Abstract
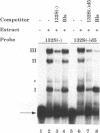
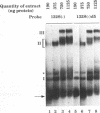
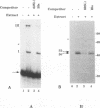
The 3' end of Sindbis virus minus-sense RNA was tested for its ability to bind proteins in mosquito cell extracts, using labeled riboprobes that represented different parts of this region. We found four domains in the first 250 nucleotides that could bind the same 50- and 52-kDa proteins, three with high affinity and one with low affinity, whereas tested domains outside this region did not bind these proteins. The first binding domain was found in the first 60 nucleotides, which represents the complement of the 5'-nontranslated region, the second in the next 60 nucleotides, the third in the following 60 nucleotides, and the fourth between nucleotides 194 and 249 (all numbering is 3' to 5'). The relative binding constants, Kr, of the first, second, and fourth sites were similar, whereas that of domain 2 was fivefold less. Deletion mapping of the first domain showed that the first 10 nucleotides were critical for binding. Deletion of nucleotides 2 to 4, deletion or replacement of nucleotide 5, or deletion of the first 15 nucleotides was deleterious for binding, deletion of nucleotides 10 to 15, 26 to 40, or 41 to 55 had little effect on the binding, and deletion of nucleotides 15 to to 25 increased the binding affinity. We also found that the corresponding riboprobes derived from two other alphaviruses, Ross River virus and Semliki Forest virus, and from rubella virus were also able to interact with the 50- and 52-kDa proteins. The Kr value for the Semliki Forest virus probe was similar to that for the Sindbis virus probe, while that for the Ross River virus probe was four times greater. The rubella virus probe was bound only weakly, consistent with the fact that mosquito cells are not permissive for rubella virus replication. We suggest that the binding of the 50- and 52-kDa proteins to the 3' end of alphavirus minus-sense RNA represents an important step in the initiation of RNA replication.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrera-Saldana H., Takahashi K., Vigneron M., Wildeman A., Davidson I., Chambon P. All six GC-motifs of the SV40 early upstream element contribute to promoter activity in vivo and in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3839–3849. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04156.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berben-Bloemheuvel G., Kasperaitis M. A., van Heugten H., Thomas A. A., van Steeg H., Voorma H. O. Interaction of initiation factors with the cap structure of chimaeric mRNA containing the 5'-untranslated regions of Semliki Forest virus RNA is related to translational efficiency. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Sep 15;208(3):581–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calzone F. J., Thézé N., Thiebaud P., Hill R. L., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Developmental appearance of factors that bind specifically to cis-regulatory sequences of a gene expressed in the sea urchin embryo. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1074–1088. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Seta F., Treich I., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A. ABF1 binding sites in yeast RNA polymerase genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15168–15175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez G., Wang C. Y., Frey T. K. Sequence of the genome RNA of rubella virus: evidence for genetic rearrangement during togavirus evolution. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):225–238. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90476-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huismans H., van Dijk A. A., Bauskin A. R. In vitro phosphorylation and purification of a nonstructural protein of bluetongue virus with affinity for single-stranded RNA. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3589–3595. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3589-3595.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jang S. K., Wimmer E. Cap-independent translation of encephalomyocarditis virus RNA: structural elements of the internal ribosomal entry site and involvement of a cellular 57-kD RNA-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1560–1572. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn R. J., Hong Z., Strauss J. H. Mutagenesis of the 3' nontranslated region of Sindbis virus RNA. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1465–1476. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1465-1476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn R. J., Niesters H. G., Hong Z., Strauss J. H. Infectious RNA transcripts from Ross River virus cDNA clones and the construction and characterization of defined chimeras with Sindbis virus. Virology. 1991 Jun;182(2):430–441. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90584-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Schlesinger S., Huang H. V. Promoter for Sindbis virus RNA-dependent subgenomic RNA transcription. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1726–1733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1726-1733.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meerovitch K., Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. A cellular protein that binds to the 5'-noncoding region of poliovirus RNA: implications for internal translation initiation. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1026–1034. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakhasi H. L., Cao X. Q., Rouault T. A., Liu T. Y. Specific binding of host cell proteins to the 3'-terminal stem-loop structure of rubella virus negative-strand RNA. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5961–5967. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5961-5967.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson R., Pelletier J., Le S. Y., Sonenberg N. Structural and functional analysis of the ribosome landing pad of poliovirus type 2: in vivo translation studies. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5886–5894. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5886-5894.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niesters H. G., Strauss J. H. Defined mutations in the 5' nontranslated sequence of Sindbis virus RNA. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4162–4168. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4162-4168.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niesters H. G., Strauss J. H. Mutagenesis of the conserved 51-nucleotide region of Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1639–1647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1639-1647.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardigon N., Strauss J. H. Cellular proteins bind to the 3' end of Sindbis virus minus-strand RNA. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):1007–1015. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.1007-1015.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raju R., Huang H. V. Analysis of Sindbis virus promoter recognition in vivo, using novel vectors with two subgenomic mRNA promoters. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2501–2510. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2501-2510.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheline C. T., Milocco L. H., Jones K. A. Two distinct nuclear transcription factors recognize loop and bulge residues of the HIV-1 TAR RNA hairpin. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2508–2520. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somma M. P., Pisano C., Lavia P. The housekeeping promoter from the mouse CpG island HTF9 contains multiple protein-binding elements that are functionally redundant. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jun 11;19(11):2817–2824. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.11.2817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsiang M., Weiss B. G., Schlesinger S. Effects of 5'-terminal modifications on the biological activity of defective interfering RNAs of Sindbis virus. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):47–53. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.47-53.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Angel R. M., Papavassiliou A. G., Fernández-Tomás C., Silverstein S. J., Racaniello V. R. Cell proteins bind to multiple sites within the 5' untranslated region of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8299–8303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]