Abstract
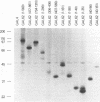
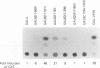
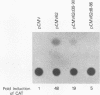
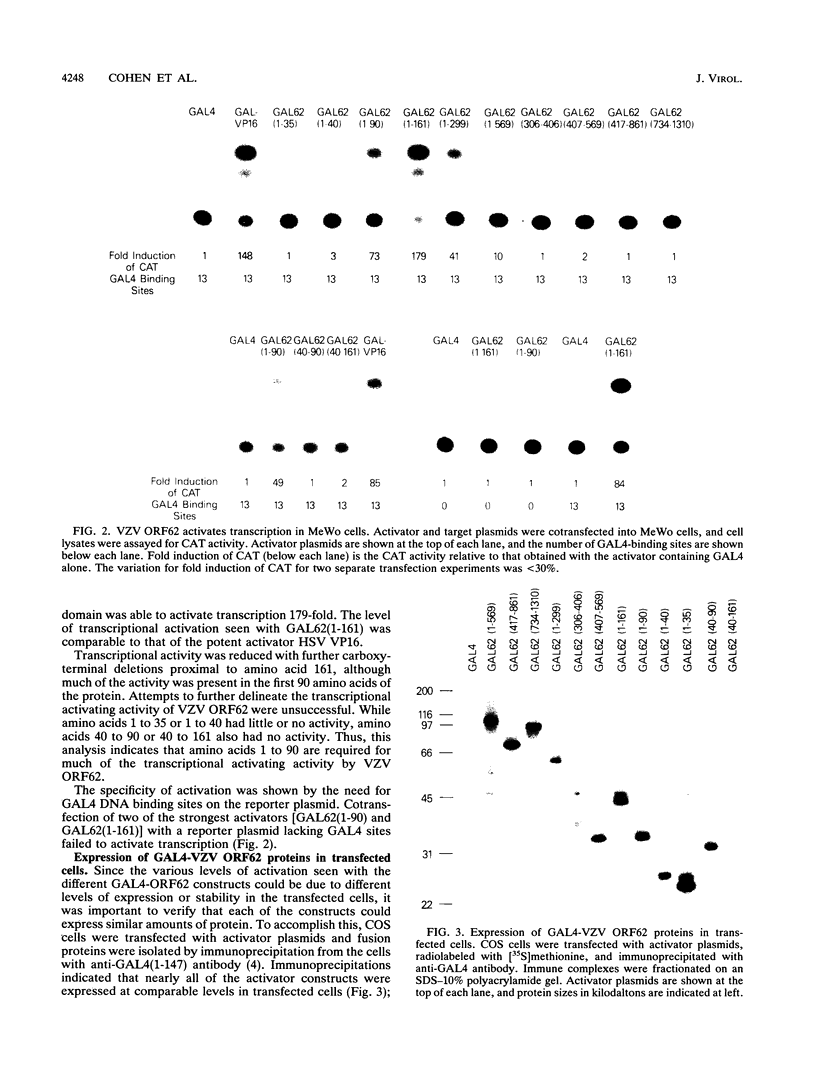
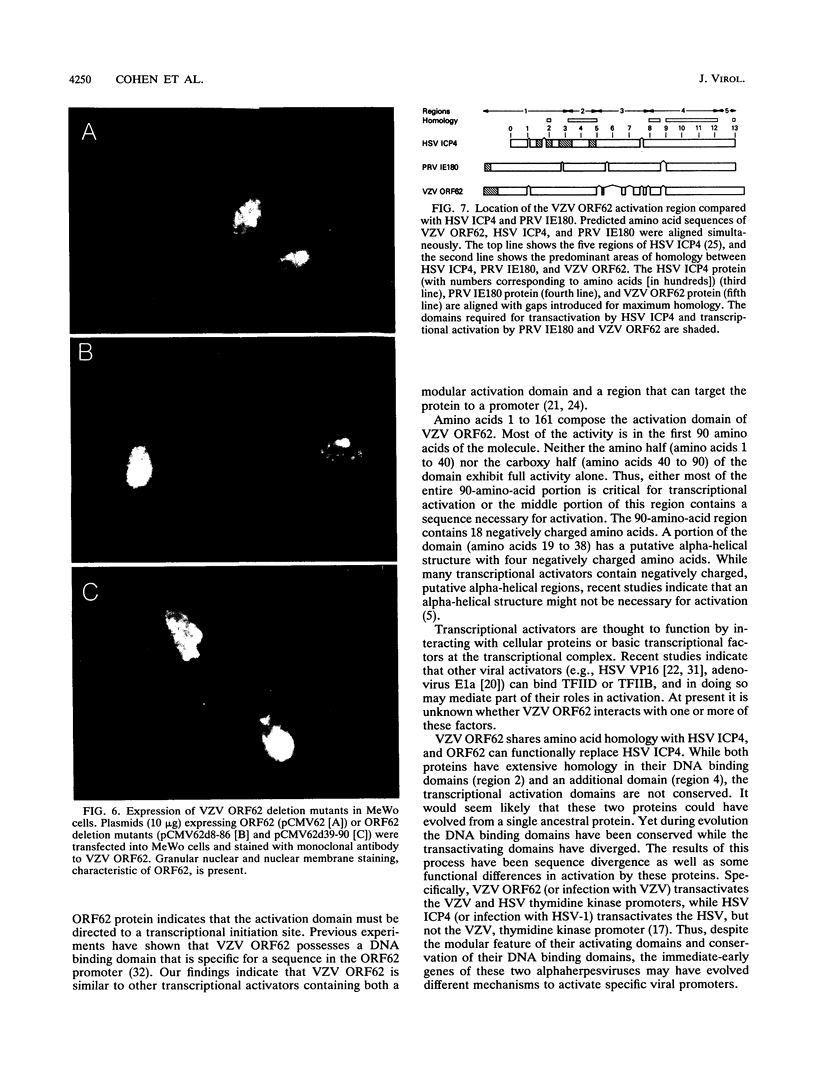
Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) open reading frame 62 (ORF62) encodes an immediate-early protein that transactivates expression of VZV, herpes simplex virus (HSV), and cellular genes in transient expression assays. VZV ORF62 is homologous to HSV ICP4 and pseudorabies virus immediate-early (IE180) proteins. All three viral proteins have conserved DNA binding domains that recognize similar sites in their corresponding promoters. Here, we show that the transcriptional activation domain of ORF62 is located near the amino terminus of the protein and is not conserved with the activation domain of ICP4. A 161-amino-acid activation domain of ORF62 activates transcription to a level comparable to that of the potent HSV VP16 activation domain; much of the activity is contained in the first 90 amino acids of ORF62. Deletion of the activation domain from full-length ORF62 markedly reduced transactivating activity. These experiments indicate that while VZV ORF62 and HSV ICP4 have conserved amino acid sequences, including their DNA binding domains, the transcriptional activation domains are poorly conserved.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvin A. M., Sharp M., Smith S., Koropchak C. M., Diaz P. S., Kinchington P., Ruyechan W., Hay J. Equivalent recognition of a varicella-zoster virus immediate early protein (IE62) and glycoprotein I by cytotoxic T lymphocytes of either CD4+ or CD8+ phenotype. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):257–264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. K. Cloning of the latency gene and the early protein 0 gene of pseudorabies virus. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5260–5271. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5260-5271.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung A. K. DNA nucleotide sequence analysis of the immediate-early gene of pseudorabies virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4637–4646. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. I., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus nuclear protein 2 domain essential for transformation is a direct transcriptional activator. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5880–5885. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5880-5885.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cress W. D., Triezenberg S. J. Critical structural elements of the VP16 transcriptional activation domain. Science. 1991 Jan 4;251(4989):87–90. doi: 10.1126/science.1846049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Scott J. E. The complete DNA sequence of varicella-zoster virus. J Gen Virol. 1986 Sep;67(Pt 9):1759–1816. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-9-1759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Wilkie N. M. Location and orientation of homologous sequences in the genomes of five herpesviruses. J Gen Virol. 1983 Sep;64(Pt 9):1927–1942. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-9-1927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca N. A., Schaffer P. A. Activities of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) ICP4 genes specifying nonsense peptides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4491–4511. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disney G. H., Everett R. D. A herpes simplex virus type 1 recombinant with both copies of the Vmw175 coding sequences replaced by the homologous varicella-zoster virus open reading frame. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71(Pt 11):2681–2689. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-11-2681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disney G. H., McKee T. A., Preston C. M., Everett R. D. The product of varicella-zoster virus gene 62 autoregulates its own promoter. J Gen Virol. 1990 Dec;71(Pt 12):2999–3003. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-12-2999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D. Trans activation of transcription by herpes virus products: requirement for two HSV-1 immediate-early polypeptides for maximum activity. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3135–3141. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02270.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felser J. M., Kinchington P. R., Inchauspe G., Straus S. E., Ostrove J. M. Cell lines containing varicella-zoster virus open reading frame 62 and expressing the "IE" 175 protein complement ICP4 mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2076–2082. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2076-2082.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forghani B., Mahalingam R., Vafai A., Hurst J. W., Dupuis K. W. Monoclonal antibody to immediate early protein encoded by varicella-zoster virus gene 62. Virus Res. 1990 Jun;16(2):195–210. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(90)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Brunel P. A. Varicella-zoster virus: isolation and propagation in human melanoma cells at 36 and 32 degrees C. Infect Immun. 1978 Jan;19(1):199–203. doi: 10.1128/iai.19.1.199-203.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Nagpal S., Ostrove J. M. Mapping of two varicella-zoster virus-encoded genes that activate the expression of viral early and late genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):700–709. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inchauspe G., Ostrove J. M. Differential regulation by varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and herpes simplex virus type-1 trans-activating genes. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):710–714. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90584-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan L., Gill G., Ptashne M. Separation of DNA binding from the transcription-activating function of a eukaryotic regulatory protein. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):699–704. doi: 10.1126/science.3080805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinchington P. R., Hougland J. K., Arvin A. M., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. The varicella-zoster virus immediate-early protein IE62 is a major component of virus particles. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):359–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.359-366.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. S., Kao C. C., Bryant G. O., Liu X., Berk A. J. Adenovirus E1A activation domain binds the basic repeat in the TATA box transcription factor. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):39–44. doi: 10.1038/338039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Mechanism of action of an acidic transcriptional activator in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):971–981. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90321-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry P. W., Solem S., Watson B. N., Koropchak C. M., Thackray H. M., Kinchington P. R., Ruyechan W. T., Ling P., Hay J., Arvin A. M. Immunity in strain 2 guinea-pigs inoculated with vaccinia virus recombinants expressing varicella-zoster virus glycoproteins I, IV, V or the protein product of the immediate early gene 62. J Gen Virol. 1992 Apr;73(Pt 4):811–819. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-4-811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. J., Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Transcriptional activation by the pseudorabies virus immediate early protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2376–2382. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Brauer D. H. Complete DNA sequence of the short repeat region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1727–1745. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson T., Everett R. D. Mutational dissection of the HSV-1 immediate-early protein Vmw175 involved in transcriptional transactivation and repression. Virology. 1988 Sep;166(1):186–196. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90160-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Mosca J. D., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. Regulation of varicella-zoster virus gene expression in human T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5298–5304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5298-5304.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perera L. P., Mosca J. D., Sadeghi-Zadeh M., Ruyechan W. T., Hay J. The varicella-zoster virus immediate early protein, IE62, can positively regulate its cognate promoter. Virology. 1992 Nov;191(1):346–354. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90197-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepard A. A., Imbalzano A. N., DeLuca N. A. Separation of primary structural components conferring autoregulation, transactivation, and DNA-binding properties to the herpes simplex virus transcriptional regulatory protein ICP4. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3714–3728. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3714-3728.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. L., Wilcox K. W. The conserved DNA-binding domains encoded by the herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP4, pseudorabies virus IE180, and varicella-zoster virus ORF62 genes recognize similar sites in the corresponding promoters. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1149–1159. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1149-1159.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]