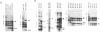Abstract
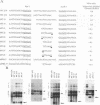
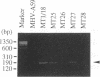
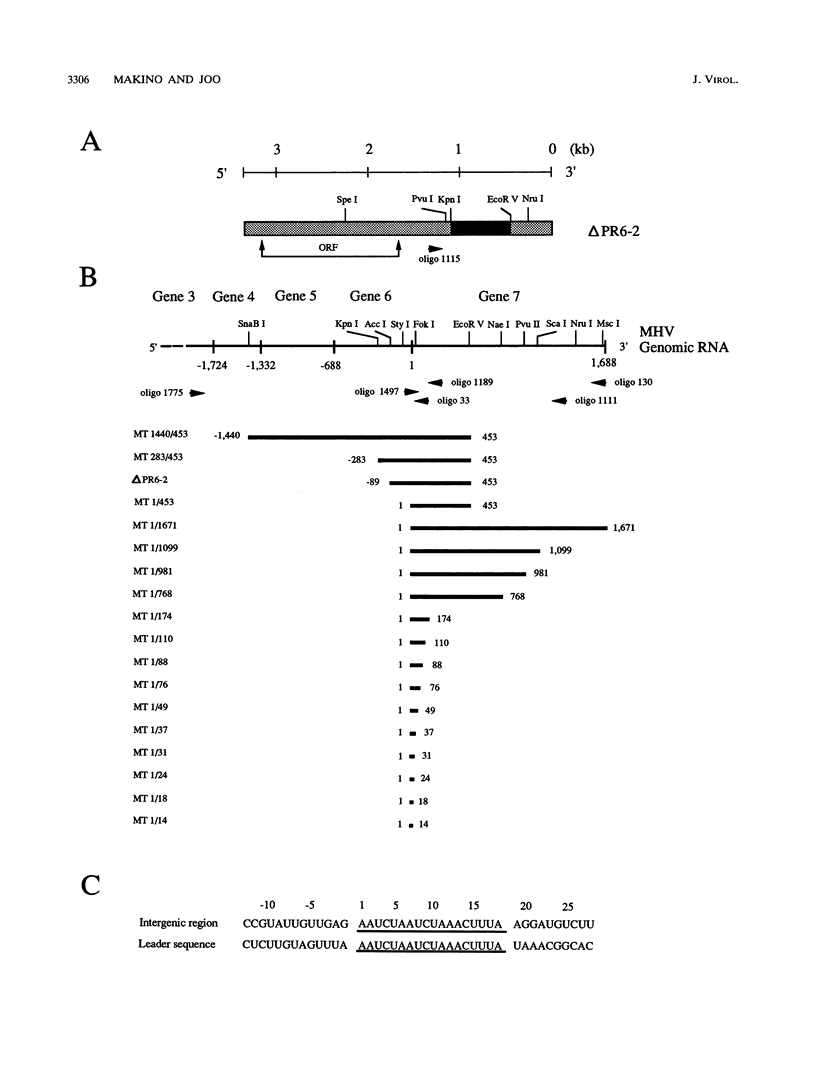
Insertion of a region, including the 18-nucleotide-long intergenic sequence between genes 6 and 7 of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV) genomic RNA, into an MHV defective interfering (DI) RNA leads to transcription of subgenomic DI RNA in helper virus-infected cells (S. Makino, M. Joo, and J. K. Makino, J. Virol. 66:6031-6041, 1991). In this study, the subgenomic DI RNA system was used to determine how sequences flanking the intergenic region affect MHV RNA transcription and to identify the minimum intergenic sequence required for MHV transcription. DI cDNAs containing the intergenic region between genes 6 and 7, but with different lengths of upstream or downstream flanking sequences, were constructed. All DI cDNAs had an 18-nucleotide-long intergenic region that was identical to the 3' region of the genomic leader sequence, which contains two UCUAA repeat sequences. These constructs included 0 to 1,440 nucleotides of upstream flanking sequence and 0 to 1,671 nucleotides of downstream flanking sequence. An analysis of intracellular genomic DI RNA and subgenomic DI RNA species revealed that there were no significant differences in the ratios of subgenomic to genomic DI RNA for any of the DI RNA constructs. DI cDNAs which lacked the intergenic region flanking sequences and contained a series of deletions within the 18-nucleotide-long intergenic sequence were constructed to determine the minimum sequence necessary for subgenomic DI RNA transcription. Small amounts of subgenomic DI RNA were synthesized from genomic DI RNAs with the intergenic consensus sequences UCUAAAC and GCUAAAC, whereas no subgenomic DI RNA transcription was observed from DI RNAs containing UCUAAAG and GCTAAAG sequences. These analyses demonstrated that the sequences flanking the intergenic sequence between genes 6 and 7 did not play a role in subgenomic DI RNA transcription regulation and that the UCUAAAC consensus sequence was sufficient for subgenomic DI RNA transcription.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlquist P., Strauss E. G., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H., Haseloff J., Zimmern D. Sindbis virus proteins nsP1 and nsP2 contain homology to nonstructural proteins from several RNA plant viruses. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):536–542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.536-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. C., Lai M. M. An in vitro system for the leader-primed transcription of coronavirus mRNAs. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4173–4179. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07641.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baric R. S., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. Characterization of replicative intermediate RNA of mouse hepatitis virus: presence of leader RNA sequences on nascent chains. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):633–640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.633-640.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosmire J. A., Hwang K., Makino S. Identification and characterization of a coronavirus packaging signal. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3522–3530. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3522-3530.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French R., Ahlquist P. Characterization and engineering of sequences controlling in vivo synthesis of brome mosaic virus subgenomic RNA. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2411–2420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2411-2420.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano N., Fujiwara K., Hino S., Matumoto M. Replication and plaque formation of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-2) in mouse cell line DBT culture. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;44(3):298–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01240618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeong Y. S., Makino S. Mechanism of coronavirus transcription: duration of primary transcription initiation activity and effects of subgenomic RNA transcription on RNA replication. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3339–3346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3339-3346.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joo M., Makino S. Mutagenic analysis of the coronavirus intergenic consensus sequence. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6330–6337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6330-6337.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Baric R. S., Brayton P. R., Stohlman S. A. Characterization of leader RNA sequences on the virion and mRNAs of mouse hepatitis virus, a cytoplasmic RNA virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3626–3630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Brayton P. R., Armen R. C., Patton C. D., Pugh C., Stohlman S. A. Mouse hepatitis virus A59: mRNA structure and genetic localization of the sequence divergence from hepatotropic strain MHV-3. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):823–834. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.823-834.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M. Coronavirus: organization, replication and expression of genome. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:303–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Baric R. S., Stohlman S. A. Presence of leader sequences in the mRNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1027-1033.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Stohlman S. A. RNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):236–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.236-242.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. J., Shieh C. K., Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., La Monica N., Tuler J., Bagdzhadzhyan A., Lai M. M. The complete sequence (22 kilobases) of murine coronavirus gene 1 encoding the putative proteases and RNA polymerase. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):567–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90071-I. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., Wilhelmsen K. C., Bond C. W. The virus-specific intracellular RNA species of two murine coronaviruses: MHV-a59 and MHV-JHM. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):39–51. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90250-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Schlesinger S., Huang H. V. Promoter for Sindbis virus RNA-dependent subgenomic RNA transcription. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1726–1733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1726-1733.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Joo M., Makino J. K. A system for study of coronavirus mRNA synthesis: a regulated, expressed subgenomic defective interfering RNA results from intergenic site insertion. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6031–6041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6031-6041.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Lai M. M. Evolution of the 5'-end of genomic RNA of murine coronaviruses during passages in vitro. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):227–232. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90060-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Lai M. M. High-frequency leader sequence switching during coronavirus defective interfering RNA replication. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5285–5292. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5285-5292.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Shieh C. K., Keck J. G., Lai M. M. Defective-interfering particles of murine coronavirus: mechanism of synthesis of defective viral RNAs. Virology. 1988 Mar;163(1):104–111. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90237-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Soe L. H., Shieh C. K., Lai M. M. Discontinuous transcription generates heterogeneity at the leader fusion sites of coronavirus mRNAs. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3870–3873. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3870-3873.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Taguchi F., Hirano N., Fujiwara K. Analysis of genomic and intracellular viral RNAs of small plaque mutants of mouse hepatitis virus, JHM strain. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):138–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90335-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Yokomori K., Lai M. M. Analysis of efficiently packaged defective interfering RNAs of murine coronavirus: localization of a possible RNA-packaging signal. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6045–6053. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6045-6053.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachuk C. J., Bredenbeek P. J., Zoltick P. W., Spaan W. J., Weiss S. R. Molecular cloning of the gene encoding the putative polymerase of mouse hepatitis coronavirus, strain A59. Virology. 1989 Jul;171(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90520-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfleiderer M., Skinner M. A., Siddell S. G. Coronavirus MHV-JHM: nucleotide sequence of the mRNA that encodes the membrane protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6338–6338. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki S. G., Sawicki D. L. Coronavirus minus-strand RNA synthesis and effect of cycloheximide on coronavirus RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):328–334. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.328-334.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki S. G., Sawicki D. L. Coronavirus transcription: subgenomic mouse hepatitis virus replicative intermediates function in RNA synthesis. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1050–1056. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1050-1056.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethna P. B., Hofmann M. A., Brian D. A. Minus-strand copies of replicating coronavirus mRNAs contain antileaders. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):320–325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.320-325.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sethna P. B., Hung S. L., Brian D. A. Coronavirus subgenomic minus-strand RNAs and the potential for mRNA replicons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5626–5630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh C. K., Soe L. H., Makino S., Chang M. F., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. The 5'-end sequence of the murine coronavirus genome: implications for multiple fusion sites in leader-primed transcription. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90412-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Ebner D., Siddell S. G. Coronavirus MHV-JHM mRNA 5 has a sequence arrangement which potentially allows translation of a second, downstream open reading frame. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):581–592. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Siddell S. G. Coding sequence of coronavirus MHV-JHM mRNA 4. J Gen Virol. 1985 Mar;66(Pt 3):593–596. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-3-593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokomori K., Banner L. R., Lai M. M. Coronavirus mRNA transcription: UV light transcriptional mapping studies suggest an early requirement for a genomic-length template. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4671–4678. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4671-4678.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokomori K., Lai M. M. Mouse hepatitis virus S RNA sequence reveals that nonstructural proteins ns4 and ns5a are not essential for murine coronavirus replication. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5605–5608. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5605-5608.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Most R. G., Bredenbeek P. J., Spaan W. J. A domain at the 3' end of the polymerase gene is essential for encapsidation of coronavirus defective interfering RNAs. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3219–3226. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3219-3226.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]