Abstract
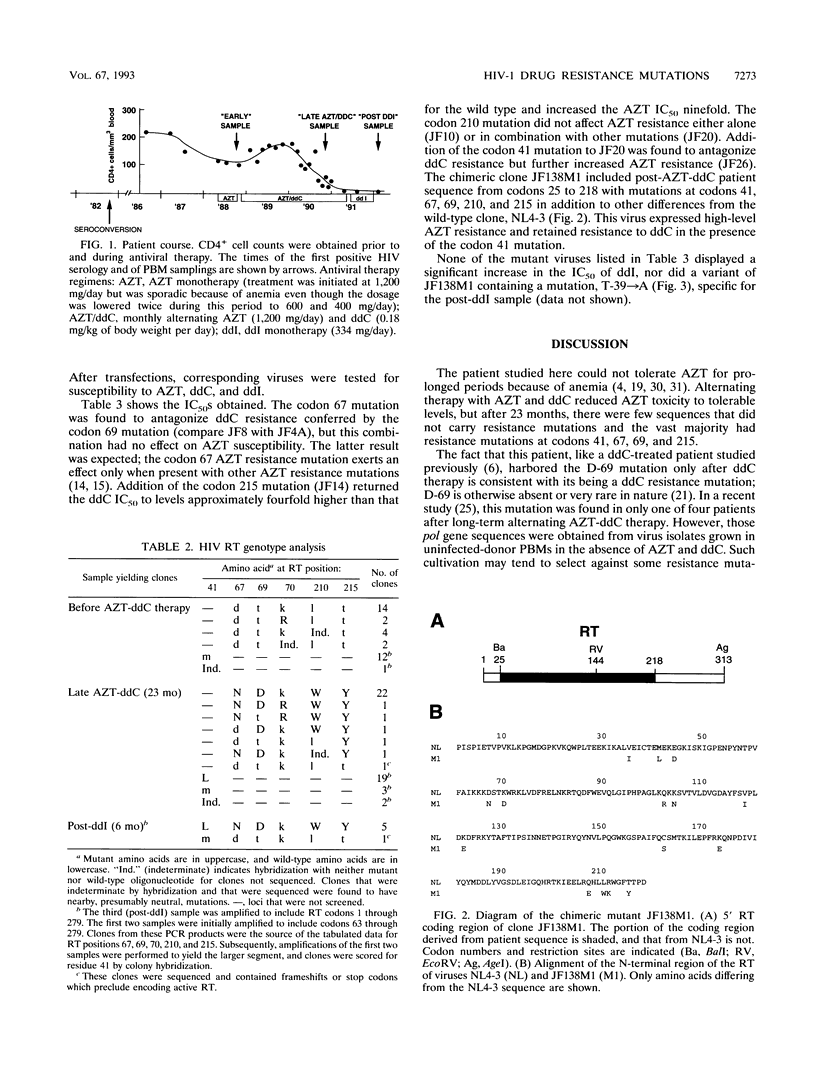
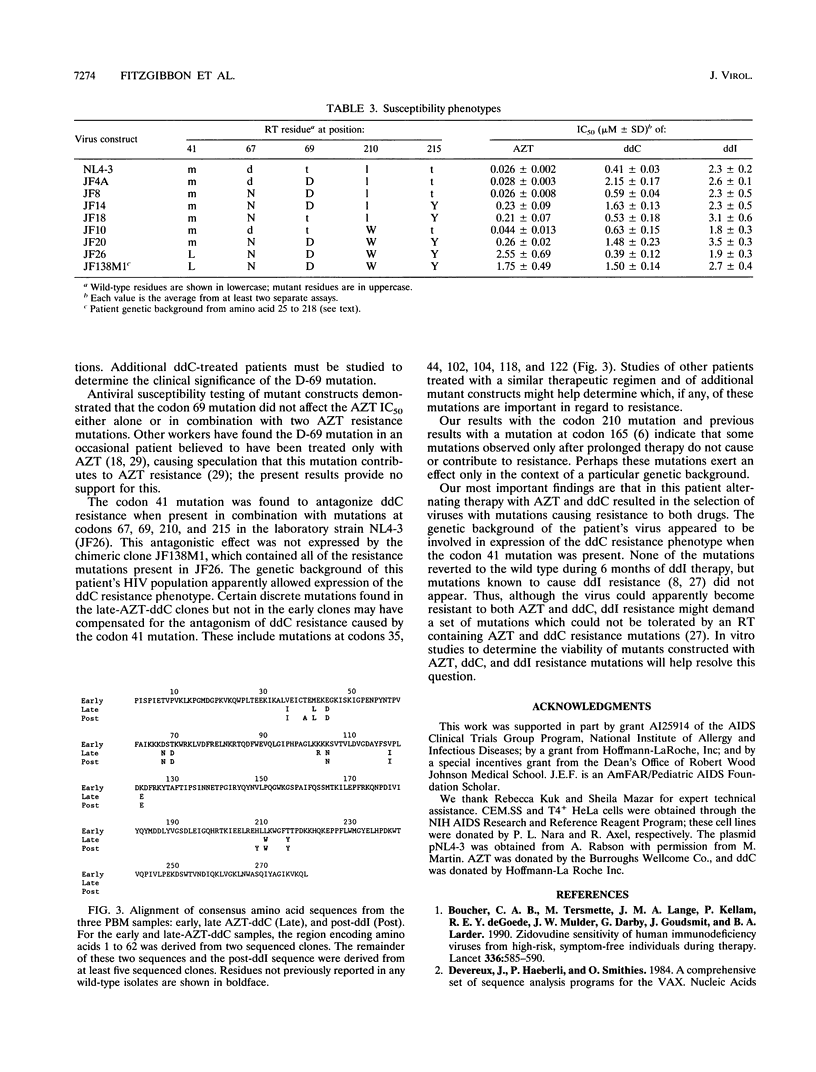
Multiple mutations were found in the human immunodeficiency virus pol gene following treatment of an AIDS patient with antiretroviral drugs. After approximately 2.5 years of monthly alternating therapy with 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine (AZT) and 2',3'-dideoxycytidine (ddC), most of the pol sequences amplified from the patient's peripheral blood mononuclear cell DNA contained known AZT resistance mutations at codons 41, 67, and 215 and a putative ddC resistance mutation at codon 69 as well as other novel mutations. These mutations persisted for 6 months after the patient was switched to 2',3'-dideoxyinosine monotherapy. Mutations known to be associated with 2',3'-dideoxyinosine resistance did not occur during this time. Antiviral susceptibility testing of point mutants, introduced into the genetic background of laboratory strain NL4-3, showed that the codon 41 mutation antagonized ddC resistance when present with the codon 69 mutation. However, this antagonism was not found with a chimeric mutant containing the patient's pol gene sequence from codons 25 to 218, implying that other mutations compensated for the antagonism. Thus, alternating therapy with AZT and ddC resulted in the selection of viruses resistant to both drugs.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boucher C. A., Tersmette M., Lange J. M., Kellam P., de Goede R. E., Mulder J. W., Darby G., Goudsmit J., Larder B. A. Zidovudine sensitivity of human immunodeficiency viruses from high-risk, symptom-free individuals during therapy. Lancet. 1990 Sep 8;336(8715):585–590. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)93391-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Richman D. D., Causey D. M., Grieco M. H., Bryson Y., Mildvan D., Laskin O. L., Groopman J. E., Volberding P. A., Schooley R. T. Prolonged zidovudine therapy in patients with AIDS and advanced AIDS-related complex. AZT Collaborative Working Group. JAMA. 1989 Nov 3;262(17):2405–2410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Richman D. D., Grieco M. H., Gottlieb M. S., Volberding P. A., Laskin O. L., Leedom J. M., Groopman J. E., Mildvan D., Schooley R. T. The efficacy of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):185–191. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgibbon J. E., Howell R. M., Haberzettl C. A., Sperber S. J., Gocke D. J., Dubin D. T. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 pol gene mutations which cause decreased susceptibility to 2',3'-dideoxycytidine. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Jan;36(1):153–157. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.1.153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgibbon J. E., Howell R. M., Schwartzer T. A., Gocke D. J., Dubin D. T. In vivo prevalence of azidothymidine (AZT) resistance mutations in an AIDS patient before and after AZT therapy. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1991 Mar;7(3):265–269. doi: 10.1089/aid.1991.7.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu Z., Gao Q., Li X., Parniak M. A., Wainberg M. A. Novel mutation in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase gene that encodes cross-resistance to 2',3'-dideoxyinosine and 2',3'-dideoxycytidine. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7128–7135. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7128-7135.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. N., Hunt H. D., Horton R. M., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):51–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90358-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellam P., Boucher C. A., Larder B. A. Fifth mutation in human immunodeficiency virus type 1 reverse transcriptase contributes to the development of high-level resistance to zidovudine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1934–1938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land S., Terloar G., McPhee D., Birch C., Doherty R., Cooper D., Gust I. Decreased in vitro susceptibility to zidovudine of HIV isolates obtained from patients with AIDS. J Infect Dis. 1990 Feb;161(2):326–329. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.2.326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Chesebro B., Richman D. D. Susceptibilities of zidovudine-susceptible and -resistant human immunodeficiency virus isolates to antiviral agents determined by using a quantitative plaque reduction assay. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1990 Mar;34(3):436–441. doi: 10.1128/aac.34.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Darby G., Richman D. D. HIV with reduced sensitivity to zidovudine (AZT) isolated during prolonged therapy. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1731–1734. doi: 10.1126/science.2467383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kellam P., Kemp S. D. Zidovudine resistance predicted by direct detection of mutations in DNA from HIV-infected lymphocytes. AIDS. 1991 Feb;5(2):137–144. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199102000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larder B. A., Kemp S. D. Multiple mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase confer high-level resistance to zidovudine (AZT). Science. 1989 Dec 1;246(4934):1155–1158. doi: 10.1126/science.2479983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayers D. L., McCutchan F. E., Sanders-Buell E. E., Merritt L. I., Dilworth S., Fowler A. K., Marks C. A., Ruiz N. M., Richman D. D., Roberts C. R. Characterization of HIV isolates arising after prolonged zidovudine therapy. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1992;5(8):749–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merigan T. C., Skowron G., Bozzette S. A., Richman D., Uttamchandani R., Fischl M., Schooley R., Hirsch M., Soo W., Pettinelli C. Circulating p24 antigen levels and responses to dideoxycytidine in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infections. A phase I and II study. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Feb 1;110(3):189–194. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-3-189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D., Hidalgo J., Sugland B. W., Chaisson R. E. Zidovudine and the natural history of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991 May 16;324(20):1412–1416. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105163242006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Grimes J. M., Lagakos S. W. Effect of stage of disease and drug dose on zidovudine susceptibilities of isolates of human immunodeficiency virus. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1990;3(8):743–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Guatelli J. C., Grimes J., Tsiatis A., Gingeras T. Detection of mutations associated with zidovudine resistance in human immunodeficiency virus by use of the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1991 Dec;164(6):1075–1081. doi: 10.1093/infdis/164.6.1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooke R., Tremblay M., Soudeyns H., DeStephano L., Yao X. J., Fanning M., Montaner J. S., O'Shaughnessy M., Gelmon K., Tsoukas C. Isolation of drug-resistant variants of HIV-1 from patients on long-term zidovudine therapy. Canadian Zidovudine Multi-Centre Study Group. AIDS. 1989 Jul;3(7):411–415. doi: 10.1097/00002030-198907000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasaka T., Yarchoan R., O'Brien M. C., Husson R. N., Anderson B. D., Kojima E., Shimada T., Broder S., Mitsuya H. Changes in drug sensitivity of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 during therapy with azidothymidine, dideoxycytidine, and dideoxyinosine: an in vitro comparative study. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):562–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skowron G., Bozzette S. A., Lim L., Pettinelli C. B., Schaumburg H. H., Arezzo J., Fischl M. A., Powderly W. G., Gocke D. J., Richman D. D. Alternating and intermittent regimens of zidovudine and dideoxycytidine in patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. Ann Intern Med. 1993 Mar 1;118(5):321–330. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-118-5-199303010-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Clair M. H., Martin J. L., Tudor-Williams G., Bach M. C., Vavro C. L., King D. M., Kellam P., Kemp S. D., Larder B. A. Resistance to ddI and sensitivity to AZT induced by a mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Science. 1991 Sep 27;253(5027):1557–1559. doi: 10.1126/science.1716788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahlberg J., Albert J., Lundeberg J., Cox S., Wahren B., Uhlén M. Dynamic changes in HIV-1 quasispecies from azidothymidine (AZT)-treated patients. FASEB J. 1992 Jul;6(10):2843–2847. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.10.1634047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Klecker R. W., Weinhold K. J., Markham P. D., Lyerly H. K., Durack D. T., Gelmann E., Lehrman S. N., Blum R. M., Barry D. W. Administration of 3'-azido-3'-deoxythymidine, an inhibitor of HTLV-III/LAV replication, to patients with AIDS or AIDS-related complex. Lancet. 1986 Mar 15;1(8481):575–580. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92808-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarchoan R., Perno C. F., Thomas R. V., Klecker R. W., Allain J. P., Wills R. J., McAtee N., Fischl M. A., Dubinsky R., McNeely M. C. Phase I studies of 2',3'-dideoxycytidine in severe human immunodeficiency virus infection as a single agent and alternating with zidovudine (AZT). Lancet. 1988 Jan 16;1(8577):76–81. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)90283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


