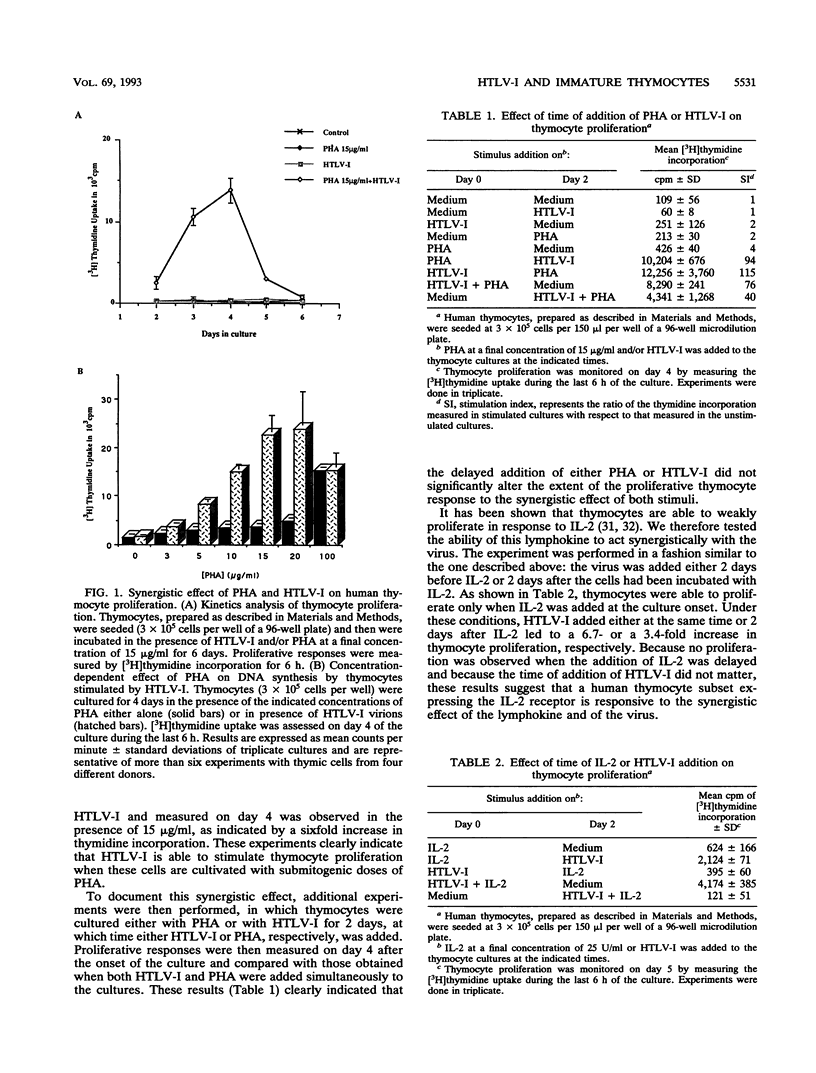
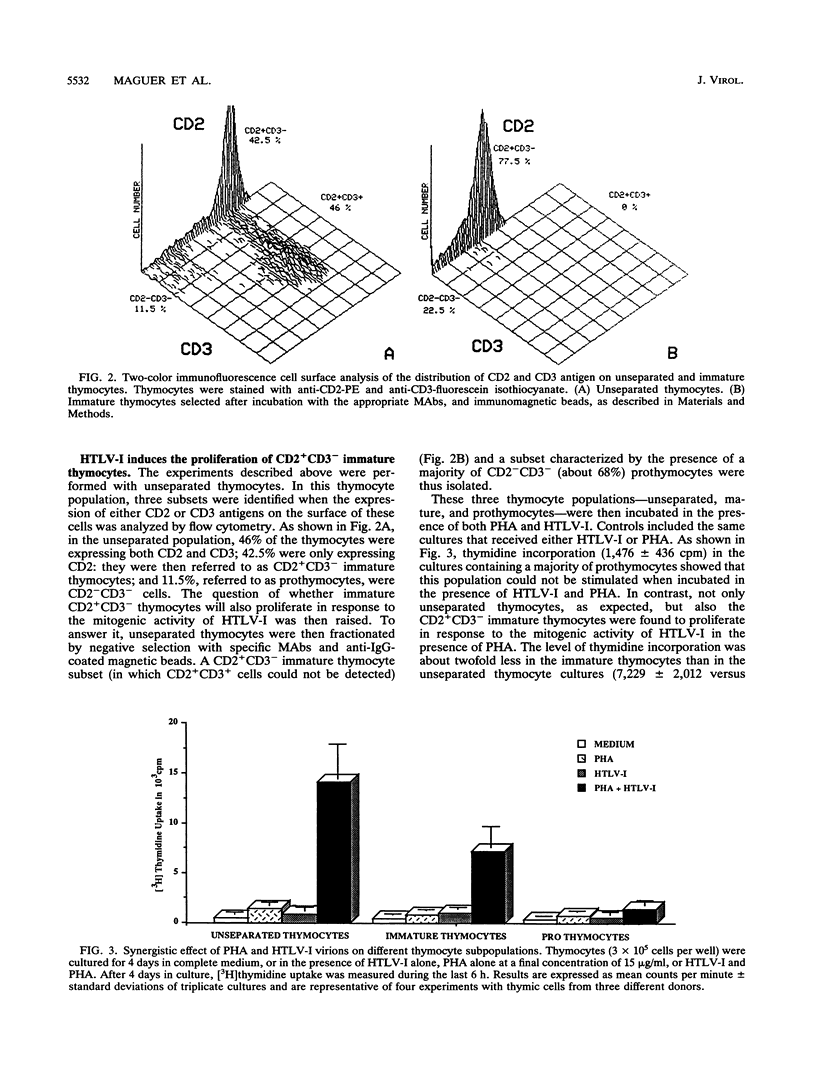
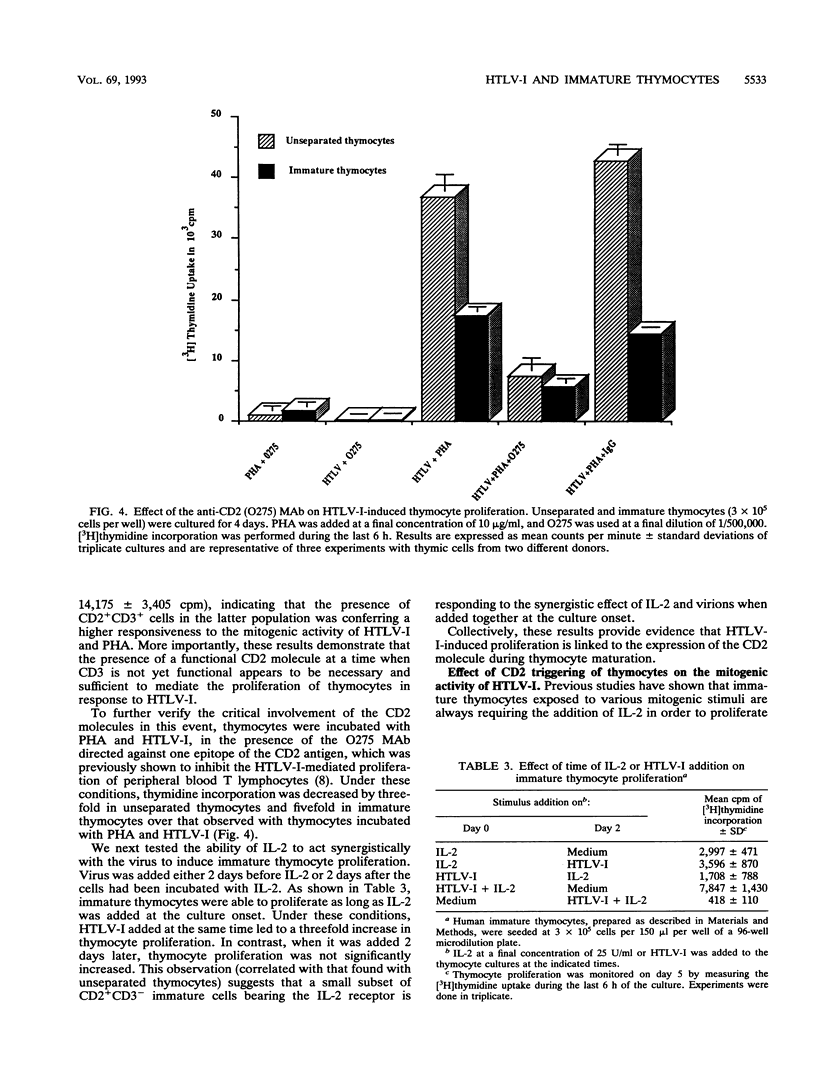
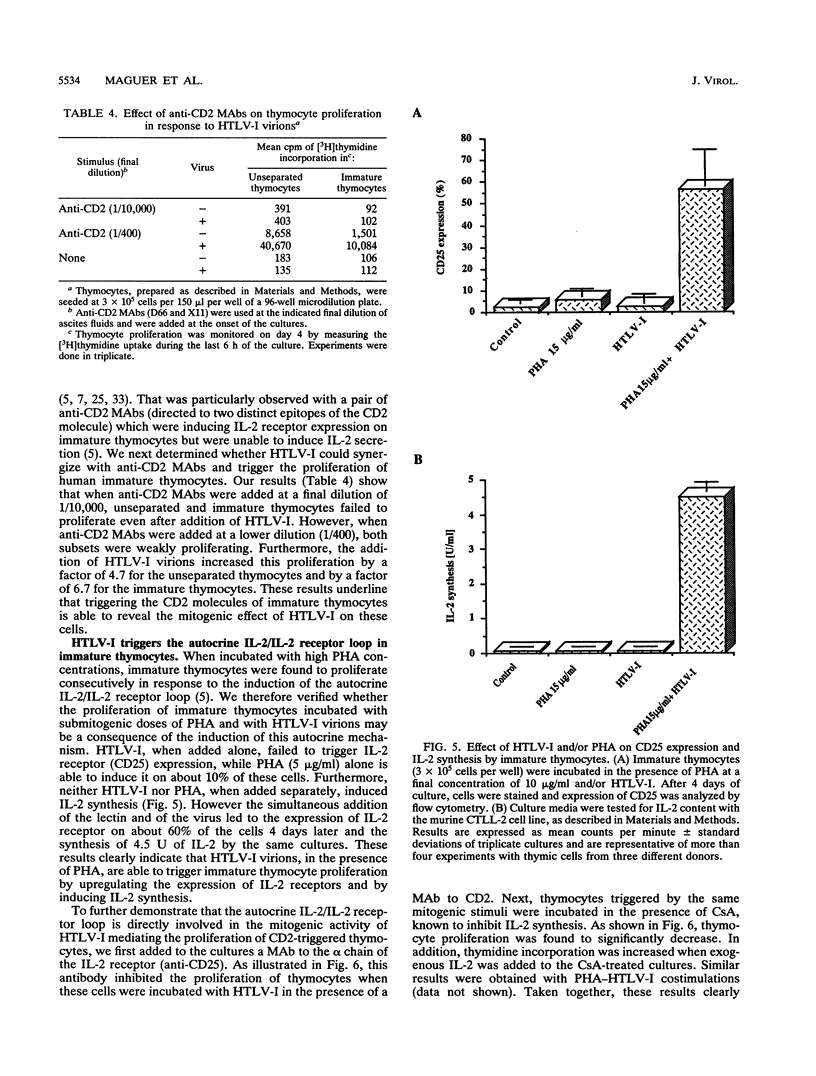
Abstract
The mitogenic activity of human T-cell leukemia virus type I (HTLV-I) is triggering the proliferation of human resting T lymphocytes through the induction of the interleukin-2 (IL-2)/IL-2 receptor autocrine loop. This HTLV-I-induced proliferation was found to be mainly mediated by the CD2 T-cell antigen, which is first expressed on double-negative lymphoid precursors after colonization of the thymus. Thus, immature thymocytes express the CD2 antigen before that of the CD3-TCR complex. We therefore investigated the responsiveness of these CD2+CD3- immature thymocytes and compared it with that of unseparated thymocytes, containing a majority of the CD2+CD3+ mature thymocytes, and that of the CD2-CD3- prothymocytes. Both immature and unseparated thymocytes were incorporating [3H]thymidine in response to the virus, provided that they were cultivated in the presence of submitogenic doses of phytohemagglutinin. In contrast, the prothymocytes did not proliferate. Downmodulation of the CD2 molecule by incubating unseparated and immature thymocytes with a single anti-CD2 monoclonal antibody inhibited the proliferative response to HTLV-I. These results clearly underline that the expression of the CD2 molecule is exclusively required in mediating the proliferative response to the synergistic effect of phytohemagglutinin and HTLV-I. Immature thymocytes treated with a pair of anti-CD2 monoclonal antibodies were shown to proliferate in response to HTLV-I, even in the absence of exogenous IL-2. We further verified that the proliferation of human thymocytes is consecutive to the expression of IL-2 receptors and the synthesis of IL-2. These observations provide evidence that the mitogenic stimulus delivered by HTLV-I is more efficient than that provided by other conventional mitogenic stimuli, which are unable to trigger the synthesis of endogenous IL-2. Collectively, these results show that the mitogenic activity of HTLV-I is able to trigger the proliferation of cells which are at an early stage of T-cell development. They might therefore represent target cells in which HTLV-I infection could favor the initiation of the multistep lymphoproliferative process leading to adult T-cell leukemia.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arthur L. O., Bess J. W., Jr, Sowder R. C., 2nd, Benveniste R. E., Mann D. L., Chermann J. C., Henderson L. E. Cellular proteins bound to immunodeficiency viruses: implications for pathogenesis and vaccines. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1935–1938. doi: 10.1126/science.1470916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Wano Y., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. HTLV-I tax induces cellular proteins that activate the kappa B element in the IL-2 receptor alpha gene. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1652–1655. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daenke S., Nightingale S., Cruickshank J. K., Bangham C. R. Sequence variants of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis and adult T-cell leukemia do not distinguish neurological from leukemic isolates. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1278–1282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1278-1282.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalloul A. H., Mossalayi M. D., Dellagi K., Bertho J. M., Debré P. Factor requirements for activation and proliferation steps of human CD2+CD3-CD4-CD8- early thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Nov;19(11):1985–1990. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans J. P., Wilkins J. A., Caixia S., Pruski E., Pilarski L. M. Prolonged expression of high molecular mass CD45RA isoform during the differentiation of human progenitor thymocytes to CD3+ cells in vitro. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4060–4068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denning S. M., Dustin M. L., Springer T. A., Singer K. H., Haynes B. F. Purified lymphocyte function-associated antigen-3 (LFA-3) activates human thymocytes via the CD2 pathway. J Immunol. 1988 Nov 1;141(9):2980–2985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodon M. D., Bernard A., Gazzolo L. Peripheral T-lymphocyte activation by human T-cell leukemia virus type I interferes with the CD2 but not with the CD3/TCR pathway. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5413–5419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5413-5419.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duc Dodon M., Gazzolo L. Loss of interleukin-2 requirement for the generation of T colonies defines an early event of human T-lymphotropic virus type I infection. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):12–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumontet C., Dodon M. D., Gazzolo L., Gerlier D. Human T-cell leukemia virus type I-induced proliferation of human thymocytes requires the presence of a comitogen. Cell Immunol. 1988 Apr 1;112(2):391–401. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzolo L., Duc Dodon M. Molecular and cellular events at the onset of the lymphoproliferative process induced by HTLV-I (human T-cell leukemia virus, type I). Bull Cancer. 1991;78(3):291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessain A., Barin F., Vernant J. C., Gout O., Maurs L., Calender A., de Thé G. Antibodies to human T-lymphotropic virus type-I in patients with tropical spastic paraparesis. Lancet. 1985 Aug 24;2(8452):407–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92734-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gessain A., Louie A., Gout O., Gallo R. C., Franchini G. Human T-cell leukemia-lymphoma virus type I (HTLV-I) expression in fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with tropical spastic paraparesis/HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1628–1633. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1628-1633.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Denning S. M., Singer K. H., Kurtzberg J. Ontogeny of T-cell precursors: a model for the initial stages of human T-cell development. Immunol Today. 1989 Mar;10(3):87–91. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimata J. T., Palker T. J., Ratner L. The mitogenic activity of human T-cell leukemia virus type I is T-cell associated and requires the CD2/LFA-3 activation pathway. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3134–3141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3134-3141.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimata J. T., Ratner L. Temporal regulation of viral and cellular gene expression during human T-lymphotropic virus type I-mediated lymphocyte immortalization. J Virol. 1991 Aug;65(8):4398–4407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.8.4398-4407.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. C., Jamieson B. D., Reddy K., Bali N., Concepcion R. J., Ahmed R. Viral infection of the thymus. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):3155–3160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.3155-3160.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Tsujimoto A., Shimotohno K. Sequence variations in LTR and env regions of HTLV-I do not discriminate between the virus from patients with HTLV-I-associated myelopathy and adult T-cell leukemia. Int J Cancer. 1991 Feb 20;47(4):491–495. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komurian F., Pelloquin F., de Thé G. In vivo genomic variability of human T-cell leukemia virus type I depends more upon geography than upon pathologies. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3770–3778. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3770-3778.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korostoff J. M., Nakada M. T., Faas S. J., Blank K. J., Gaulton G. N. Neonatal exposure to thymotropic gross murine leukemia virus induces virus-specific immunologic nonresponsiveness. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1765–1775. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy E. L., Hanchard B., Figueroa J. P., Gibbs W. N., Lofters W. S., Campbell M., Goedert J. J., Blattner W. A. Modelling the risk of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma in persons infected with human T-lymphotropic virus type I. Int J Cancer. 1989 Feb 15;43(2):250–253. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres A., Cerdan C., Lopez M., Mawas C., Olive D. "CD3low" human thymocyte populations can readily be triggered via the CD2 and/or CD28 activation pathways whereas the CD3 pathway remains nonfunctional. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 15;144(4):1202–1207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poiesz B. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gazdar A. F., Bunn P. A., Minna J. D., Gallo R. C. Detection and isolation of type C retrovirus particles from fresh and cultured lymphocytes of a patient with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7415–7419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Lange-Wantzin G., Sarin P. S., Mann D., Gallo R. C. Transformation of human umbilical cord blood T cells by human T-cell leukemia/lymphoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5402–5406. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiki M., Inoue J., Takeda T., Yoshida M. Direct evidence that p40x of human T-cell leukemia virus type I is a trans-acting transcriptional activator. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):561–565. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04247.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Feinberg M. B., Holbrook N., Wong-Staal F., Greene W. C. Activation of interleukin 2 and interleukin 2 receptor (Tac) promoter expression by the trans-activator (tat) gene product of human T-cell leukemia virus, type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5389–5393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Greene W. C. Molecular biology of the type I human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-I) and adult T-cell leukemia. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):761–766. doi: 10.1172/JCI115078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turka L. A., Fletcher M. C., Craighead N., Thompson C. B., June C. H. Defective signal transduction by the CD2 molecule in immature T-cell receptor/CD3- thymocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 15;89(18):8706–8710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.18.8706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turka L. A., Ledbetter J. A., Lee K., June C. H., Thompson C. B. CD28 is an inducible T cell surface antigen that transduces a proliferative signal in CD3+ mature thymocytes. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1646–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turka L. A., Linsley P. S., Paine R., 3rd, Schieven G. L., Thompson G. B., Ledbetter J. A. Signal transduction via CD4, CD8, and CD28 in mature and immature thymocytes. Implications for thymic selection. J Immunol. 1991 Mar 1;146(5):1428–1436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wano Y., Feinberg M., Hosking J. B., Bogerd H., Greene W. C. Stable expression of the tax gene of type I human T-cell leukemia virus in human T cells activates specific cellular genes involved in growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9733–9737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watry D., Hedrick J. A., Siervo S., Rhodes G., Lamberti J. J., Lambris J. D., Tsoukas C. D. Infection of human thymocytes by Epstein-Barr virus. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):971–980. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wucherpfennig K. W., Höllsberg P., Richardson J. H., Benjamin D., Hafler D. A. T-cell activation by autologous human T-cell leukemia virus type I-infected T-cell clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Miyoshi I., Hinuma Y. Isolation and characterization of retrovirus from cell lines of human adult T-cell leukemia and its implication in the disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2031–2035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Osame M., Kawai H., Toita M., Kuwasaki N., Nishida Y., Hiraki Y., Takahashi K., Nomura K., Sonoda S. Increased replication of HTLV-I in HTLV-I-associated myelopathy. Ann Neurol. 1989 Sep;26(3):331–335. doi: 10.1002/ana.410260304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Cann A. J., Lugo J. P., Chen I. S. HIV-1 production from infected peripheral blood T cells after HTLV-I induced mitogenic stimulation. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1026–1029. doi: 10.1126/science.2835813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


