Abstract
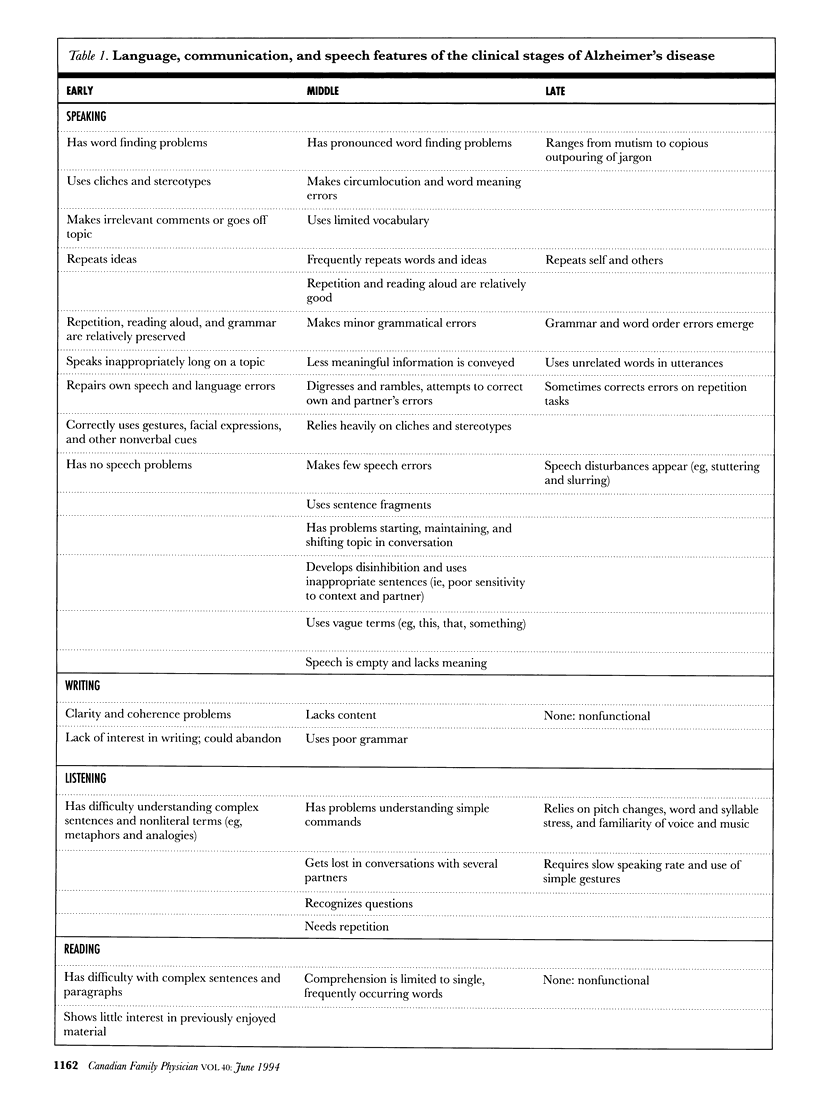
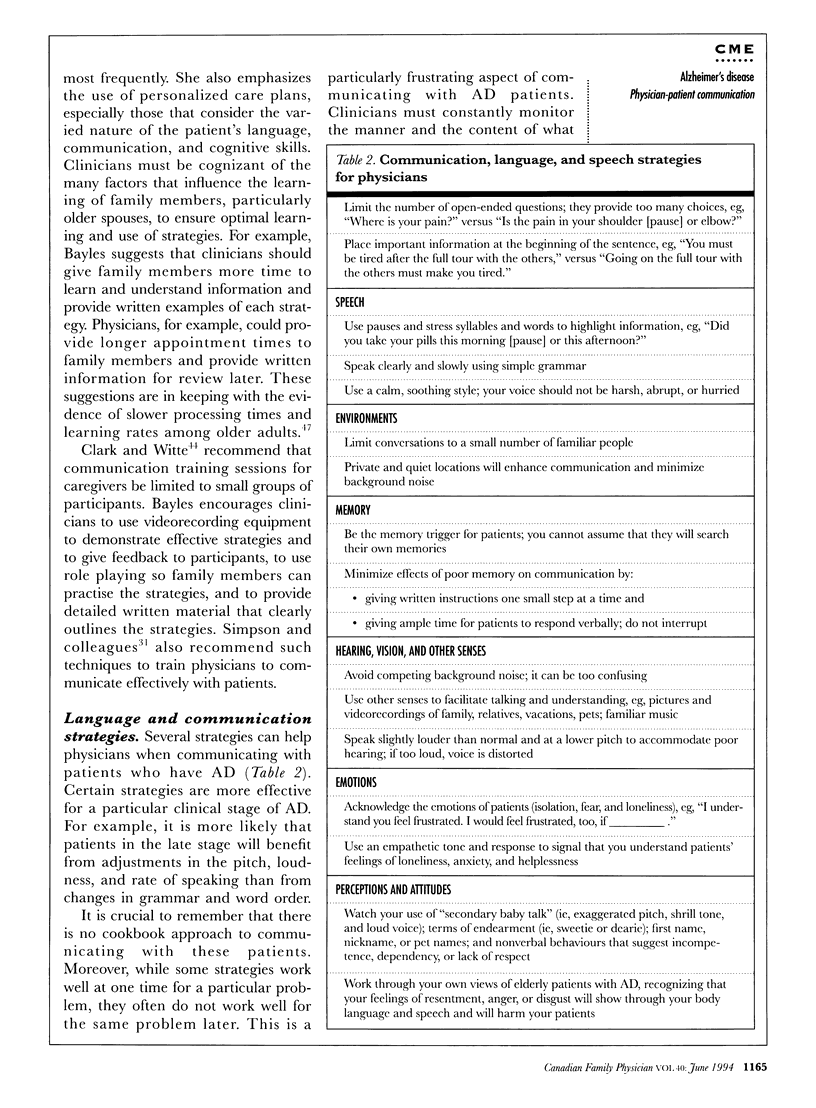
The number of cognitively impaired elderly in Canada has increased greatly during the past two decades; nearly all have Alzheimer's disease (AD). The memory problems and changes in language and communication of these patients place tremendous strain on physicians who are searching for a differential diagnosis and are trying to communicate with them. Reviewing the salient language and communication features of AD patients leads to strategies for improving effective physician-patient communication.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck C., Heacock P., Mercer S., Thatcher R., Sparkman C. The impact of cognitive skills remediation training on persons with Alzheimer's disease or mixed dementia. J Geriatr Psychiatry. 1988;21(1):73–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois M. S. Communication treatment for adults with dementia. J Speech Hear Res. 1991 Aug;34(4):831–844. doi: 10.1044/jshr.3404.831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois M. S. Enhancing conversation skills in patients with Alzheimer's disease using a prosthetic memory aid. J Appl Behav Anal. 1990 Spring;23(1):29–42. doi: 10.1901/jaba.1990.23-29. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgeois M. S. Evaluating memory wallets in conversations with persons with dementia. J Speech Hear Res. 1992 Dec;35(6):1344–1357. doi: 10.1044/jshr.3506.1344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckwalter K. C., Cusack D., Kruckeberg T., Shoemaker A. Family involvement with communication-impaired residents in long-term care settings. Appl Nurs Res. 1991 May;4(2):77–84. doi: 10.1016/s0897-1897(05)80059-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. L., Benson F., Hill M. A., Read S. Aphasia in dementia of the Alzheimer type. Neurology. 1985 Mar;35(3):394–397. doi: 10.1212/wnl.35.3.394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings J. L., Houlihan J. P., Hill M. A. The pattern of reading deterioration in dementia of the Alzheimer type: observations and implications. Brain Lang. 1986 Nov;29(2):315–323. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(86)90051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flicker C., Ferris S. H., Crook T., Bartus R. T. Implications of memory and language dysfunction in the naming deficit of senile dementia. Brain Lang. 1987 Jul;31(2):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(87)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner J., Dawson D. V., Heyman A., Fish A. M. The usefulness of the Western Aphasia Battery for differential diagnosis of Alzheimer dementia and focal stroke syndromes: preliminary evidence. Brain Lang. 1992 Jan;42(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(92)90057-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horner J., Heyman A., Dawson D., Rogers H. The relationship of agraphia to the severity of dementia in Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol. 1988 Jul;45(7):760–763. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520310066019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff F. J., Corkin S., Growdon J. H. Semantic impairment and anomia in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Lang. 1986 Jul;28(2):235–249. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(86)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempler D., Curtiss S., Jackson C. Syntactic preservation in Alzheimer's disease. J Speech Hear Res. 1987 Sep;30(3):343–350. doi: 10.1044/jshr.3003.343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirshner H. S., Webb W. G., Kelly M. P. The naming disorder of dementia. Neuropsychologia. 1984;22(1):23–30. doi: 10.1016/0028-3932(84)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nebes R. D., Boller F., Holland A. Use of semantic context by patients with Alzheimer's disease. Psychol Aging. 1986 Sep;1(3):261–269. doi: 10.1037//0882-7974.1.3.261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas M., Obler L. K., Albert M. L., Helm-Estabrooks N. Empty speech in Alzheimer's disease and fluent aphasia. J Speech Hear Res. 1985 Sep;28(3):405–410. doi: 10.1044/jshr.2803.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen B., Bundgaard Larsen B., Dahl R., Lindqvist N., Mygind N. Powder administration of pure budesonide for the treatment of seasonal allergic rhinitis. Allergy. 1991 Nov;46(8):582–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1991.tb00627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabins P. V., Mace N. L., Lucas M. J. The impact of dementia on the family. JAMA. 1982 Jul 16;248(3):333–335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripich D. N., Terrell B. Y. Patterns of discourse cohesion and coherence in Alzheimer's disease. J Speech Hear Disord. 1988 Feb;53(1):8–15. doi: 10.1044/jshd.5301.08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ripich D. N., Vertes D., Whitehouse P., Fulton S., Ekelman B. Turn-taking and speech act patterns in the discourse of senile dementia of the Alzheimer's type patients. Brain Lang. 1991 Apr;40(3):330–343. doi: 10.1016/0093-934x(91)90133-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman M. D., Mandel E. Communication training of relatives and friends of institutionalized elderly persons. Gerontologist. 1988 Dec;28(6):797–799. doi: 10.1093/geront/28.6.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson M., Buckman R., Stewart M., Maguire P., Lipkin M., Novack D., Till J. Doctor-patient communication: the Toronto consensus statement. BMJ. 1991 Nov 30;303(6814):1385–1387. doi: 10.1136/bmj.303.6814.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


