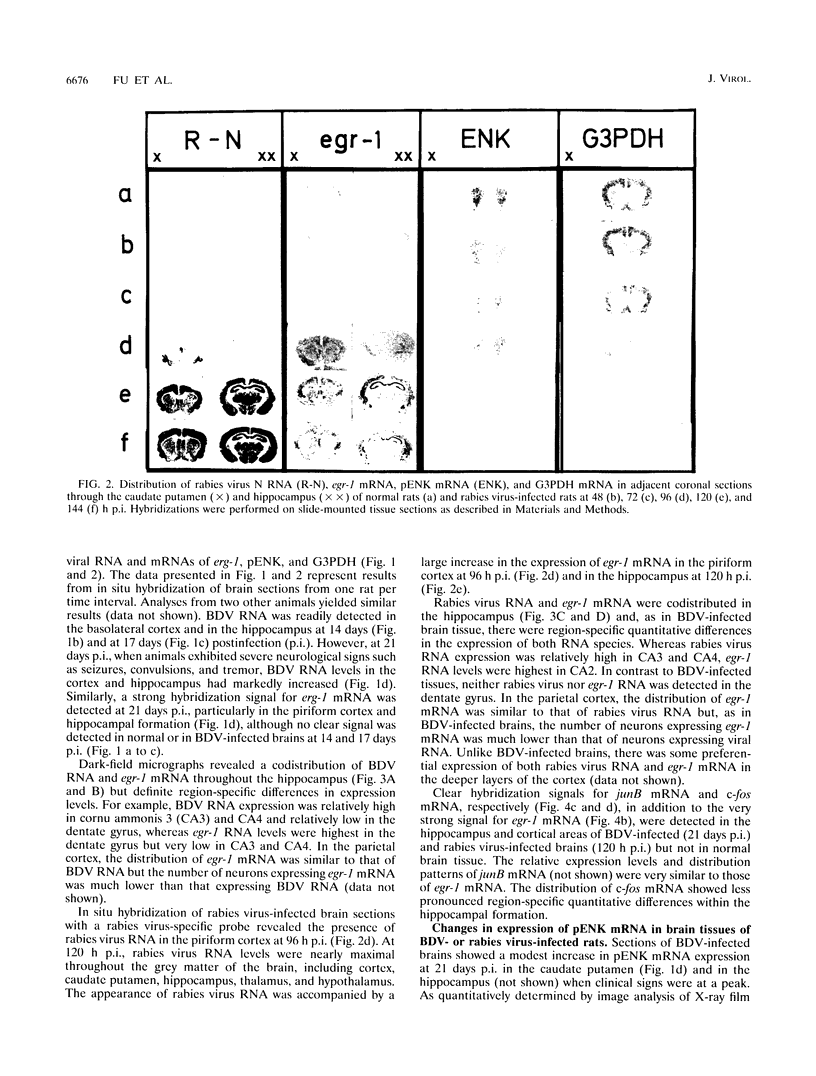
Abstract
In situ hybridization and Northern blot analysis were used to examine expression of the immediate-early-response genes (IEGs) egr-1, junB, and c-fos, and the late response gene encoding enkephalin in the brains of rats infected intranasally with Borna disease virus (BDV) or rabies virus. In both Borna disease and rabies virus infections, a dramatic and specific induction of IEGs was detected in particular regions of the hippocampus and the cortex. Increased IEG mRNA expression overlapped with the characteristic expression patterns of BDV RNA and rabies virus RNA, although relative expression levels of viral RNA and IEG mRNA differed, particularly in the hippocampal formation. Furthermore, the temporal relationship between viral RNA synthesis and activation of IEG mRNA expression in BDV infection differed markedly from that in rabies virus infection, suggesting that IEG expression is upregulated by different mechanisms. Expression of proenkephalin (pENK) mRNA was also significantly increased in BDV infection, whereas in rabies virus infection, pENK mRNA levels and also the levels of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA were reduced at terminal stages of the disease, probably reflecting a generalized suppression of cellular protein synthesis due to massive production of rabies virus mRNA. The correlation between activated IEG mRNA expression and the strong increase in viral RNA raises the possibility that IEG products induce some phenotypic changes in neurons that render them more susceptible to viral replication.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonilla E., Hernández H., Salazar M., Rangel P. Effect of Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus infection on brain choline acetyltransferase and acetylcholinesterase activities. Brain Res. 1982 Dec 16;253(1-2):330–333. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90703-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne J. A., Oldstone M. B. Biology of cloned cytotoxic T lymphocytes specific for lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus: clearance of virus in vivo. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.682-686.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X. M., Koski R. A., Gashler A., McKiernan M., Morris C. F., Gaffney R., Hay R. V., Sukhatme V. P. Identification and characterization of the Egr-1 gene product, a DNA-binding zinc finger protein induced by differentiation and growth signals. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):1931–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone K. M., Duchala C. S., Narayan O. Borna disease. An immunopathologic response to viral infection in the CNS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;540:661–662. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb27204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbone K. M., Rubin S. A., Sierra-Honigmann A. M., Lederman H. M. Characterization of a glial cell line persistently infected with borna disease virus (BDV): influence of neurotrophic factors on BDV protein and RNA expression. J Virol. 1993 Mar;67(3):1453–1460. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.3.1453-1460.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Abate C., Cohen D. R., Macgregor P. F., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Sonnenberg J. L., Connor J. A., Morgan J. I. Inducible proto-oncogene transcription factors: third messengers in the brain? Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:225–234. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Gordon M. B., Rubino K. L., Sambucetti L. C. Isolation and characterization of the c-fos(rat) cDNA and analysis of post-translational modification in vitro. Oncogene. 1987;2(1):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Kao M., Zheng Y. M., Chen Z. Y., Maul G., Fu Z. F., Rupprecht C. E., Koprowski H. Delineation of putative mechanisms involved in antibody-mediated clearance of rabies virus from the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):7252–7256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.7252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ding A. H., Nathan C. F., Stuehr D. J. Release of reactive nitrogen intermediates and reactive oxygen intermediates from mouse peritoneal macrophages. Comparison of activating cytokines and evidence for independent production. J Immunol. 1988 Oct 1;141(7):2407–2412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Dunlop M. B., Parish C. R., Zinkernagel R. M. Inflammatory process in murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis is maximal in H-2K or H-2D compatible interactions. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Z. F., Dietzschold B., Schumacher C. L., Wunner W. H., Ertl H. C., Koprowski H. Rabies virus nucleoprotein expressed in and purified from insect cells is efficacious as a vaccine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):2001–2005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda J., Kurata T. Loss of membrane excitability after herpes simplex virus infection in tissue-cultured nerve cells from adult mammals. Brain Res. 1981 Apr 27;211(1):235–241. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90090-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourmelon P., Briet D., Clarençon D., Court L., Tsiang H. Sleep alterations in experimental street rabies virus infection occur in the absence of major EEG abnormalities. Brain Res. 1991 Jul 19;554(1-2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90184-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gourmelon P., Briet D., Court L., Tsiang H. Electrophysiological and sleep alterations in experimental mouse rabies. Brain Res. 1986 Nov 19;398(1):128–140. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)91258-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Pert C. B. Light microscopic localization of brain opiate receptors: a general autoradiographic method which preserves tissue quality. J Neurosci. 1982 Aug;2(8):1129–1149. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-08-01129.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herschman H. R. Primary response genes induced by growth factors and tumor promoters. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:281–319. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiraly M., Dolivo M. Alteration of the electrophysiological activity in sympathetic ganglia infected with a neurotropic virus. I. Presynaptic origin of the spontaneous bioelectric activity. Brain Res. 1982 May 20;240(1):43–54. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)90642-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koprowski H., Zheng Y. M., Heber-Katz E., Fraser N., Rorke L., Fu Z. F., Hanlon C., Dietzschold B. In vivo expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in experimentally induced neurologic diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):3024–3027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.3024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima L., Walder R., Obregón F., Drujan B. Serotonin turnover rate in raphe and cortex of mice infected with Venezuelan equine encephalomyelitis virus. J Neurosci Res. 1987;17(4):428–434. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490170415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin W. I., Battenberg E. L., Bloom F. E., Oldstone M. B. Viral infection of neurons can depress neurotransmitter mRNA levels without histologic injury. Brain Res. 1988 Jun 7;451(1-2):333–339. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90779-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipkin W. I., Carbone K. M., Wilson M. C., Duchala C. S., Narayan O., Oldstone M. B. Neurotransmitter abnormalities in Borna disease. Brain Res. 1988 Dec 20;475(2):366–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90627-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madore H. P., England J. M. Rabies virus protein synthesis in infected BHK-21 cells. J Virol. 1977 Apr;22(1):102–112. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.1.102-112.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., James M. H., Russell R. J., Kelly J. S., Pasternak C. A. Changes in excitability induced by herpes simplex viruses in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Neurosci. 1986 Feb;6(2):391–402. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-02-00391.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure M. A., Thibault K. J., Hatalski C. G., Lipkin W. I. Sequence similarity between Borna disease virus p40 and a duplicated domain within the paramyxovirus and rhabdovirus polymerase proteins. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6572–6577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6572-6577.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan P. F., Linnoila M. Regional induction of c-fos mRNA by NMDA: a quantitative in-situ hybridization study. Neuroreport. 1991 May;2(5):251–254. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199105000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narayan O., Herzog S., Frese K., Scheefers H., Rott R. Pathogenesis of Borna disease in rats: immune-mediated viral ophthalmoencephalopathy causing blindness and behavioral abnormalities. J Infect Dis. 1983 Aug;148(2):305–315. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.2.305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pechan P. A., Chowdhury K., Seifert W. Free radicals induce gene expression of NGF and bFGF in rat astrocyte culture. Neuroreport. 1992 Jun;3(6):469–472. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199206000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder K., Lau L. F., Nathans D. A gene activated by growth factors is related to the oncogene v-jun. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1487–1491. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer M. K., Day R., Ortega M. R., Akil H., Watson S. J. Proenkephalin messenger RNA is expressed both in the rat anterior and posterior pituitary. Neuroendocrinology. 1990 Apr;51(4):444–448. doi: 10.1159/000125372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shankar V., Kao M., Hamir A. N., Sheng H., Koprowski H., Dietzschold B. Kinetics of virus spread and changes in levels of several cytokine mRNAs in the brain after intranasal infection of rats with Borna disease virus. J Virol. 1992 Feb;66(2):992–998. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.2.992-998.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson L. L. The study of clostridial and related toxins. The search for unique mechanisms and common denominators. J Physiol (Paris) 1990;84(2):143–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smeyne R. J., Vendrell M., Hayward M., Baker S. J., Miao G. G., Schilling K., Robertson L. M., Curran T., Morgan J. I. Continuous c-fos expression precedes programmed cell death in vivo. Nature. 1993 May 13;363(6425):166–169. doi: 10.1038/363166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonnenberg J. L., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Morgan J. I., Curran T. Regulation of proenkephalin by Fos and Jun. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1622–1625. doi: 10.1126/science.2512642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitz L., Sobbe M., Bilzer T. Preventive effects of early anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 treatment on Borna disease in rats. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3316–3323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3316-3323.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sukhatme V. P. Early transcriptional events in cell growth: the Egr family. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1990 Dec;1(6):859–866. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V16859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tso J. Y., Sun X. H., Kao T. H., Reece K. S., Wu R. Isolation and characterization of rat and human glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase cDNAs: genomic complexity and molecular evolution of the gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2485–2502. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitfield H. J., Jr, Brady L. S., Smith M. A., Mamalaki E., Fox R. J., Herkenham M. Optimization of cRNA probe in situ hybridization methodology for localization of glucocorticoid receptor mRNA in rat brain: a detailed protocol. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1990 Mar;10(1):145–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00733641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler R. J., Stauffer E. K. Mumps virus-induced alterations in cellular excitability during persistent infections. J Gen Virol. 1987 Sep;68(Pt 9):2501–2507. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-9-2501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








