Abstract
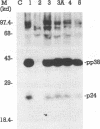
The identification of unique Marek's disease (MD) virus (MDV) antigens expressed not only in lytically infected cells but also in latently infected MD lymphoblastoid tumor cell lines is important in understanding the molecular mechanisms of latency and transformation by MDV, an oncogenic lymphotropic herpesvirus of chickens. Through cDNA and nucleotide sequence analysis, an open reading frame (designated the pp38 ORF) which encodes a predicted polypeptide of 290 amino acids was identified in BamHI-H. Demonstration that the pp38 ORF spans the junction of the MDV long unique and long internal repeat regions (MDV has an alphaherpesvirus genome structure) precludes the presence of the gene encoding the B-antigen complex (gp100, gp60, and gp49) in the same region of BamHI-H, where it was originally thought to exist. Duplication of the complete pp38 ORF was not observed in BamHI-D, but part of it (encoding 45 amino acids) was found in the long terminal repeat region of the fragment. By use of trpE-pp38 fusion proteins, antisera against pp38 were prepared. By immunoprecipitation and sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, a predominant virus-specific 38,000-dalton polypeptide (designated pp38) and a minor 24,000-dalton polypeptide (designated p24) were found. No precursor-product relationship was found between pp38 and p24 by pulse-chase analysis, and only pp38 was detected by Western blot (immunoblot) analysis with antiserum to pp38. pp38 was found to be phosphorylated and present in oncogenic serotype 1-but not nononcogenic serotype 3-infected cells. Expression of the gene encoding pp38 was relatively insensitive to phosphonoacetic acid inhibition, suggesting that pp38 may belong to one of the early classes of herpesvirus proteins. pp38 was also detected in the latently infected MSB-1 lymphoblastoid tumor cell line. The detection of antibody against pp38 in immune chicken sera indicates that pp38 is an immunogen in birds with MD. Most of the properties described here for a protein detected by methods based on finding the ORF first are identical to those of a 38-kDa phosphoprotein reported by others, suggesting that they are the same. Collectively, the data reported here provide (i) more definitive information on the complete ORF of another MDV gene and the protein that it encodes, (ii) clarification of the gene content within a specific region of the MDV genome, and (iii) the molecular means to conduct further studies to determine whether pp38 plays a role in MDV latency and transformation.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama Y., Kato S. Two cell lines from lymphomas of Marek's disease. Biken J. 1974 Sep;17(3):105–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley G., Hayashi M., Lancz G., Tanaka A., Nonoyama M. Structure of the Marek's disease virus BamHI-H gene family: genes of putative importance for tumor induction. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2534–2542. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2534-2542.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calnek B. W. Marek's disease--a model for herpesvirus oncology. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1986;12(4):293–320. doi: 10.3109/10408418509104432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. B., Velicer L. F. Multiple bidirectional initiations and terminations of transcription in the Marek's disease virus long repeat regions. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2445–2451. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2445-2451.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui Z. Z., Yan D., Lee L. F. Marek's disease virus gene clones encoding virus-specific phosphorylated polypeptides and serological characterization of fusion proteins. Virus Genes. 1990 Apr;3(4):309–322. doi: 10.1007/BF00569038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Lynch D., Furukawa Y., Griffin J., Piwnica-Worms H., Huang C. M., Livingston D. M. The product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene has properties of a cell cycle regulatory element. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1085–1095. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90507-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn K., Nazerian K. Induction of Marek's disease virus antigens by IdUrd in a chicken lymphoblastoid cell line. J Gen Virol. 1977 Mar;34(3):413–419. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-3-413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glaubiger C., Nazerian K., Velicer L. F. Marek's disease herpesviruses. IV. Molecular characterization of Marek's disease herpesvirus A antigen. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1228–1234. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1228-1234.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HABEL K. SPECIFIC COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIGENS IN POLYOMA TUMORS AND TRANSFORMED CELLS. Virology. 1965 Jan;25:55–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta K., Nakajima K., Naito M., Ann S. H., Ueda S., Kato S., Hirai K. Identification of Marek's disease virus-specific antigens in Marek's disease lymphoblastoid cell lines using monoclonal antibody against virus-specific phosphorylated polypeptides. Int J Cancer. 1985 Feb 15;35(2):257–264. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta K., Ueda S., Kato S., Hirai K. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with the surface and secreted glycoproteins of Marek's disease virus and herpesvirus of turkeys. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2597–2610. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta K., Ueda S., Kato S., Hirai K. Processing of glycoprotein gB related to neutralization of Marek's disease virus and herpesvirus of turkeys. Microbiol Immunol. 1984;28(8):923–933. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1984.tb00748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isfort R. J., Sithole I., Kung H. J., Velicer L. F. Molecular characterization of Marek's disease herpesvirus B antigen. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):411–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.411-419.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Davis R. L., Watanabe S. M., Ponticelli A. S., Schiff-Maker L., Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. Only site-directed antibodies reactive with the highly conserved src-homologous region of the v-abl protein neutralize kinase activity. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):223–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.223-232.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lahijani R. S., Otteson E. W., Adlish J. D., St Jeor S. C. Characterization of a human cytomegalovirus 1.6-kilobase late mRNA and identification of its putative protein product. J Virol. 1991 Jan;65(1):373–381. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.1.373-381.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maray T., Malkinson M., Becker Y. RNA transcripts of Marek's disease virus (MDV) serotype-1 in infected and transformed cells. Virus Genes. 1988 Oct;2(1):49–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00569736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Inhibition of RNA cleavage but not polyadenylation by a point mutation in mRNA 3' consensus sequence AAUAAA. Nature. 1983 Oct 13;305(5935):600–605. doi: 10.1038/305600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima K., Ikuta K., Naito M., Ueda S., Kato S., Hirai K. Analysis of Marek's disease virus serotype 1-specific phosphorylated polypeptides in virus-infected cells and Marek's disease lymphoblastoid cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1379–1389. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazerian K., Lee L. F. Selective inhibition by phosphonoacetic acid of MDV DNA replication in a lymphoblastoid cell line. Virology. 1976 Oct 1;74(1):188–193. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross L. J., Sanderson M., Scott S. D., Binns M. M., Doel T., Milne B. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the Marek's disease virus homologue of glycoprotein B of herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1989 Jul;70(Pt 7):1789–1804. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-7-1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schat K. A., Buckmaster A., Ross L. J. Partial transcription map of Marek's disease herpesvirus in lytically infected cells and lymphoblastoid cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1989 Jul 15;44(1):101–109. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva R. F., Lee L. F. Monoclonal antibody-mediated immunoprecipitation of proteins from cells infected with Marek's disease virus or turkey herpesvirus. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugaya K., Bradley G., Nonoyama M., Tanaka A. Latent transcripts of Marek's disease virus are clustered in the short and long repeat regions. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):5773–5782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.5773-5782.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]