Abstract
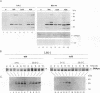
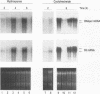
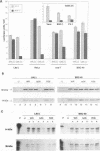
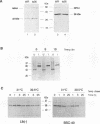
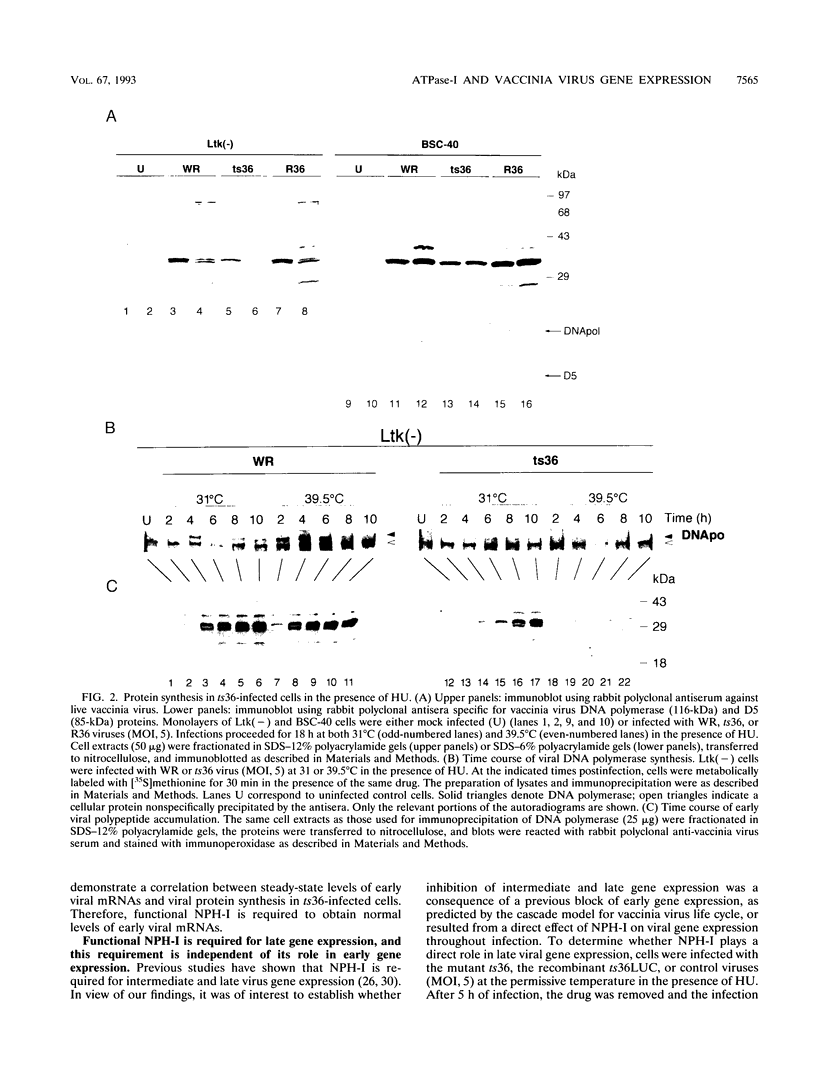
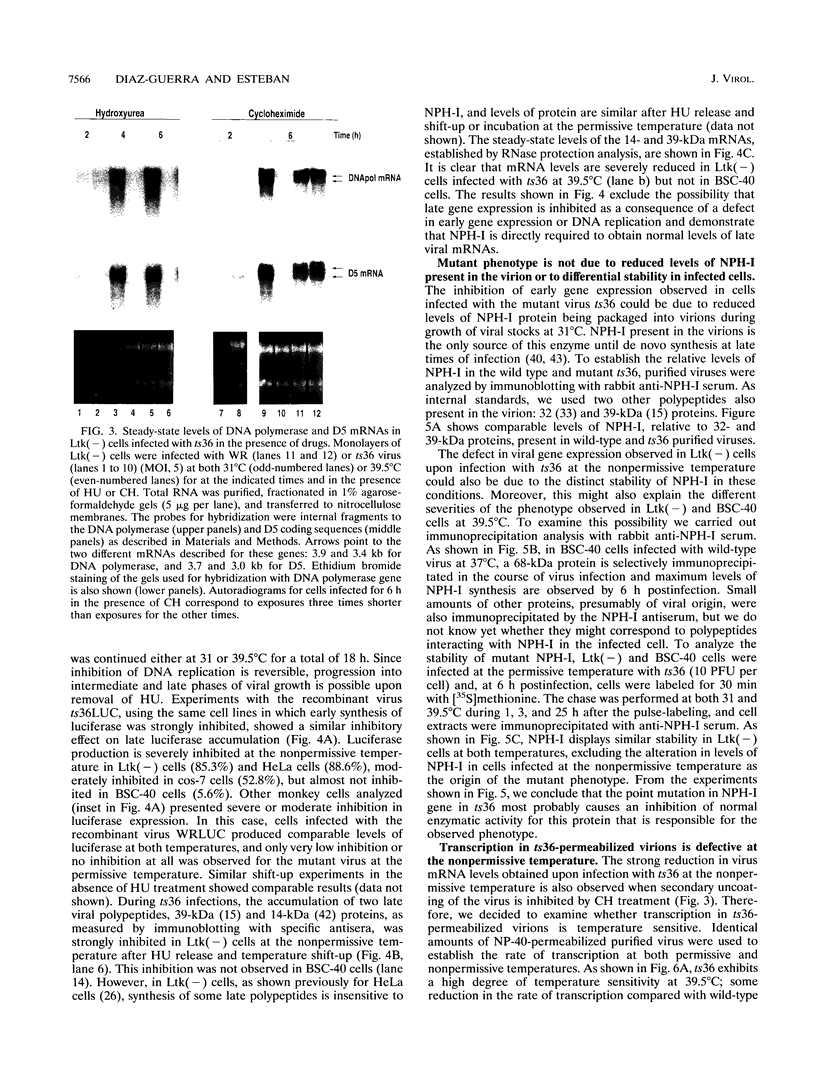
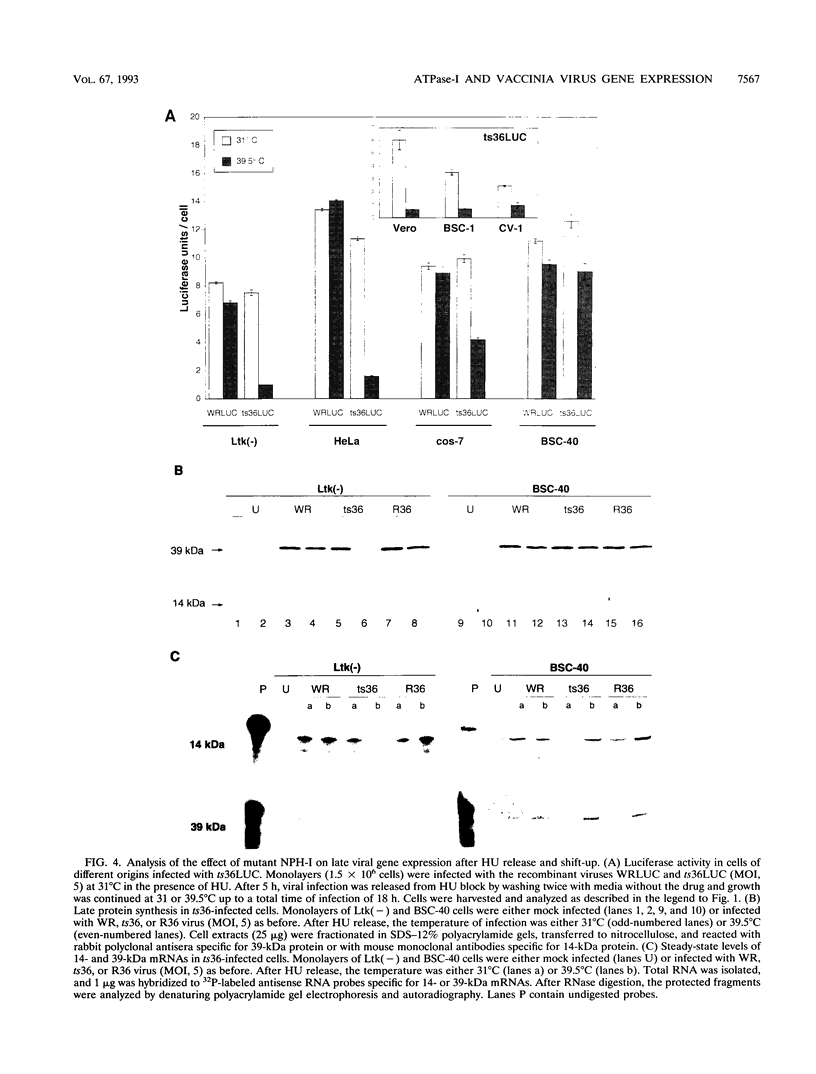
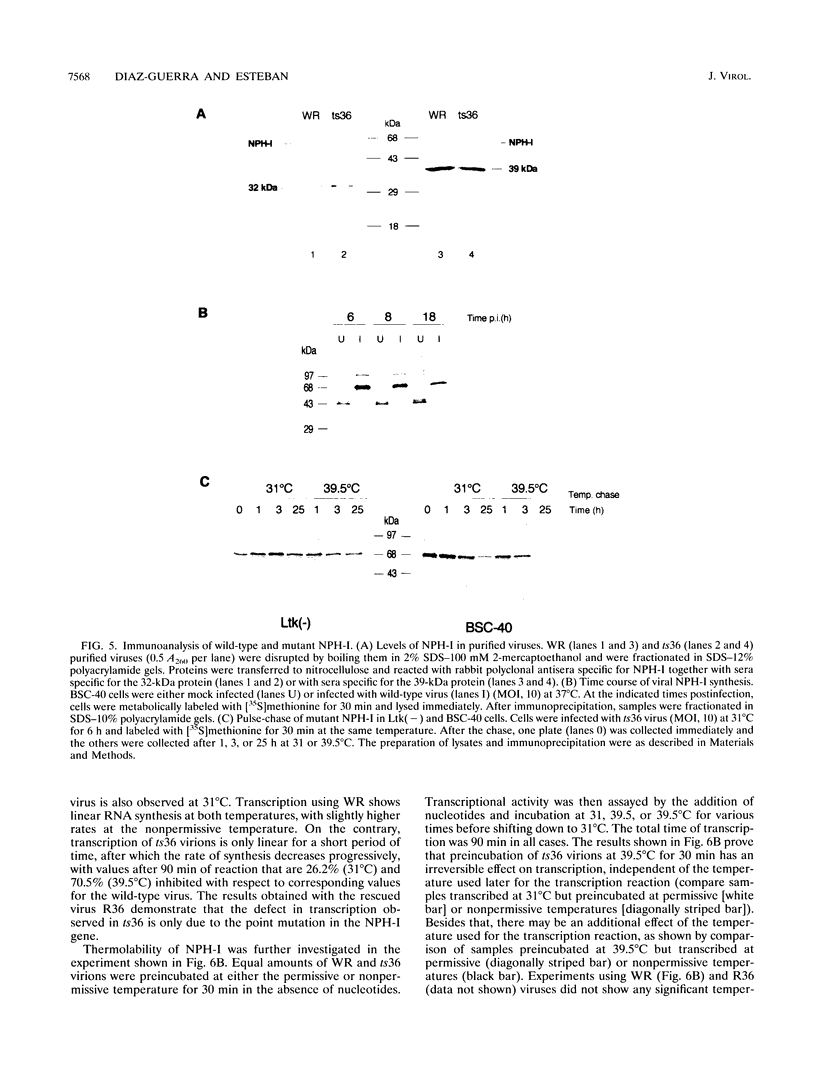
We have carried out a detailed analysis of viral mRNAs and proteins produced in cultured cells infected with a temperature-sensitive vaccinia virus mutant (ts36) containing a modified nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase I (NPH-I), a nucleic acid-dependent ATPase. Using a recombinant virus (ts36LUC) which expresses the luciferase marker, we showed in seven different cell lines that early expression of the receptor gene is strongly inhibited (73.8 to 98.7%) at the nonpermissive temperature. The steady-state levels of different early viral polypeptides were also severely reduced. Analysis of steady-state mRNA levels for two early genes (DNA polymerase and D5) showed that inhibition of early polypeptide synthesis correlated with a reduction in the levels of mRNA accumulated at the nonpermissive temperature. Analysis of steady-state levels of late viral polypeptides and of mRNAs indicated that NPH-I regulation of intermediate and late gene expression is direct and not simply a consequence of its role in inhibiting early gene expression. Characterization of a rescued virus (R36) demonstrated that the temperature-sensitive phenotype of ts36 is due solely to the point mutation in the NPH-I gene. The mutant phenotype is not due to reduced levels of NPH-I present in ts36 virions or to the differential stability of this enzyme in cells infected at the nonpermissive temperature but to inhibition of normal enzymatic activity for this protein. Measurement of viral transcriptional activity in permeabilized purified virions demonstrated that NPH-I is required for normal rates of transcription in vaccinia virus. Our findings show ts36 to be a strongly defective early mutant of vaccinia virus and prove that NPH-I plays a key role in the control of early and late virus gene expression, possibly by way of an auxiliary function which regulates mRNA transcription during the virus growth cycle.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn B. Y., Moss B. RNA polymerase-associated transcription specificity factor encoded by vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3536–3540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aso T., Vasavada H. A., Kawaguchi T., Germino F. J., Ganguly S., Kitajima S., Weissman S. M., Yasukochi Y. Characterization of cDNA for the large subunit of the transcription initiation factor TFIIF. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):461–464. doi: 10.1038/355461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss C. D., Condit R. C. Temperature-sensitive mutants in the vaccinia virus A18R gene increase double-stranded RNA synthesis as a result of aberrant viral transcription. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):254–262. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Flores O., Krauskopf A., Reinberg D., Aloni Y. Role of the mammalian transcription factors IIF, IIS, and IIX during elongation by RNA polymerase II. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1195–1206. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasier A. R., Tate J. E., Habener J. F. Optimized use of the firefly luciferase assay as a reporter gene in mammalian cell lines. Biotechniques. 1989 Nov-Dec;7(10):1116–1122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S. A role for ATP hydrolysis in vaccinia virus early gene transcription. Dissociation of the early transcription factor-promoter complex. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15545–15548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Fesler B. S. Vaccinia virus gene encoding a component of the viral early transcription factor. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1523–1529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1523-1529.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Moss B. DNA-dependent ATPase activity associated with vaccinia virus early transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10761–10765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Moss B. Sedimentation of an RNA polymerase complex from vaccinia virus that specifically initiates and terminates transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):7–14. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broyles S. S., Yuen L., Shuman S., Moss B. Purification of a factor required for transcription of vaccinia virus early genes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10754–10760. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christen L., Higman M. A., Niles E. G. Phenotypic characterization of three temperature-sensitive mutations in the vaccinia virus early gene transcription initiation factor. J Gen Virol. 1992 Dec;73(Pt 12):3155–3167. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-12-3155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condit R. C., Motyczka A. Isolation and preliminary characterization of temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):224–241. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condit R. C., Motyczka A., Spizz G. Isolation, characterization, and physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):429–443. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLange A. M. Identification of temperature-sensitive mutants of vaccinia virus that are defective in conversion of concatemeric replicative intermediates to the mature linear DNA genome. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2437–2444. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2437-2444.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demkowicz W. E., Maa J. S., Esteban M. Identification and characterization of vaccinia virus genes encoding proteins that are highly antigenic in animals and are immunodominant in vaccinated humans. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):386–398. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.386-398.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteban M., Holowczak J. A. Replication of vaccinia DNA in mouse L cells. IV. Protein synthesis and viral DNA replication. Virology. 1978 May 15;86(2):376–390. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90078-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Traktman P. Molecular genetic analysis of a vaccinia virus gene with an essential role in DNA replication. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3152–3162. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3152-3162.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein A., Kostrub C. F., Li J., Chavez D. P., Wang B. Q., Fang S. M., Greenblatt J., Burton Z. F. A cDNA encoding RAP74, a general initiation factor for transcription by RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1992 Jan 30;355(6359):464–467. doi: 10.1038/355464a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon P. D., Moss B. Early transcription factor subunits are encoded by vaccinia virus late genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4401–4405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershowitz A., Boone R. F., Moss B. Multiple roles for ATP in the synthesis and processing of mRNA by vaccinia virus: specific inhibitory effects of adenosine (beta,gamma-imido) triphosphate. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):399–408. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.399-408.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gong S. C., Lai C. F., Dallo S., Esteban M. A single point mutation of Ala-25 to Asp in the 14,000-Mr envelope protein of vaccinia virus induces a size change that leads to the small plaque size phenotype of the virus. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4507–4514. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4507-4514.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooda-Dhingra U., Thompson C. L., Condit R. C. Detailed phenotypic characterization of five temperature-sensitive mutants in the 22- and 147-kilodalton subunits of vaccinia virus DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):714–729. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.714-729.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. The preparation and characteristics of highly purified radioactively labelled poxvirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 20;61:290–301. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn J. S., Esteban M. Identification of the point mutations in two vaccinia virus nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase I temperature-sensitive mutants and role of this DNA-dependent ATPase enzyme in virus gene expression. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90100-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J. R., McAuslan B. R. Messenger RNA synthesis by a "coated" viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):314–320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck J. G., Baldick C. J., Jr, Moss B. Role of DNA replication in vaccinia virus gene expression: a naked template is required for transcription of three late trans-activator genes. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90190-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koonin E. V., Senkevich T. G. Vaccinia virus encodes four putative DNA and/or RNA helicases distantly related to each other. J Gen Virol. 1992 Apr;73(Pt 4):989–993. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-4-989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Künzi M. S., Traktman P. Genetic evidence for involvement of vaccinia virus DNA-dependent ATPase I in intermediate and late gene expression. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3999–4010. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3999-4010.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Broyles S. S. Recruitment of vaccinia virus RNA polymerase to an early gene promoter by the viral early transcription factor. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 5;268(4):2773–2780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Hagler J., Shuman S. Discrete functional stages of vaccinia virus early transcription during a single round of RNA synthesis in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13303–13310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maa J. S., Rodriguez J. F., Esteban M. Structural and functional characterization of a cell surface binding protein of vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1569–1577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald W. F., Crozel-Goudot V., Traktman P. Transient expression of the vaccinia virus DNA polymerase is an intrinsic feature of the early phase of infection and is unlinked to DNA replication and late gene expression. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):534–547. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.534-547.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Ahn B. Y., Amegadzie B., Gershon P. D., Keck J. G. Cytoplasmic transcription system encoded by vaccinia virus. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1355–1358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Paoletti E., Grace J. T., Jr RNA polymerase activity in purified infectious vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2280–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda K. I., Joklik W. K. Hybridization and sedimentation studies on "early" and "late" vaccinia messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):395–419. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pacha R. F., Meis R. J., Condit R. C. Structure and expression of the vaccinia virus gene which prevents virus-induced breakdown of RNA. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3853–3863. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3853-3863.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paoletti E., Moss B. Two nucleic acid-dependent nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolases from vaccinia virus. Nucleotide substrate and polynucleotide cofactor specificities. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3281–3286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rempel R. E., Traktman P. Vaccinia virus B1 kinase: phenotypic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants and enzymatic characterization of recombinant proteins. J Virol. 1992 Jul;66(7):4413–4426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.7.4413-4426.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Janeczko R., Esteban M. Isolation and characterization of neutralizing monoclonal antibodies to vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):482–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.482-488.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Kahn J. S., Esteban M. Molecular cloning, encoding sequence, and expression of vaccinia virus nucleic acid-dependent nucleoside triphosphatase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9566–9570. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. F., Rodriguez D., Rodriguez J. R., McGowan E. B., Esteban M. Expression of the firefly luciferase gene in vaccinia virus: a highly sensitive gene marker to follow virus dissemination in tissues of infected animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1667–1671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrmann G., Yuen L., Moss B. Transcription of vaccinia virus early genes by enzymes isolated from vaccinia virions terminates downstream of a regulatory sequence. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1029–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90702-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SADLER J. R., NOVICK A. THE PROPERTIES OF REPRESSOR AND THE KINETICS OF ITS ACTION. J Mol Biol. 1965 Jun;12:305–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80255-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebring E. D., Salzman N. P. Metabolic properties of early and late vaccinia virus messenger ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Jun;1(3):550–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.3.550-558.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto J., Celenza L. M., Condit R. C., Niles E. G. Genetic map of the vaccinia virus HindIII D Fragment. Virology. 1987 Sep;160(1):110–119. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Broyles S. S., Moss B. Purification and characterization of a transcription termination factor from vaccinia virions. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 5;262(25):12372–12380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Moss B. Bromouridine triphosphate inhibits transcription termination and mRNA release by vaccinia virions. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21356–21360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S., Spencer E., Furneaux H., Hurwitz J. The role of ATP in in vitro vaccinia virus RNA synthesis effects of AMP-PNP and ATP gamma S. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5396–5403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuman S. Vaccinia virus RNA helicase: an essential enzyme related to the DE-H family of RNA-dependent NTPases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10935–10939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopta M., Burton Z. F., Greenblatt J. Structure and associated DNA-helicase activity of a general transcription initiation factor that binds to RNA polymerase II. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):410–414. doi: 10.1038/341410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. F., Keck J. G., Tsai M. M., Moss B. A transcription factor for expression of vaccinia virus late genes is encoded by an intermediate gene. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3715–3720. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3715-3720.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu M. H., King J. Surface amino acids as sites of temperature-sensitive folding mutations in the P22 tailspike protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1424–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]