Abstract
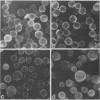
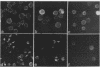
We have investigated the role of the cytoplasmic domains of the influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) and the parainfluenza virus type 3 (PI3) fusion (F) glycoproteins as a determinant of their ability to undergo antibody-induced redistribution on plasma membranes. The viral envelope genes were truncated in their cytoplasmic domains by using oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis and expressed by using recombinant vaccinia viruses. In HeLa cells, the truncated HA (HAt), like the full-length HA, did not cap in response to specific antibody. In CV-1 cells, HAt showed patchy surface immunofluorescence with few caps, whereas full-length HA exhibited capping in many cells in response to bivalent antibody. Quantitation of cap formation indicated a sevenfold decrease in the frequency of capping of HAt in comparison with full-length HA. Similarly, truncated F also exhibited a significant decrease in cap formation in comparison with full-length F. These results indicate that the ability of influenza virus HA and PI3 F to undergo redistribution in response to bivalent antibody has been altered by truncation of the viral glycoproteins and suggest that capping may involve interactions between the cytoplasmic domain of the viral glycoproteins and host cell components.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bourguignon L. Y., Bourguignon G. J. Capping and the cytoskeleton. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;87:195–224. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62443-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti S., Brechling K., Moss B. Vaccinia virus expression vector: coexpression of beta-galactosidase provides visual screening of recombinant virus plaques. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3403–3409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle C., Roth M. G., Sambrook J., Gething M. J. Mutations in the cytoplasmic domain of the influenza virus hemagglutinin affect different stages of intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;100(3):704–714. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle C., Sambrook J., Gething M. J. Analysis of progressive deletions of the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of influenza hemagglutinin. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1193–1204. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edidin M., Kuo S. C., Sheetz M. P. Lateral movements of membrane glycoproteins restricted by dynamic cytoplasmic barriers. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1379–1382. doi: 10.1126/science.1835798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edidin M., Zuniga M. Lateral diffusion of wild-type and mutant Ld antigens in L cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2333–2335. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuerst T. R., Niles E. G., Studier F. W., Moss B. Eukaryotic transient-expression system based on recombinant vaccinia virus that synthesizes bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8122–8126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holifield B. F., Ishihara A., Jacobson K. Comparative behavior of membrane protein-antibody complexes on motile fibroblasts: implications for a mechanism of capping. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2499–2512. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath A. R., Kellie S. Regulation of integrin mobility and cytoskeletal association in normal and RSV-transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. J Cell Sci. 1990 Oct;97(Pt 2):307–315. doi: 10.1242/jcs.97.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph B. S., Oldstone M. B. Antibody-induced redistribution of measles virus antigens on the cell surface. J Immunol. 1974 Oct;113(4):1205–1209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh E., Benveniste M., Prywes R., Felder S., Kam Z., Schlessinger J. Large deletions in the cytoplasmic kinase domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor do not affect its laternal mobility. J Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;103(2):327–331. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loor F., Forni L., Pernis B. The dynamic state of the lymphocyte membrane. Factors affecting the distribution and turnover of surface immunoglobulins. Eur J Immunol. 1972 Jun;2(3):203–212. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lydy S. L., Basak S., Compans R. W. Host cell-dependent lateral mobility of viral glycoproteins. Microb Pathog. 1990 Dec;9(6):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90056-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Fujinami R. S., Lampert P. W. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in virus-infected cells induced by interactions of antiviral antibody with surface viral antigen. Prog Med Virol. 1980;26:45–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in B lymphocytes induced by ligand-surface immunoglobulin interaction. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:37–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scullion B. F., Hou Y., Puddington L., Rose J. K., Jacobson K. Effects of mutations in three domains of the vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein on its lateral diffusion in the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):69–75. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheetz M. P. Membrane skeletal dynamics: role in modulation of red cell deformability, mobility of transmembrane proteins, and shape. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):175–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozawa J. A., Brandts J. F., Jacobson B. S. Binding of plasma membrane glycoproteins to the cytoskeleton during patching and capping is consistent with an entropy-enhancement model. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Apr 28;980(3):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade W. F., Freed J. H., Edidin M. Translational diffusion of class II major histocompatibility complex molecules is constrained by their cytoplasmic domains. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3325–3331. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir J. P., Bajszár G., Moss B. Mapping of the vaccinia virus thymidine kinase gene by marker rescue and by cell-free translation of selected mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1210–1214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. T. Proof without prejudice: use of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for the analysis of histograms from flow systems and other sources. J Histochem Cytochem. 1977 Jul;25(7):935–941. doi: 10.1177/25.7.894009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Crise B., Su B., Hou Y., Rose J. K., Bothwell A., Jacobson K. Lateral diffusion of membrane-spanning and glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked proteins: toward establishing rules governing the lateral mobility of membrane proteins. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):75–84. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Brabander M., Nuydens R., Ishihara A., Holifield B., Jacobson K., Geerts H. Lateral diffusion and retrograde movements of individual cell surface components on single motile cells observed with Nanovid microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):111–124. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]