pr65gag and a p30-related protein in a nuclear fraction of infected cells. We also found evidence that a highly conserved amino acid sequence, which is shared by p30 and U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein 70-kDa protein, is a component of the nuclear targeting sequence for Pr65gag. Immunoelectron microscopy studies with a monoclonal anti-p12 antibody established that approximately 18% of gag-containing proteins of MoMuLV are located in the nucleus. Such gag-containing proteins from a mutant MoMuLV that lacks N-terminal myristic acid had greater affinity for the nucleus, suggesting that fatty acid acylation of Pr65gag plays a role in overcoming the proposed nuclear transport signal. The possible roles that nuclear gag proteins may play in retroviral replication are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcement L. J., Karshin W. L., Naso R. B., Arlinghaus R. B. "gag" polyprotein precursors of Rauscher murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):284–297. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Hull M. A., Finch E. A. The isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive transformation mutants of Moloney sarcoma virus. Virology. 1979 Jun;95(2):303–316. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90486-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani E., Helm K. V., Duesberg P. Evidence for 30-40S RNA as precursor of the 60-70S RNA of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):401–405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. P. Fluorographic detection of radioactivity in polyacrylamide gels with the water-soluble fluor, sodium salicylate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):132–135. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90716-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Britt W., Evans L., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Cloyd M. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive with murine leukemia viruses: use in analysis of strains of friend MCF and Friend ecotropic murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):134–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker G. L., Valdizan M. C., Wessel G. M., Lennarz W. J. Developmental distribution of a cell surface glycoprotein in the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol. 1988 Oct;129(2):339–349. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90381-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Laskey R. A. Nuclear targeting sequences--a consensus? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Dec;16(12):478–481. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H., Baltimore D. RNA metabolism of murine leukemia virus: detection of virus-specific RNA sequences in infected and uninfected cells and identification of virus-specific messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 15;80(1):93–117. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feeney R. J., Zieve G. W. Nuclear exchange of the U1 and U2 snRNP-specific proteins. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):871–881. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallick G. E., Arlinghaus R. B. Incorporation of lipids into variants of Moloney sarcoma virus which produce gag-mos fusion proteins. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):228–232. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90444-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Bustos J., Heitman J., Hall M. N. Nuclear protein localization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Mar 7;1071(1):83–101. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(91)90013-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamelin R., Kabat K., Blair D., Arlinghaus R. B. Temperature-sensitive splicing defect of ts110 Moloney murine sarcoma virus is virus encoded. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):301–309. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.301-309.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Krutzsch H. C., Oroszlan S. Myristyl amino-terminal acylation of murine retrovirus proteins: an unusual post-translational proteins modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. P., Wood T. G., Blair D. G., Arlinghaus R. B. Partial characterization of a moloney murine sarcoma virus 85,000-dalton polypeptide whose expression correlates with the transformed phenotype in cells infected with a temperature-sensitive mutant virus. Virology. 1980 Sep;105(2):516–525. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90052-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn J. P., Wood T. G., Murphy E. C., Jr, Blair D. G., Arlinghaus R. B. A selective temperature-sensitive defect in viral RNA expression in cells infected with a ts transformation mutant of murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90229-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang L. S., Park J., Gilboa E. Role of intron-contained sequences in formation of moloney murine leukemia virus env mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2289–2297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junghans R. P., Murphy E. C., Jr, Arlinghaus R. B. Electron microscopic analysis of ts1 10 Moloney mouse sarcoma virus, a variant of wild-type virus with two RNAs containing large deletions. J Mol Biol. 1982 Oct 25;161(2):229–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90150-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell S., Arlinghaus R. B. In vitro proteolytic cleavage of Gazdar murine sarcoma virus p65gag. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):963–967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.963-967.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murti K. G., Bondurant M., Tereba A. Secondary structural features in the 70S RNAs of Moloney murine leukemia and Rous sarcoma viruses as observed by electron microscopy. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.411-419.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash M. A., Brizzard B. L., Wong J. L., Murphy E. C., Jr Murine sarcoma virus ts110 RNA transcripts: origin from a single proviral DNA and sequence of the gag-mos junctions in both the precursor and spliced viral RNAs. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):624–633. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.624-633.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash M., Brown N. V., Wong J. L., Arlinghaus R. B., Murphy E. C., Jr S1 nuclease mapping of viral RNAs from a temperature-sensitive transformation mutant of murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):478–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.478-488.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naso R. B., Arcement L. J., Arlinghaus R. B. Biosynthesis of Rauscher leukemia viral proteins. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):31–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90130-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naso R. B., Karshin W. L., Wu Y. H., Arlinghaus R. B. Characterization of 40,000- and 25,000-dalton intermediate precursors to Rauscher murine leukemia virus gag gene products. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):187–198. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.187-198.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A., Baeuerle P. A., Lührmann R. Nuclear import-export: in search of signals and mechanisms. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90135-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odawara T., Yoshikura H., Ohshima M., Tanaka T., Jones D. S., Nemoto F., Kuchino Y., Iwamoto A. Analysis of Moloney murine leukemia virus revertants mutated at the gag-pol junction. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6376–6379. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6376-6379.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prats A. C., Roy C., Wang P. A., Erard M., Housset V., Gabus C., Paoletti C., Darlix J. L. cis elements and trans-acting factors involved in dimer formation of murine leukemia virus RNA. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):774–783. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.774-783.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Query C. C., Keene J. D. A human autoimmune protein associated with U1 RNA contains a region of homology that is cross-reactive with retroviral p30gag antigen. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90148-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., McClure M. R., Rice N. R., Luftig R. B., Schultz A. M. Myristylation site in Pr65gag is essential for virus particle formation by Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7246–7250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer M., Cerutti M., Gay B., Hong S. S., Devauchelle G., Boulanger P. Functional domains of HIV-1 gag-polyprotein expressed in baculovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1991 Sep;184(1):417–422. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90861-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. In vivo modification of retroviral gag gene-encoded polyproteins by myristic acid. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):355–361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.355-361.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanker L. H., Gallick G. E., Kloetzer W. S., Murphy E. C., Jr, Arlinghaus R. B. P85: a gag-mos polyprotein encoded by ts110 Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1183–1189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1183-1189.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., van Straaten F., Galleshaw J. A., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence of the genome of a murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90364-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]