Abstract
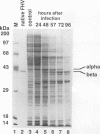
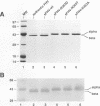
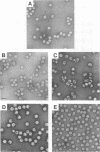
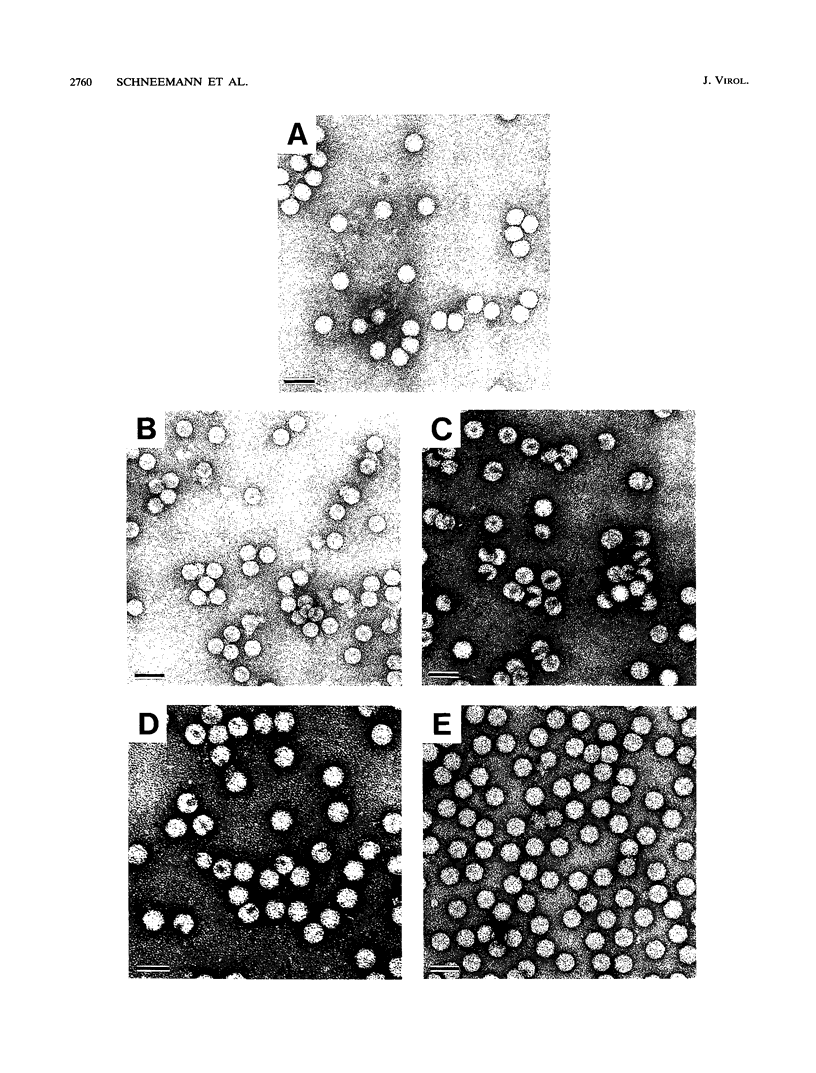
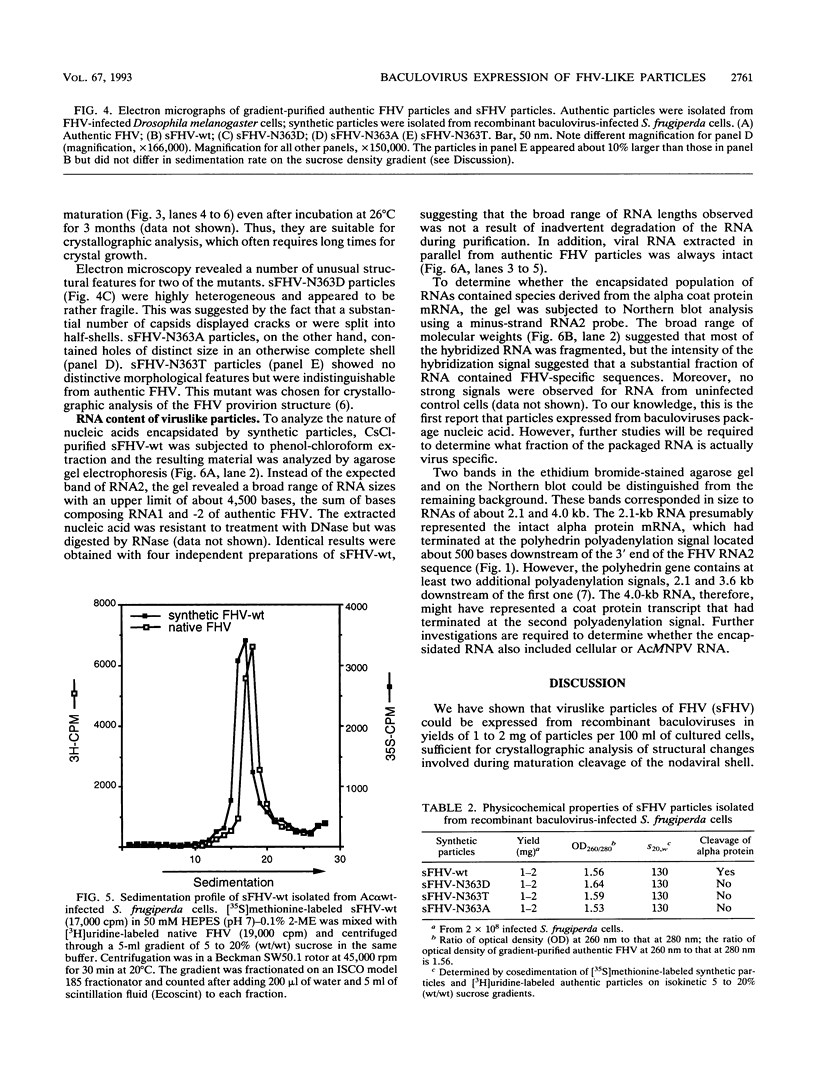
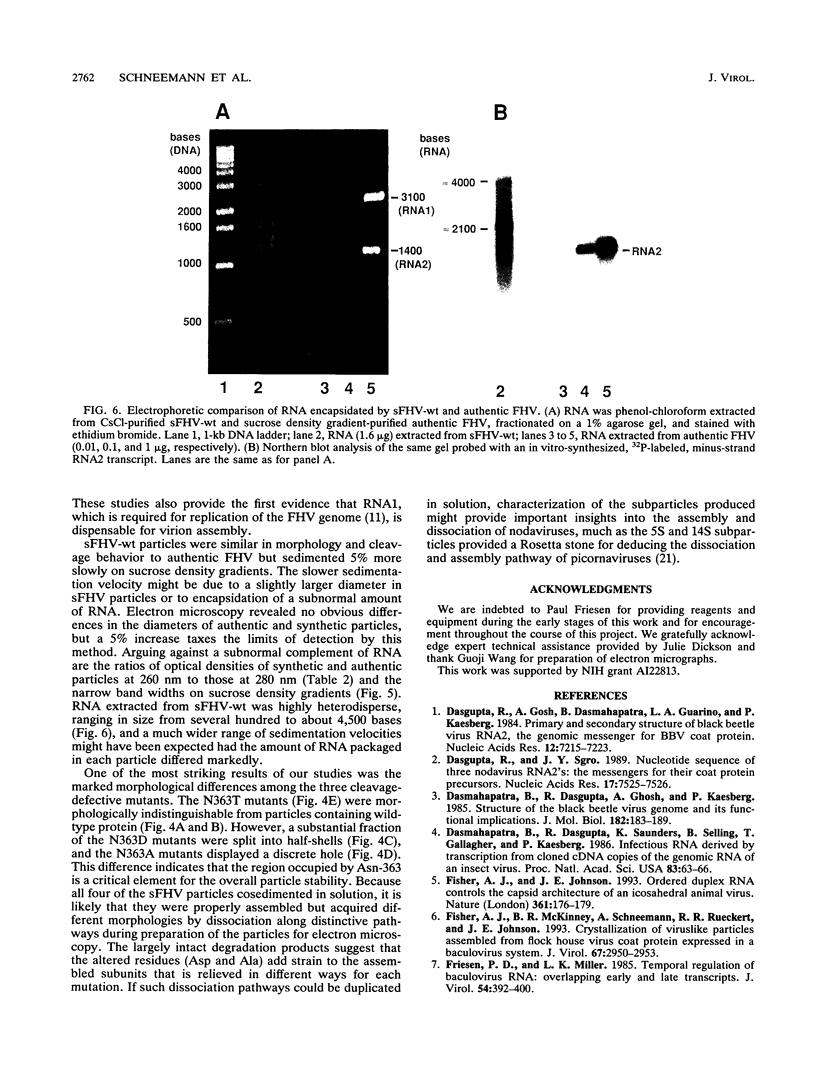
Flock house virus (FHV) is a small icosahedral insect virus of the family Nodaviridae. Its genome consists of two messenger-sense RNA molecules, both of which are encapsidated in the same particle. RNA1 (3.1 kb) encodes proteins required for viral RNA replication; RNA2 (1.4 kb) encodes protein alpha (43 kDa), the precursor of the coat protein. When Spodoptera frugiperda cells were infected with a recombinant baculovirus containing a cDNA copy of RNA2, coat protein alpha assembled into viruslike precursor particles (provirions) that matured normally by autocatalytic cleavage of protein alpha into polypeptide chains beta (38 kDa) and gamma (5 kDa). The particles were morphologically indistinguishable from authentic FHV and contained RNA derived from the coat protein message. These results showed that RNA1 was required neither for virion assembly nor for maturation of provirions. Expression of mutants in which Asn-363 at the beta-gamma cleavage site of protein alpha was replaced by either aspartate, threonine, or alanine resulted in assembly of particles that were cleavage defective. For two of the mutants, unusual structural features were observed after preparation for electron microscopy. Particles containing Asp at position 363 were labile and showed a strong tendency to break into half-shells. Particles in which Asn-363 was replaced by Ala displayed a distinct hole in an otherwise complete shell. The third mutant, containing Thr at position 363, was indistinguishable in morphology from authentic FHV.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown C. S., Van Lent J. W., Vlak J. M., Spaan W. J. Assembly of empty capsids by using baculovirus recombinants expressing human parvovirus B19 structural proteins. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2702–2706. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2702-2706.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta R., Ghosh A., Dasmahapatra B., Guarino L. A., Kaesberg P. Primary and secondary structure of black beetle virus RNA2, the genomic messenger for BBV coat protein precursor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7215–7223. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta R., Sgro J. Y. Nucleotide sequences of three Nodavirus RNA2's: the messengers for their coat protein precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7525–7526. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasmahapatra B., Dasgupta R., Ghosh A., Kaesberg P. Structure of the black beetle virus genome and its functional implications. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90337-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasmahapatra B., Dasgupta R., Saunders K., Selling B., Gallagher T., Kaesberg P. Infectious RNA derived by transcription from cloned cDNA copies of the genomic RNA of an insect virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):63–66. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. J., Johnson J. E. Ordered duplex RNA controls capsid architecture in an icosahedral animal virus. Nature. 1993 Jan 14;361(6408):176–179. doi: 10.1038/361176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. J., McKinney B. R., Schneemann A., Rueckert R. R., Johnson J. E. Crystallization of viruslike particles assembled from flock house virus coat protein expressed in a baculovirus system. J Virol. 1993 May;67(5):2950–2953. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.5.2950-2953.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Temporal regulation of baculovirus RNA: overlapping early and late transcripts. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):392–400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.392-400.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Rueckert R. R. Black beetle virus: messenger for protein B is a subgenomic viral RNA. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):986–995. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.986-995.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Rueckert R. R. Early and late functions in a bipartite RNA virus: evidence for translational control by competition between viral mRNAs. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):116–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.116-124.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Rueckert R. R. Synthesis of Black Beetle Virus Proteins in Cultured Drosophila Cells: Differential Expression of RNAs 1 and 2. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):876–886. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.876-886.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. M., Friesen P. D., Rueckert R. R. Autonomous replication and expression of RNA 1 from black beetle virus. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):481–489. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.481-489.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. M., Rueckert R. R. Assembly-dependent maturation cleavage in provirions of a small icosahedral insect ribovirus. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3399–3406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3399-3406.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Ghosh A., Dasmahapatra B., Dasgupta R., Kaesberg P. Sequence of the black beetle virus subgenomic RNA and its location in the viral genome. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):199–203. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Kaesberg P. Isolation and Characterization of an RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase from Black Beetle Virus-Infected Drosophila melanogaster Cells. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):379–386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.379-386.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosur M. V., Schmidt T., Tucker R. C., Johnson J. E., Gallagher T. M., Selling B. H., Rueckert R. R. Structure of an insect virus at 3.0 A resolution. Proteins. 1987;2(3):167–176. doi: 10.1002/prot.340020302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K. Baculoviruses as gene expression vectors. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1988;42:177–199. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.42.100188.001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman J. F., Brown F. Further physicochemical characterization of Nodamura virus. Evidence that the divided genome occurs in a single component. J Gen Virol. 1978 Jan;38(1):83–95. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders K., Kaesberg P. Template-dependent RNA polymerase from black beetle virus-infected Drosophila melanogaster cells. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):373–381. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90139-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneemann A., Zhong W., Gallagher T. M., Rueckert R. R. Maturation cleavage required for infectivity of a nodavirus. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6728–6734. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6728-6734.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selling B. H., Rueckert R. R. Plaque assay for black beetle virus. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):251–253. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.251-253.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. L., Goodwin R. H., Tompkins G. J., McCawley P. The establishment of two cell lines from the insect Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). In Vitro. 1977 Apr;13(4):213–217. doi: 10.1007/BF02615077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]