Abstract
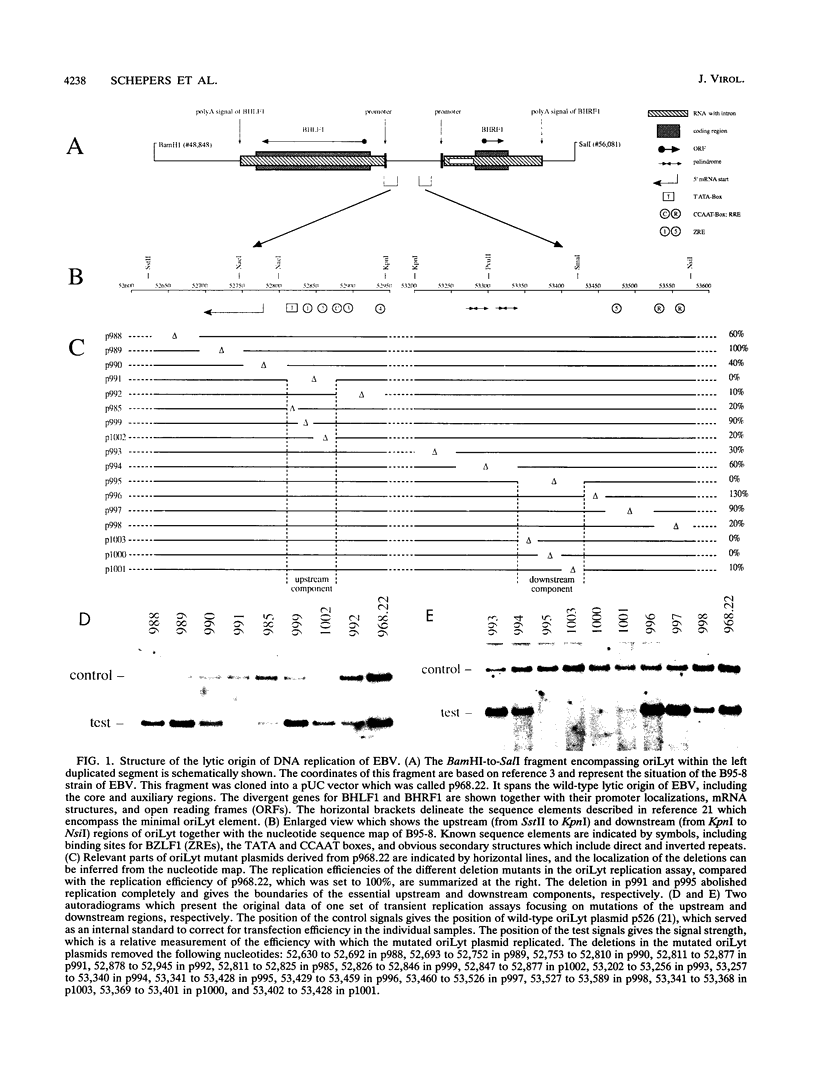
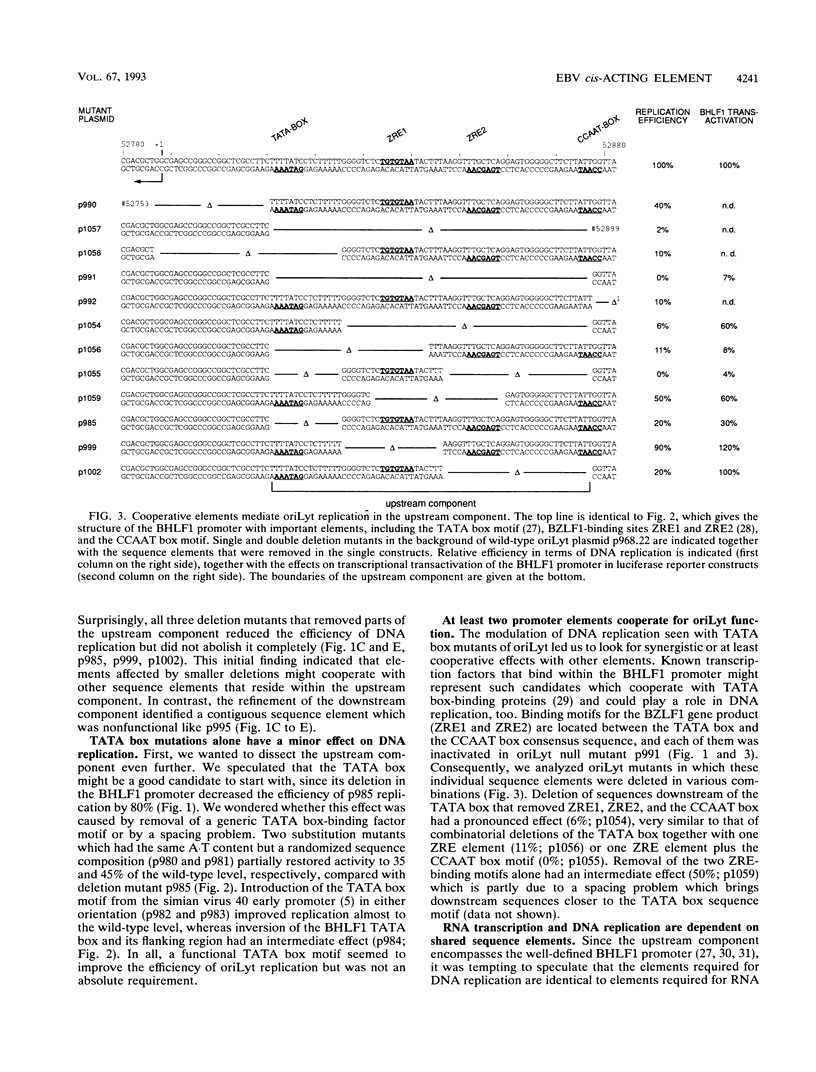
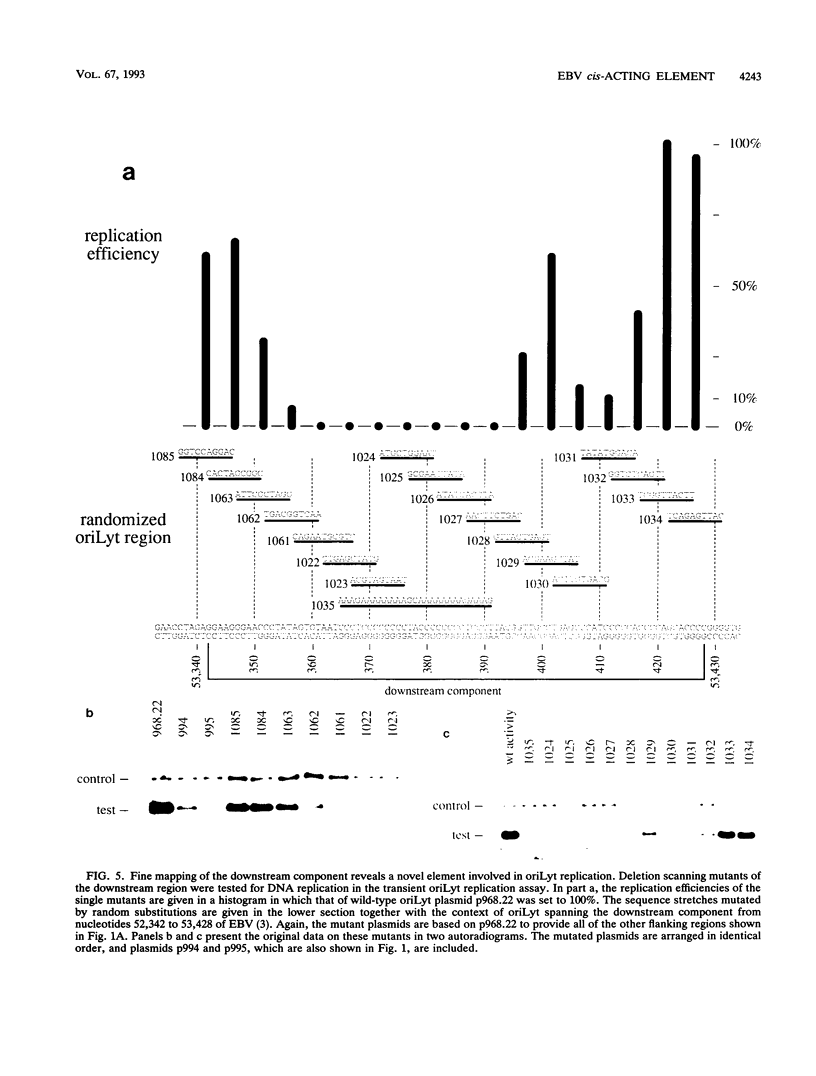
oriLyt, the cis-acting element of Epstein-Barr virus, mediates viral DNA replication in the lytic phase of the virus's life cycle. Oligonucleotide-directed in vitro mutagenesis of oriLyt plasmids allowed the identification of two noncontiguous components within the complex structure of oriLyt. Both components were indispensable for DNA replication of this origin. The upstream component colocalized with the promoter of the viral BHLF1-encoding gene, and mutants affecting DNA replication affected RNA transcription, too. The second component crucial for oriLyt function was determined to be 40 bp long and positioned approximately 530 bp downstream. It was dispensable for transcriptional transactivation but it was absolutely required for replication. Thus, the overall design of oriLyt has striking similarity to multipartite regulatory elements of transcription, consisting of proximal promoters and distal enhancers, but special elements are exclusively dedicated to DNA replication.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders D. G., Kacica M. A., Pari G., Punturieri S. M. Boundaries and structure of human cytomegalovirus oriLyt, a complex origin for lytic-phase DNA replication. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3373–3384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3373-3384.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anders D. G., Punturieri S. M. Multicomponent origin of cytomegalovirus lytic-phase DNA replication. J Virol. 1991 Feb;65(2):931–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.2.931-937.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister A. J., Cook A., Kouzarides T. In vitro DNA binding activity of Fos/Jun and BZLF1 but not C/EBP is affected by redox changes. Oncogene. 1991 Jul;6(7):1243–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruckner R. C., Crute J. J., Dodson M. S., Lehman I. R. The herpes simplex virus 1 origin binding protein: a DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2669–2674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D. A method for identifying the viral genes required for herpesvirus DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9094–9098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier-Greco A., Manet E., Chavrier P., Mosnier C., Daillie J., Sergeant A. Both Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded trans-acting factors, EB1 and EB2, are required to activate transcription from an EBV early promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3243–3249. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Countryman J., Miller G. Activation of expression of latent Epstein-Barr herpesvirus after gene transfer with a small cloned subfragment of heterogeneous viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4085–4089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Transcriptional elements as components of eukaryotic origins of DNA replication. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):635–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90398-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P., Lehman I. R. Interaction of origin binding protein with an origin of replication of herpes simplex virus 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2959–2963. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Rowe D. T., Rooney C. M., Kouzarides T. Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 trans-activator specifically binds to a consensus AP-1 site and is related to c-fos. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):127–132. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03356.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fierer D. S., Challberg M. D. Purification and characterization of UL9, the herpes simplex virus type 1 origin-binding protein. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):3986–3995. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.3986-3995.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fixman E. D., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. trans-acting requirements for replication of Epstein-Barr virus ori-Lyt. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5030–5039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5030-5039.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaser R., Nonoyama M. Host cell regulation of induction of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):174–176. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.174-176.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruffat H., Manet E., Rigolet A., Sergeant A. The enhancer factor R of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a sequence-specific DNA binding protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6835–6843. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruffat H., Moreno N., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) ORI1yt enhancer is not B-cell specific and does not respond synergistically to the EBV transcription factors R and Z. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2810–2818. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2810-2818.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerschmidt W., Sugden B. Identification and characterization of oriLyt, a lytic origin of DNA replication of Epstein-Barr virus. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):427–433. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamzeh F. M., Lietman P. S., Gibson W., Hayward G. S. Identification of the lytic origin of DNA replication in human cytomegalovirus by a novel approach utilizing ganciclovir-induced chain termination. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6184–6195. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6184-6195.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L., Rabson M., Brown N., Miller G. New Epstein-Barr virus variants from cellular subclones of P3J-HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):160–163. doi: 10.1038/295160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain V. K., Magrath I. T. A chemiluminescent assay for quantitation of beta-galactosidase in the femtogram range: application to quantitation of beta-galactosidase in lacZ-transfected cells. Anal Biochem. 1991 Nov 15;199(1):119–124. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(91)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Packham G., Cook A., Farrell P. J. The BZLF1 protein of EBV has a coiled coil dimerisation domain without a heptad leucine repeat but with homology to the C/EBP leucine zipper. Oncogene. 1991 Feb;6(2):195–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Freese U. K., Bornkamm G. W. Structure and evolution of two related transcription units of Epstein-Barr virus carrying small tandem repeats. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):987–995. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.987-995.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Berk A. J. In vitro transcriptional activation, dimerization, and DNA-binding specificity of the Epstein-Barr virus Zta protein. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2560–2568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2560-2568.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Berk A. J. The Zta trans-activator protein stabilizes TFIID association with promoter DNA by direct protein-protein interaction. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2441–2454. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Hardwick J. M., Hayward S. D. Responsiveness of the Epstein-Barr virus NotI repeat promoter to the Z transactivator is mediated in a cell-type-specific manner by two independent signal regions. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3040–3050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3040-3050.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Hardwick J. M., Sample J., Hayward G. S., Hayward S. D. The zta transactivator involved in induction of lytic cycle gene expression in Epstein-Barr virus-infected lymphocytes binds to both AP-1 and ZRE sites in target promoter and enhancer regions. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1143–1155. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1143-1155.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGregor G. R., Caskey C. T. Construction of plasmids that express E. coli beta-galactosidase in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 25;17(6):2365–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.6.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masse M. J., Karlin S., Schachtel G. A., Mocarski E. S. Human cytomegalovirus origin of DNA replication (oriLyt) resides within a highly complex repetitive region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5246–5250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus DNA replication: the UL9 gene encodes an origin-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5414–5418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivo P. D., Nelson N. J., Challberg M. D. Herpes simplex virus type 1 gene products required for DNA replication: identification and overexpression. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):196–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.196-204.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Sugden B. trans activation of an Epstein-Barr viral transcriptional enhancer by the Epstein-Barr viral nuclear antigen 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3838–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Yates J., Sugden B. A putative origin of replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus is composed of two cis-acting components. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1822–1832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Shimizu N., Sakuma S., Ono Y. trans activation of the latent Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) genome after transfection of the EBV DNA fragment. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1016–1022. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1016-1022.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urier G., Buisson M., Chambard P., Sergeant A. The Epstein-Barr virus early protein EB1 activates transcription from different responsive elements including AP-1 binding sites. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1447–1453. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. W., Schaffer P. A. Elements in the transcriptional regulatory region flanking herpes simplex virus type 1 oriS stimulate origin function. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2601–2611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2601-2611.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. A., Nelson N. J., McGeoch D. J., Challberg M. D. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 genes required for origin-dependent DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):435–443. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.435-443.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. L., Warren N., Sugden B. Stable replication of plasmids derived from Epstein-Barr virus in various mammalian cells. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):812–815. doi: 10.1038/313812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]