Abstract
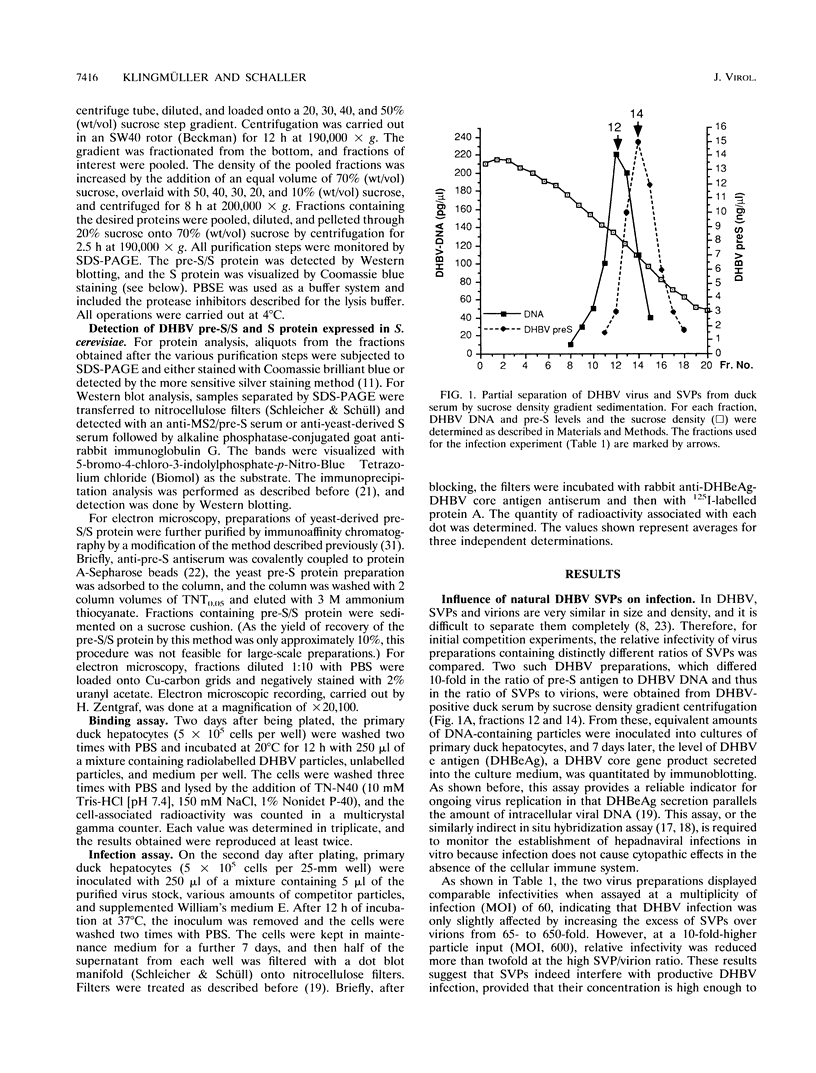
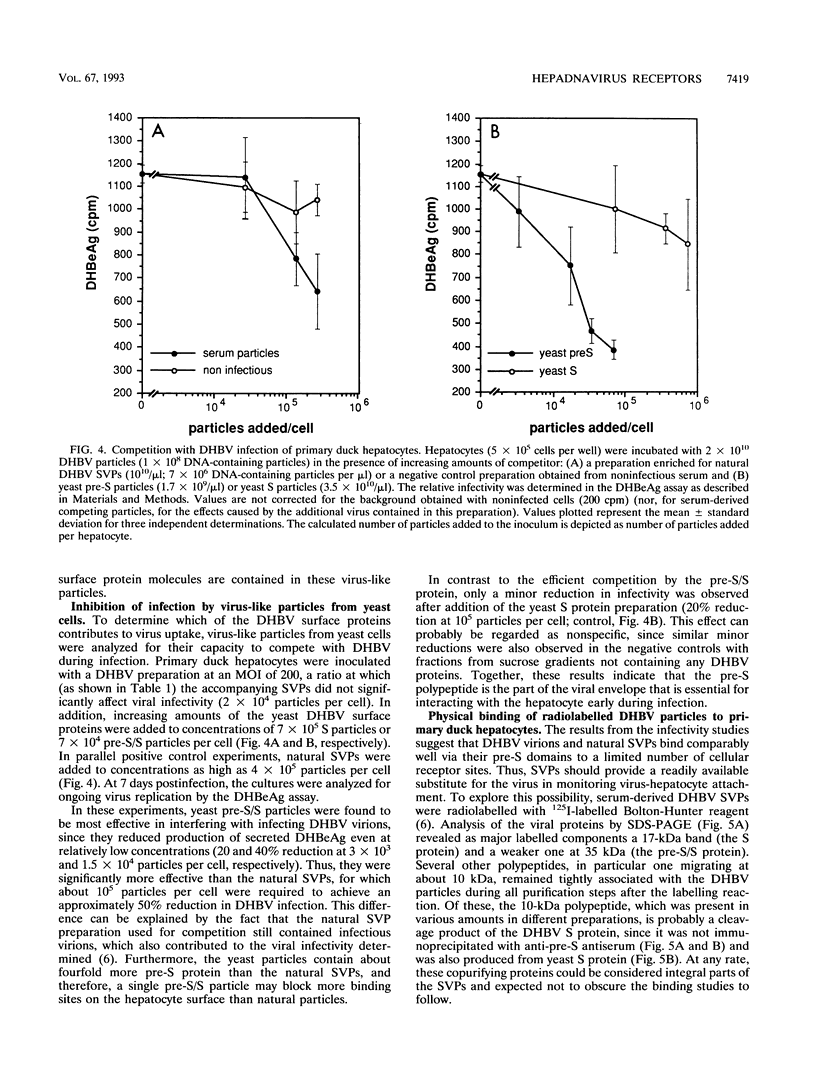
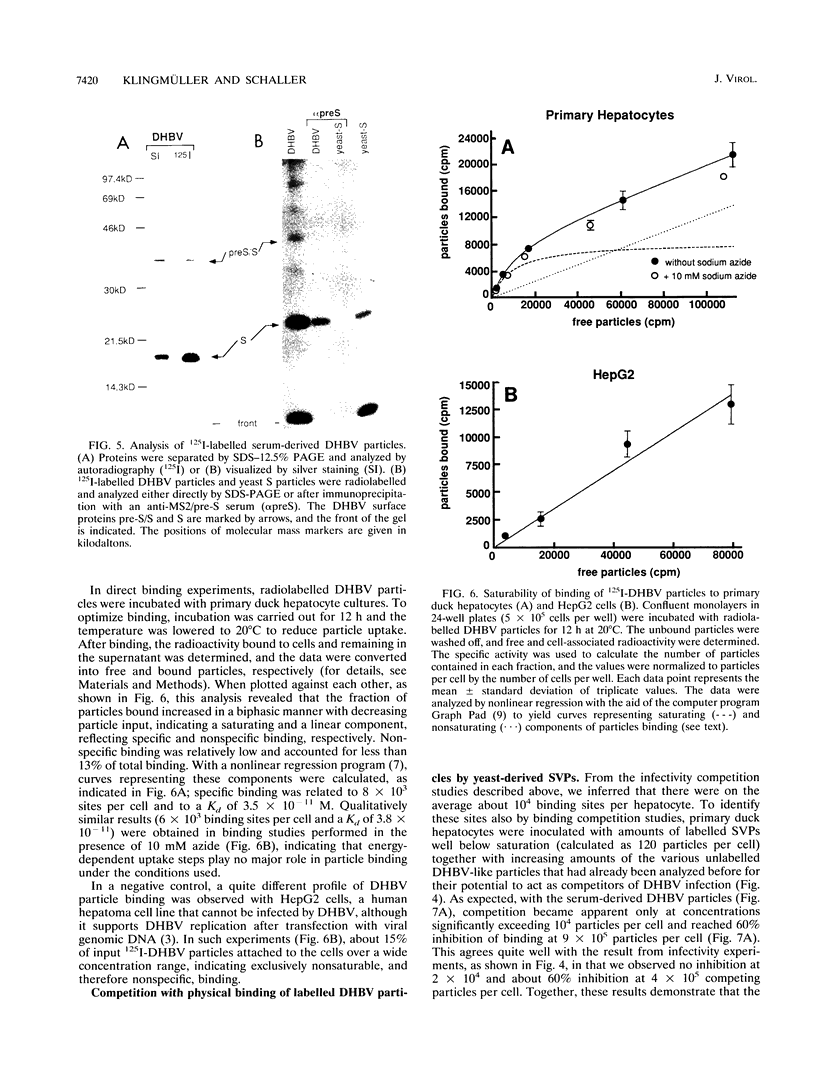
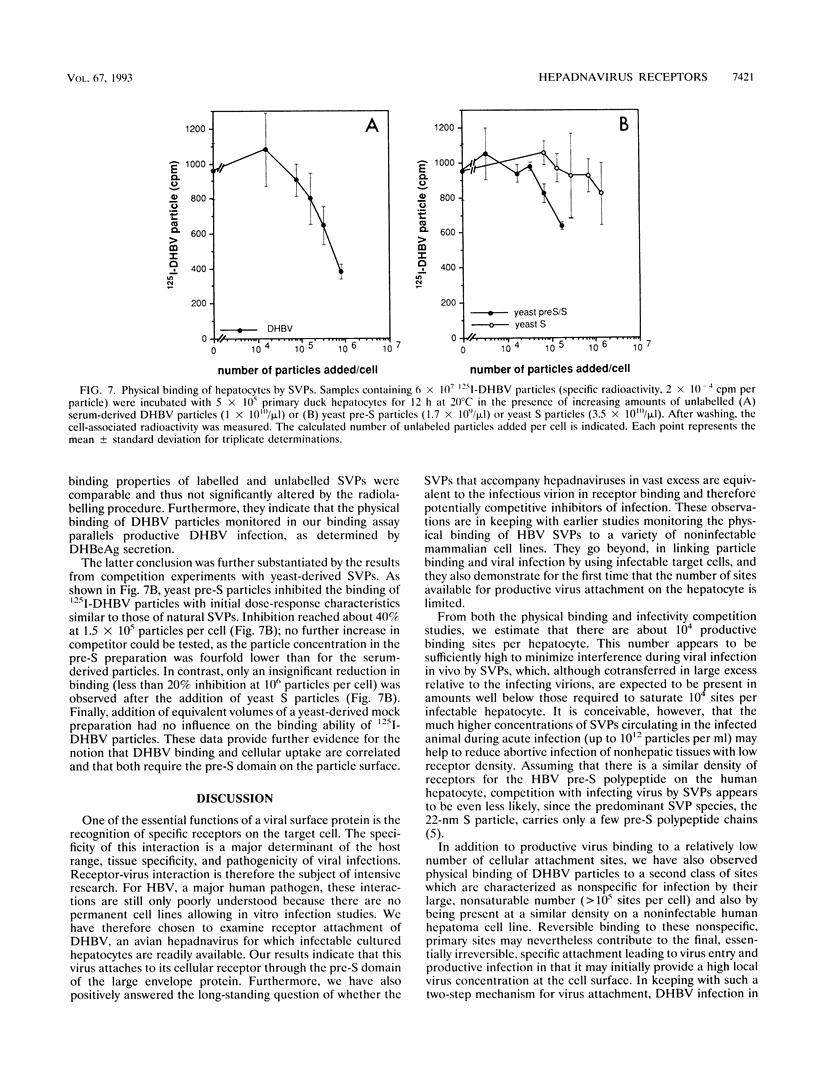
To better define the molecules involved in the initial interaction between hepadnaviruses and hepatocytes, we performed binding and infectivity studies with the duck hepatitis B virus (DHBV) and cultured primary duck hepatocytes. In competition experiments with naturally occurring subviral particles containing DHBV surface proteins, these DNA-free particles were found to interfere with viral infectivity if used at sufficiently high concentrations. In direct binding saturation experiments with radiolabelled subviral particles, a biphasic titration curve containing a saturable component was obtained. Quantitative evaluation of both the binding and the infectivity data indicates that the duck hepatocyte presents about 10(4) high-affinity binding sites for viral and subviral particles. Binding to these productive sites may be preceded by reversible virus attachment to a large number of less specific, nonsaturable primary binding sites. To identify which of the viral envelope proteins is responsible for hepatocyte-specific attachment, subviral particles containing only one of the two DHBV surface proteins were produced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In infectivity competition experiments, only particles containing the large pre-S/S protein were found to markedly reduce the efficiency of DHBV infection, while particles containing the small S protein had only a minor effect. Similarly, physical binding of radiolabelled serum-derived subviral particles to primary duck hepatocytes was inhibited well only by the yeast-derived pre-S/S particles. Together, these results strongly support the notion that hepadnaviral infection is initiated by specific attachment of the pre-S domain of the large DHBV envelope protein to a limited number of hepatocellular binding sites.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bröker M., Ragg H., Karges H. E. Expression of human antithrombin III in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 29;908(3):203–213. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90100-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung R. C., Robinson W. S., Marion P. L., Greenberg H. B. Epitope mapping of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies against duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2445–2451. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2445-2451.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galle P. R., Schlicht H. J., Kuhn C., Schaller H. Replication of duck hepatitis B virus in primary duck hepatocytes and its dependence on the state of differentiation of the host cell. Hepatology. 1989 Oct;10(4):459–465. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840100410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heermann K. H., Goldmann U., Schwartz W., Seyffarth T., Baumgarten H., Gerlich W. H. Large surface proteins of hepatitis B virus containing the pre-s sequence. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):396–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.396-402.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Seal G., Summers J. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.829-836.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAleer W. J., Buynak E. B., Maigetter R. Z., Wampler D. E., Miller W. J., Hilleman M. R. Human hepatitis B vaccine from recombinant yeast. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):178–180. doi: 10.1038/307178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassal M., Schaller H. Hepatitis B virus replication. Trends Microbiol. 1993 Sep;1(6):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(93)90136-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Parker K. Identification and chemical synthesis of a host cell receptor binding site on hepatitis B virus. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit M. A., Dubanchet S., Capel F., Voet P., Dauguet C., Hauser P. HepG2 cell binding activities of different hepatitis B virus isolates: inhibitory effect of anti-HBs and anti-preS1(21-47). Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90062-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontisso P., Petit M. A., Bankowski M. J., Peeples M. E. Human liver plasma membranes contain receptors for the hepatitis B virus pre-S1 region and, via polymerized human serum albumin, for the pre-S2 region. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):1981–1988. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.1981-1988.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pontisso P., Ruvoletto M. G., Gerlich W. H., Heermann K. H., Bardini R., Alberti A. Identification of an attachment site for human liver plasma membranes on hepatitis B virus particles. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):522–530. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90564-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Sninsky J. J., Summers J. W., Schaeffer E. Characterization of a pre-S polypeptide on the surfaces of infectious avian hepadnavirus particles. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1384–1390. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1384-1390.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. Infection and uptake of duck hepatitis B virus by duck hepatocytes maintained in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):564–572. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90199-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigg R. J., Schaller H. Duck hepatitis B virus infection of hepatocytes is not dependent on low pH. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2829–2836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2829-2836.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlicht H. J., Kuhn C., Guhr B., Mattaliano R. J., Schaller H. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the duck hepatitis B virus envelope proteins. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2280–2285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2280-2285.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Newman R. A., Sutherland D. R., Asser U., Greaves M. F. A one-step purification of membrane proteins using a high efficiency immunomatrix. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):10766–10769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G., Shieh M. T., Herold B. C., WuDunn D., Koshy T. I. Heparan sulfate glycosaminoglycans as primary cell surface receptors for herpes simplex virus. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1992;313:341–353. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-2444-5_33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Kaleta E. F., Will H. Isolation and characterization of a hepatitis B virus endemic in herons. J Virol. 1988 Oct;62(10):3832–3839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.10.3832-3839.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Kuhn C., Manso C., Will H. Cloned duck hepatitis B virus DNA is infectious in Pekin ducks. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):932–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.932-937.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprengel R., Kuhn C., Will H., Schaller H. Comparative sequence analysis of duck and human hepatitis B virus genomes. J Med Virol. 1985 Apr;15(4):323–333. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890150402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smith P. M., Horwich A. L. Hepadnavirus envelope proteins regulate covalently closed circular DNA amplification. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2819–2824. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2819-2824.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttleman J. S., Pugh J. C., Summers J. W. In vitro experimental infection of primary duck hepatocyte cultures with duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.17-25.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Medina A., Rutter W. J., Ammerer G., Hall B. D. Synthesis and assembly of hepatitis B virus surface antigen particles in yeast. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):347–350. doi: 10.1038/298347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wampler D. E., Lehman E. D., Boger J., McAleer W. J., Scolnick E. M. Multiple chemical forms of hepatitis B surface antigen produced in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6830–6834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickham T. J., Mathias P., Cheresh D. A., Nemerow G. R. Integrins alpha v beta 3 and alpha v beta 5 promote adenovirus internalization but not virus attachment. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90231-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuasa S., Cheung R. C., Pham Q., Robinson W. S., Marion P. L. Peptide mapping of neutralizing and nonneutralizing epitopes of duck hepatitis B virus pre-S polypeptide. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):14–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90465-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]