Abstract
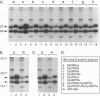
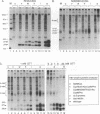
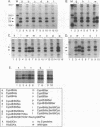
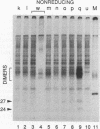
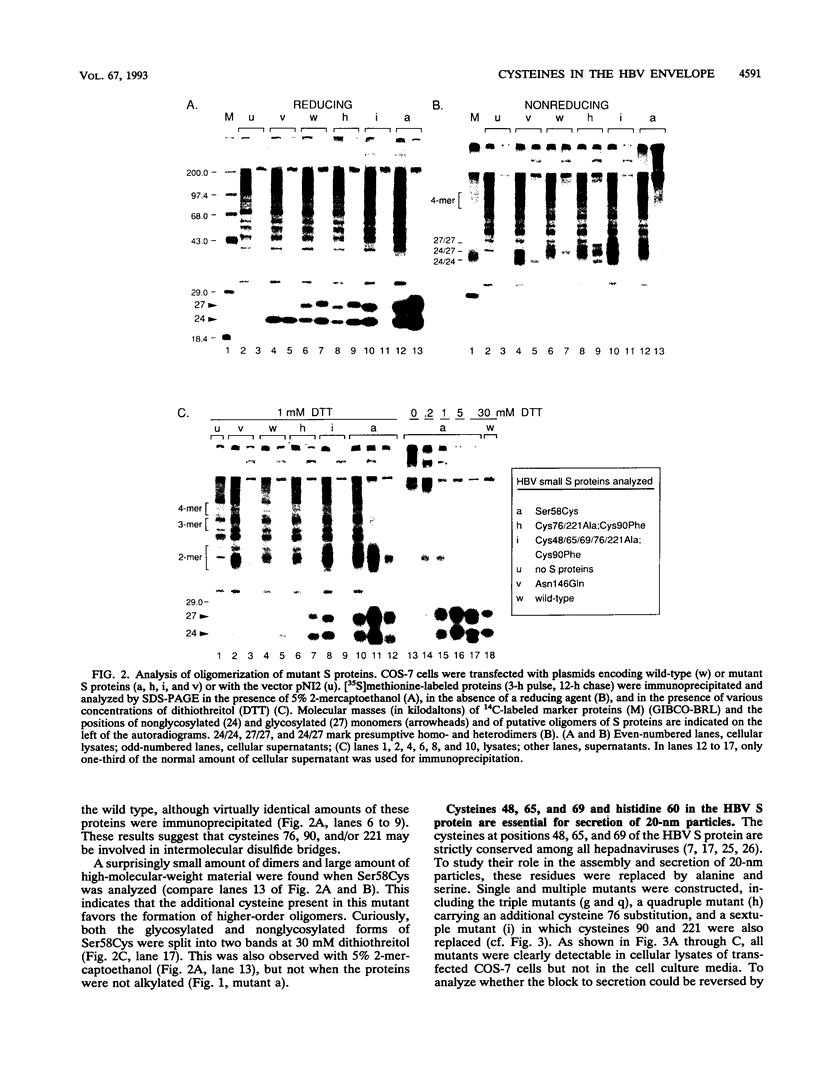
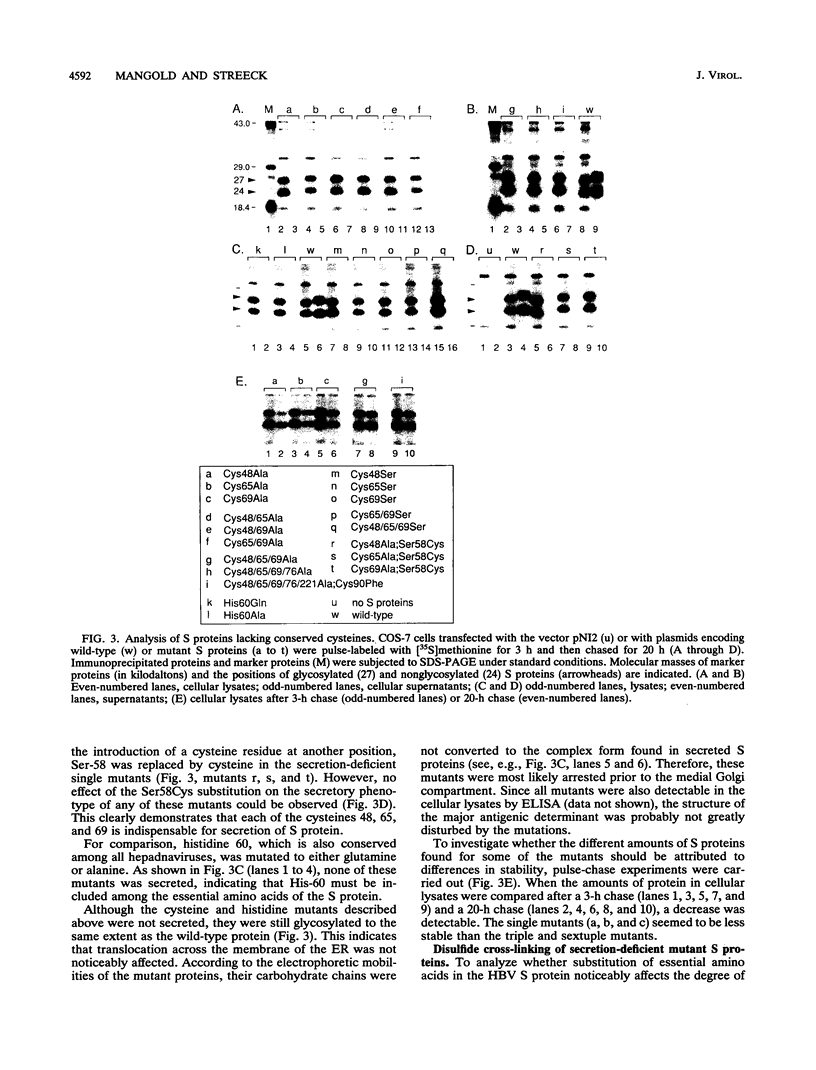
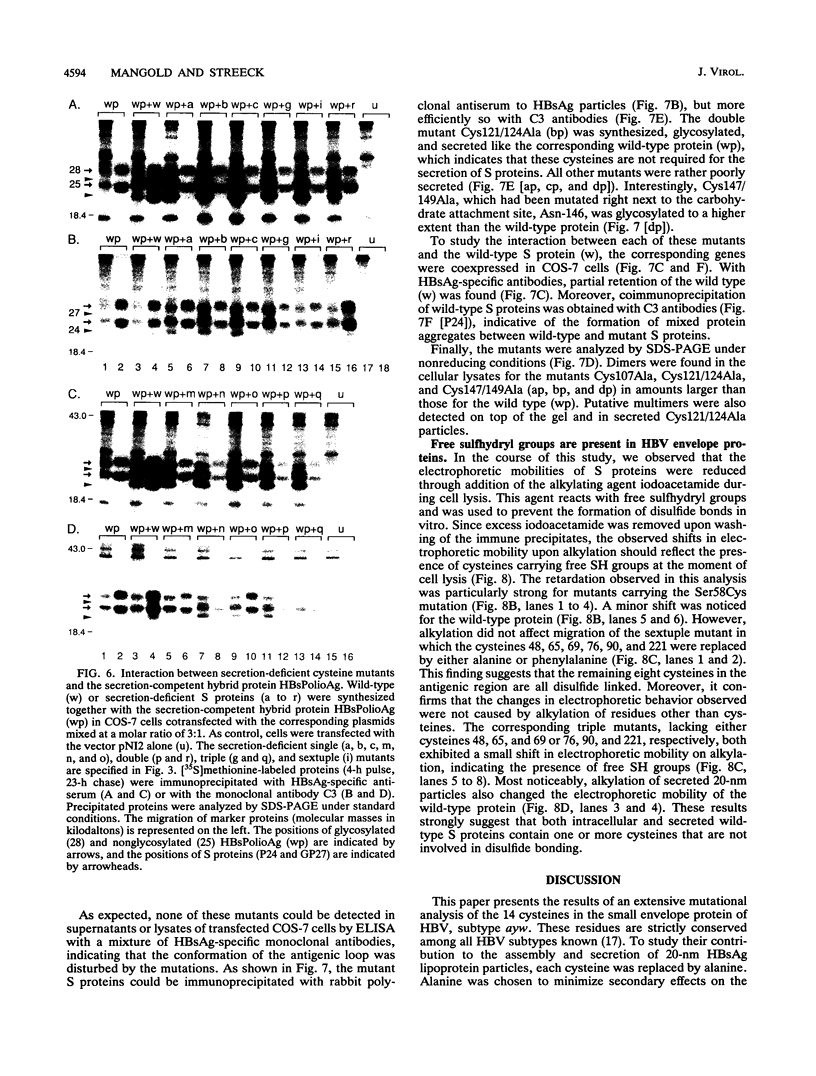
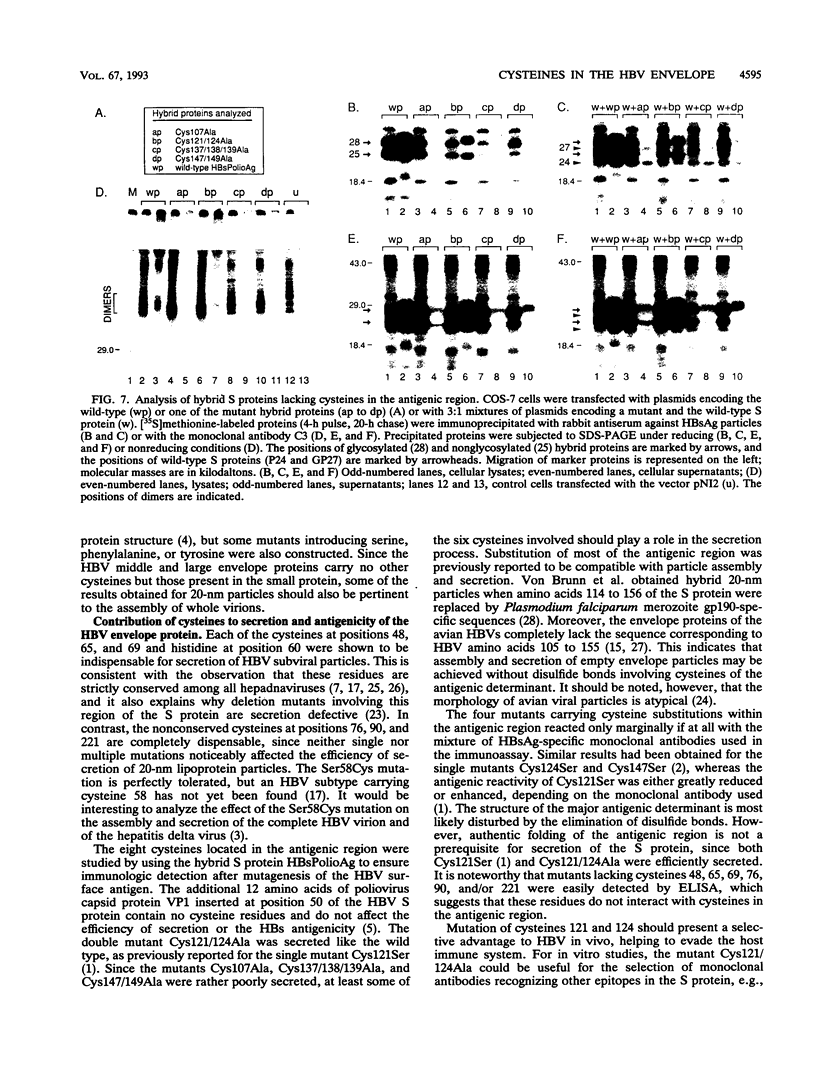
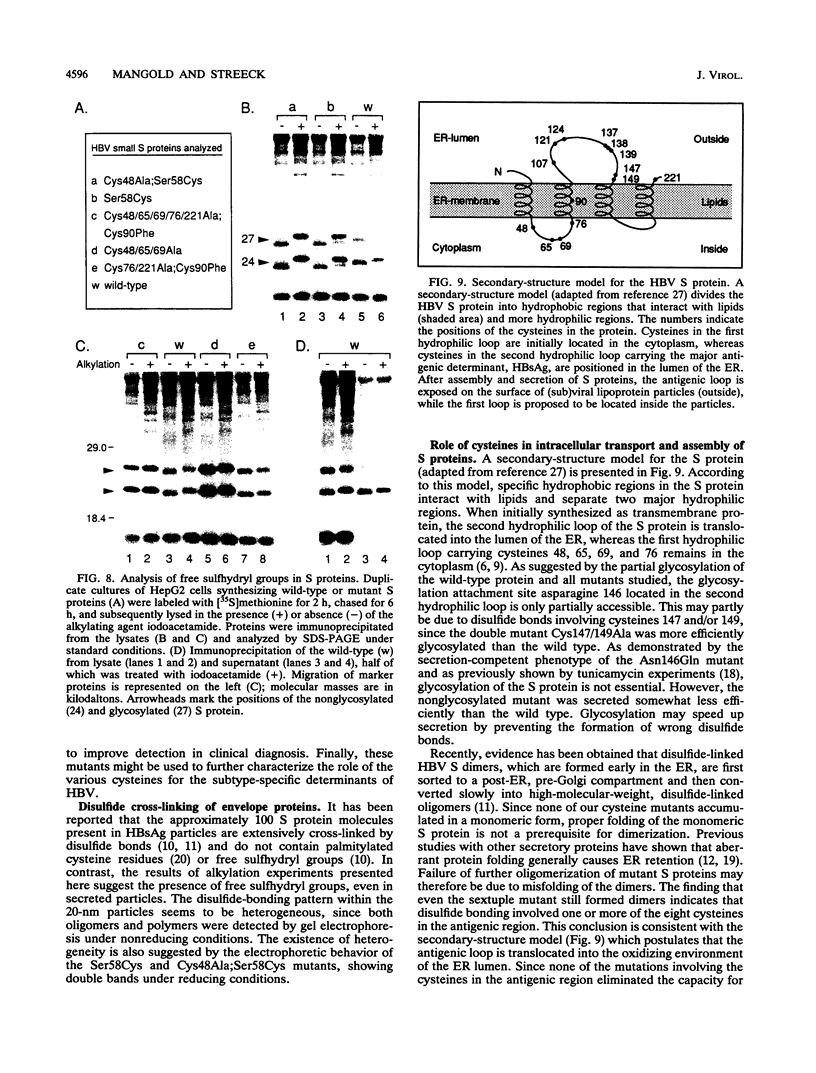
The small envelope protein of hepatitis B virus is the major component of the viral coat and is also secreted from cells as a 20-nm subviral particle, even in the absence of other viral proteins. Such empty envelope particles are composed of approximately 100 copies of this polypeptide and host-derived lipids and are stabilized by extensive intermolecular disulfide cross-linking. To study the contribution of disulfide bonds to assembly and secretion of the viral envelope, single and multiple mutants involving all 14 cysteines in HepG2 and COS-7 cells were analyzed. Of the six cysteines located outside the region carrying the surface antigen, Cys-48, Cys-65, and Cys-69 were each found to be essential for secretion of 20-nm particles, whereas Cys-76, Cys-90, and Cys-221 were dispensable. By introduction of an additional cysteine substituting serine 58, the yield of secreted particles was increased. Of four mutants involving the eight cysteines located in the antigenic region, only the double mutant lacking Cys-121 and Cys-124 was secreted with wild-type efficiency. Secretion-competent envelope proteins were intracellularly retained by secretion-deficient cysteine mutants. According to alkylation studies, both intracellular and secreted envelope proteins contained free sulfhydryl groups. Disulfide-linked oligomers were studied by gel electrophoresis under nonreducing conditions.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton-Rickardt P. G., Murray K. Mutants of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen that define some antigenically essential residues in the immunodominant a region. J Med Virol. 1989 Nov;29(3):196–203. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890290310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonino F., Heermann K. H., Rizzetto M., Gerlich W. H. Hepatitis delta virus: protein composition of delta antigen and its hepatitis B virus-derived envelope. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):945–950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.945-950.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Wells J. A. High-resolution epitope mapping of hGH-receptor interactions by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1081–1085. doi: 10.1126/science.2471267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delpeyroux F., Van Wezel E., Blondel B., Crainic R. Structural factors modulate the activity of antigenic poliovirus sequences expressed on hybrid hepatitis B surface antigen particles. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6090–6100. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6090-6100.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eble B. E., MacRae D. R., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Multiple topogenic sequences determine the transmembrane orientation of the hepatitis B surface antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3591–3601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Chen T. N., Mandart E. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned woodchuck hepatitis virus genome: comparison with the hepatitis B virus sequence. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):51–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.51-65.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Mandart E., Fitoussi F., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Nucleotide sequence of the hepatitis B virus genome (subtype ayw) cloned in E. coli. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):646–650. doi: 10.1038/281646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D. Assembly of hepadnaviral virions and subviral particles. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;168:61–83. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76015-0_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huovila A. P., Eder A. M., Fuller S. D. Hepatitis B surface antigen assembles in a post-ER, pre-Golgi compartment. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(6):1305–1320. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.6.1305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtley S. M., Helenius A. Protein oligomerization in the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:277–307. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel N., Chenciner N., Houlmann C., Streeck R. E. An expression vector for high-level protein synthesis in Vero cells. Gene. 1989 Sep 30;81(2):369–372. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90198-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutfalla G., Armbruster L., Dequin S., Bertolotti R. Construction of an EBNA-producing line of well-differentiated human hepatoma cells and of appropriate Epstein-Barr virus-based shuttle vectors. Gene. 1989 Mar 15;76(1):27–39. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90005-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandart E., Kay A., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned duck hepatitis B virus genome: comparison with woodchuck and human hepatitis B virus sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):782–792. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.782-792.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamaye K. L., Eckstein F. Inhibition of restriction endonuclease Nci I cleavage by phosphorothioate groups and its application to oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9679–9698. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norder H., Hammas B., Löfdahl S., Couroucé A. M., Magnius L. O. Comparison of the amino acid sequences of nine different serotypes of hepatitis B surface antigen and genomic classification of the corresponding hepatitis B virus strains. J Gen Virol. 1992 May;73(Pt 5):1201–1208. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-5-1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzer E. J., Nakamura G. R., Yaffe A. Intracellular transport and secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):346–353. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.346-353.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Control of protein exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. The preS1 protein of hepatitis B virus is acylated at its amino terminus with myristic acid. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1672–1677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1672-1677.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L., Nath N., Gavilanes F. Structure of hepatitis B surface antigen. Correlation of subtype with amino acid sequence and location of the carbohydrate moiety. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10414–10420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L. The structure of hepatitis B surface antigen and its antigenic sites. Bioessays. 1987 Jun;6(6):258–262. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prange R., Nagel R., Streeck R. E. Deletions in the hepatitis B virus small envelope protein: effect on assembly and secretion of surface antigen particles. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5832–5841. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5832-5841.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger C., Ganem D., Varmus H. E. Nucleotide sequence of an infectious molecularly cloned genome of ground squirrel hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):367–375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.367-375.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Kaleta E. F., Will H. Isolation and characterization of a hepatitis B virus endemic in herons. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3832–3839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3832-3839.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirk H. J., Thornton J. M., Howard C. R. A topological model for hepatitis B surface antigen. Intervirology. 1992;33(3):148–158. doi: 10.1159/000150244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Silverstein S., Lee L. S., Pellicer A., Cheng Y. c., Axel R. Transfer of purified herpes virus thymidine kinase gene to cultured mouse cells. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90333-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Brunn A., Früh K., Müller H. M., Zentgraf H. W., Bujard H. Epitopes of the human malaria parasite P. falciparum carried on the surface of HBsAg particles elicit an immune response against the parasite. Vaccine. 1991 Jul;9(7):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(91)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]