Abstract
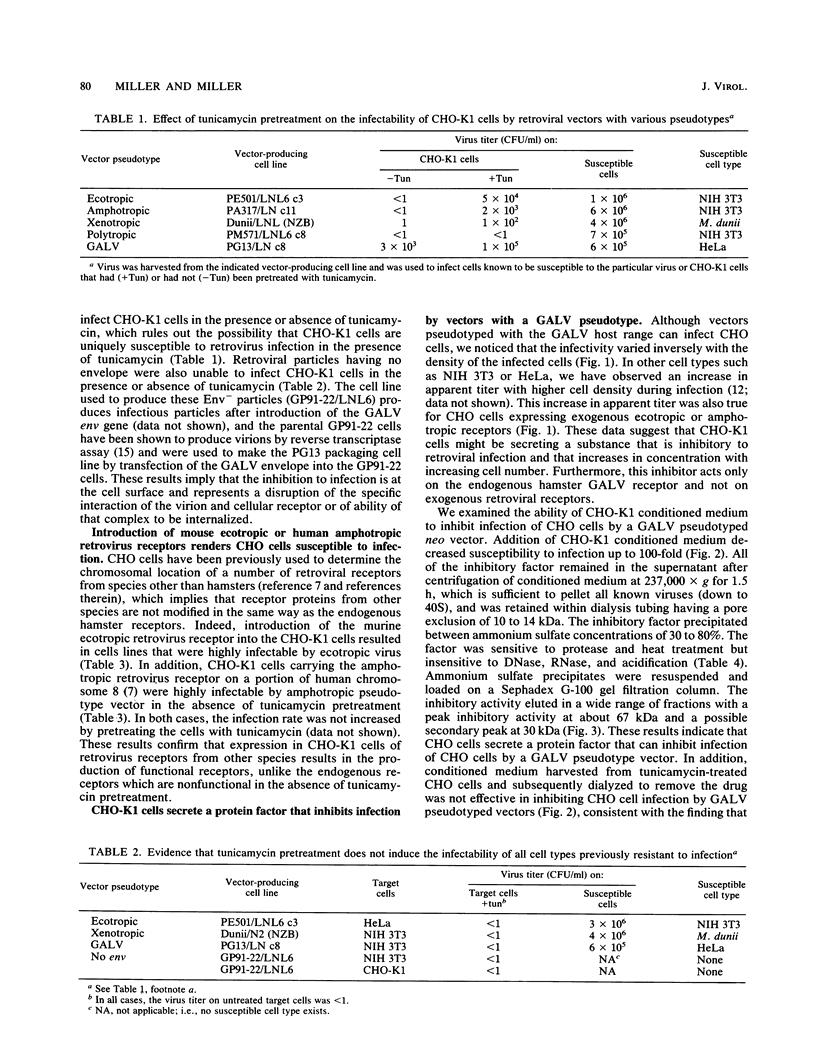
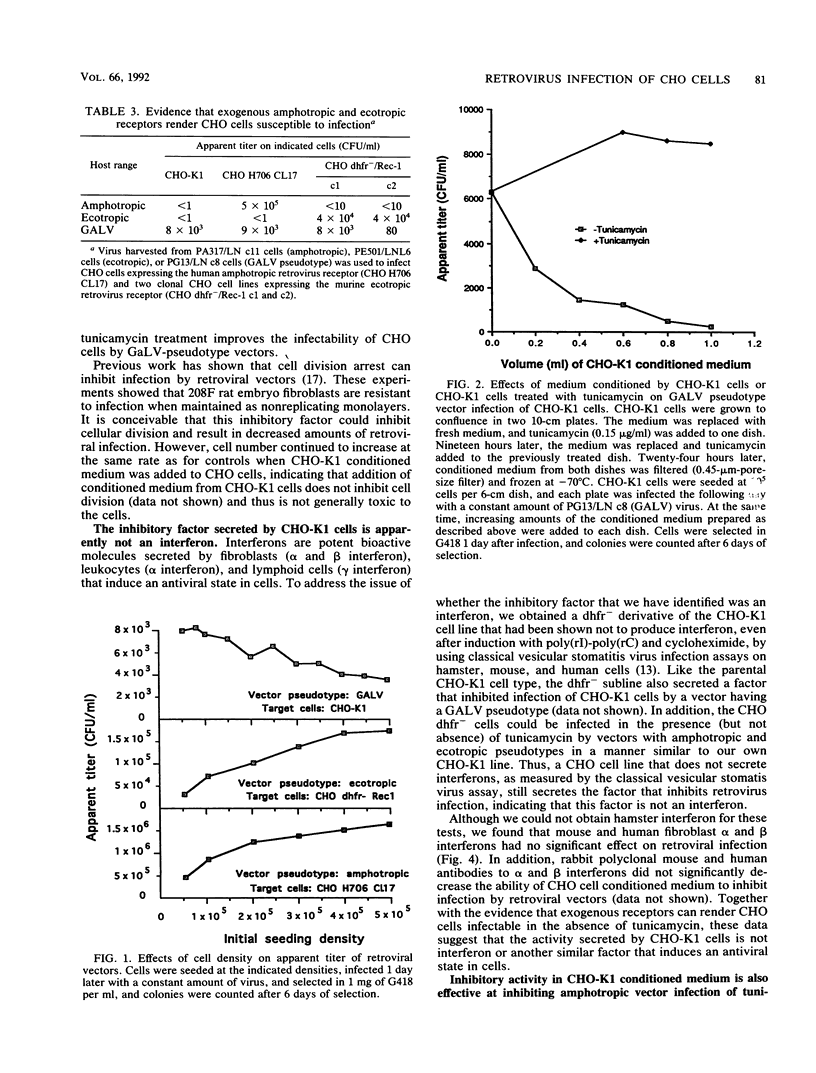
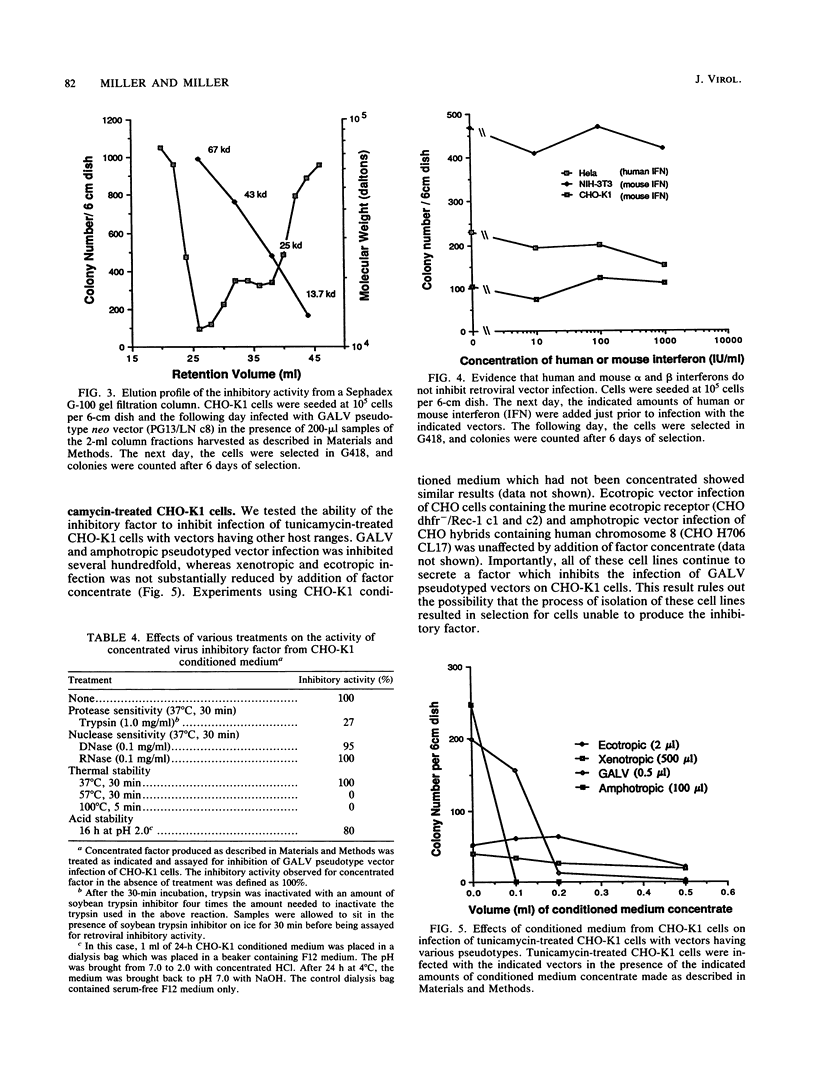
Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells are resistant to infection by all of the major classes of murine retroviruses and are partially resistant to infection by gibbon ape leukemia virus. Treatment of CHO cells with the glycosylation inhibitor tunicamycin rendered these cells susceptible to infection by retroviral vectors with ecotropic, xenotropic, and amphotropic host ranges and increased the titer of gibbon ape leukemia virus pseudotyped vectors 10-fold. Vectors having a polytropic host range did not infect CHO cells in the presence or absence of tunicamycin, showing that the effect of tunicamycin was specific and related to the pseudotype of the vector. We present evidence for three mechanisms of resistance to infection: lack of viral receptors on CHO cells, the presence of nonfunctional receptors which can be made functional by treatment with tunicamycin, and the secretion of a protein factor that blocks retroviral infection of CHO cells. Several criteria indicate that the secreted inhibitor is not an interferon, and secretion of this factor was not detected in several other cell lines that were examined.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albritton L. M., Tseng L., Scadden D., Cunningham J. M. A putative murine ecotropic retrovirus receptor gene encodes a multiple membrane-spanning protein and confers susceptibility to virus infection. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90134-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Low M. A., Lie Y. S., Keller G. A., Dinowitz M. Endogenous origin of defective retroviruslike particles from a recombinant Chinese hamster ovary cell line. Virology. 1991 Mar;181(1):305–311. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90496-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender M. A., Palmer T. D., Gelinas R. E., Miller A. D. Evidence that the packaging signal of Moloney murine leukemia virus extends into the gag region. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1639–1646. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1639-1646.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K. Different murine cell lines manifest unique patterns of interference to superinfection by murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corsaro C. M., Pearson M. L. Enhancing the efficiency of DNA-mediated gene transfer in mammalian cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1981 Sep;7(5):603–616. doi: 10.1007/BF01549662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Jones C., Miller A. D. Localization of the amphotropic murine leukemia virus receptor gene to the pericentromeric region of human chromosome 8. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6316–6319. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6316-6319.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaelbling M., Eddy R., Shows T. B., Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Jenkins N. A., Klinger H. P., O'Hara B. Localization of the human gene allowing infection by gibbon ape leukemia virus to human chromosome region 2q11-q14 and to the homologous region on mouse chromosome 2. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1743–1747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1743-1747.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao F. T., Puck T. T. Genetics of somatic mammalian cells, VII. Induction and isolation of nutritional mutants in Chinese hamster cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Aug;60(4):1275–1281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.60.4.1275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber M. M., Benveniste R. E., Livingston D. M., Todaro G. J. Mammalian cells in culture frequently release type C viruses. Science. 1973 Oct 5;182(4107):56–59. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4107.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. M., Miller A. D. Production of high-titer helper virus-free retroviral vectors by cocultivation of packaging cells with different host ranges. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3887–3890. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3887-3890.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Trahey M., Innis M., Dieckmann B., Ringold G. Inducible expression of amplified human beta interferon genes in CHO cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):166–172. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Buttimore C. Redesign of retrovirus packaging cell lines to avoid recombination leading to helper virus production. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2895–2902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Garcia J. V., von Suhr N., Lynch C. M., Wilson C., Eiden M. V. Construction and properties of retrovirus packaging cells based on gibbon ape leukemia virus. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2220–2224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2220-2224.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. G., Adam M. A., Miller A. D. Gene transfer by retrovirus vectors occurs only in cells that are actively replicating at the time of infection. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4239–4242. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. R., Buckler C. E., Theodore T. S., Martin M. A., Repaske R. Envelope and long terminal repeat sequences of a cloned infectious NZB xenotropic murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):100–106. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.100-106.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quade K. Transformation of mammalian cells by avian myelocytomatosis virus and avian erythroblastosis virus. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):461–465. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90569-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., Schultz A. M., Bader J. P., Bassin R. H. Inhibitors of glycosylation reverse retroviral interference. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90075-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D. Isolation and expression of an altered mouse dihydrofolate reductase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2495–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urlaub G., Chasin L. A. Isolation of Chinese hamster cell mutants deficient in dihydrofolate reductase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4216–4220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



